- Home/
- SSC & Railways/
- SSC CGL/
- Article
28 States of India and their Languages, Capitals & Formation Dates
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 25th, 2023

States and Capitals of India: Knowing 28 States of India and their Languages is of utmost importance for candidates who want to ace competitive exams like SSC, Railway, UPSC, etc. These exams comprise the General Knowledge section through which candidates’ knowledge of day-to-day activities or happenings around the world is tested. It is one of the most scoring subjects where candidates can attempt the maximum number of questions in less time.
Every year, this section comprises questions on the States of India, including their capitals, languages, formation dates, population, etc. Therefore, it is mandatory for the candidates to be aware of and also memorize the states and capitals of India and their languages for SSC Exam preparation. Read further to know more about it and download the states and capitals of India PDF.
Table of content
-
1.
States and Capitals of India
-
2.
Indian States and Capitals
-
3.
States and Capitals of India PDF
-
4.
States and Capitals of India: Classification
-
5.
List of States and Capitals of India
-
6.
States and Capitals of India Map
-
7.
28 States of India and their Languages
-
8.
Difference Between States and Union Territories Of India
-
9.
Indian Union Territories and Capitals
-
10.
States and Capitals of India 2023 Formation Dates
-
11.
Indian Union Territories Formation Dates
States and Capitals of India
Most candidates are often confused about the states of India and their capitals. If you are also one of them, here we are to put a stop to all your confusion and queries. Earlier, there were 29 Indian states, however, after the revocation of the special status of Jammu & Kashmir, the state was converted into a Union Territory. After the revocation, J&K and Ladakh were converted into two Union Territories of India on October 31st, 2019. This resulted into 28 states and 8 union territories of India.
Indian States and Capitals
Currently, India has 28 states and 8 Union territories. Earlier, there were 29 Indian states and 7 union territories but after the revocation of the special status of Jammu Kashmir, granted under Article 370, two new union territories of India were formed, which are Ladakh and Jammu & Kashmir. All the Indian states and union territories (UTs) are governed by the Central and State governments based on the federal structure. While the States and Capitals of India are governed by their elected government and Chief Minister as their elected head, Union Territories are administrated by the Central Government.
In this article, we have discussed about states and capitals of India, their languages, and formation dates along with the map of India. This information will be very helpful for all SSC and Railways Exams 2023, especially the ones listed below:
States and Capitals of India PDF
Even if you are not preparing for the SSC Exams you must know everything about the States of India as a responsible Indian citizen. Below, we have also provided a PDF on States and Capitals for those who are preparing for competitive exams. You can simply click on the link mentioned below to download the States of India and their capitals PDF.
States and Capitals Of India PDF
States and Capitals of India: Classification
The States and Capitals of India are categorized into administrative, legislative, and judicial capitals. The administrative capital is where the executive resides and runs the government. The judicial capital is where the high court of the state is located and the legislative capital is where the state’s legislative assembly is situated. You must note here that we are referring to the administrative capital while discussing 28 states and capitals of India below.
Also read: Famous Temples in India
List of States and Capitals of India
With effect from January 26, 2020, India’s total number of states is 28 and 8 union territories. Below, we have listed the names of all the India States and Capitals along with the population:
|
S.No |
Name of Indian State |
Capital of Indian State |
Population (2021 Estimates) |
|
1 |
Andhra Pradesh |
Amaravati |
5.27 Crores |
|
2 |
Arunachal Pradesh |
Itanagar |
15.33 Lakhs |
|
3 |
Assam |
Dispur |
3.50 Crores |
|
4 |
Bihar |
Patna |
12.30 Crores |
|
5 |
Chhattisgarh |
Raipur |
2.95 Crores |
|
6 |
Goa |
Panaji |
16 Lakhs |
|
7 |
Gujarat |
Gandhinagar |
7 Crores |
|
8 |
Haryana |
Chandigarh |
2.95 Crores |
|
9 |
Himachal Pradesh |
Shimla |
74 Lakhs |
|
10 |
Jharkhand |
Ranchi |
3.85 Crores |
|
11 |
Karnataka |
Bengaluru |
6.70 Crores |
|
12 |
Kerala |
Thiruvananthapuram |
3.55 Crores |
|
13 |
Madhya Pradesh |
Bhopal |
8.45 Crores |
|
14 |
Maharashtra |
Mumbai |
12.44 Crores |
|
15 |
Manipur |
Imphal |
31.65 Lakhs |
|
16 |
Meghalaya |
Shillong |
33 Lakhs |
|
17 |
Mizoram |
Aizawl |
12.16 Lakhs |
|
18 |
Nagaland |
Kohima |
22 Lakhs |
|
19 |
Odisha |
Bhubaneswar |
4.55 Crores |
|
20 |
Punjab |
Chandigarh |
3 Crores |
|
21 |
Rajasthan |
Jaipur |
7.92 Crores |
|
22 |
Sikkim |
Gangtok |
6.77 Lakhs |
|
23 |
Tamil Nadu |
Chennai |
7.65 Crores |
|
24 |
Telangana |
Hyderabad |
3.80 Crores |
|
25 |
Tripura |
Agartala |
41 Lakhs |
|
26 |
Uttar Pradesh |
Lucknow |
23 Crores |
|
27 |
Uttarakhand |
Dehradun |
1.14 Crores |
|
28 |
West Bengal |
Kolkata |
9.8 Crores |
States and Capitals of India Map
The below map highlights the list of States and Union Territories formed in India along with their formation dates:
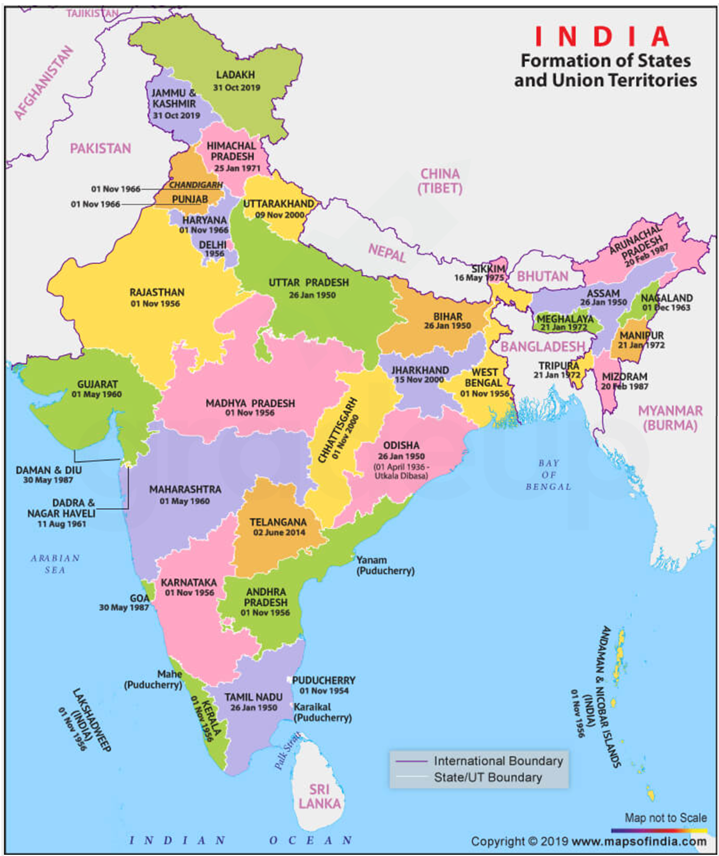
Image Credits: mapsofindia.com
28 States of India and their Languages
India is known for its diverse languages and we take pride in the fact that the language varies after a few km. Along with the 28 India States and their Capitals, you must learn the languages of India too. Indian Constitution recognizes 22 languages under the Eighth Schedule. We have divided the list into the official languages and languages spoken in every State of India.
The following is a list of 28 States of India and their Languages:
|
States of India |
Capitals of India |
Official Languages of India |
Regional Languages of India |
|
Andhra Pradesh |
Hyderabad (Proposed capital Amaravati) |
Telugu |
Telugu, Urdu, Hindi, Tamil and Marathi |
|
Arunachal Pradesh |
Itanagar |
English |
Nishi, Adi, Bengali, Nepali and Hindi |
|
Assam |
Dispur |
Assamese |
Assamese, Bengali, Hindi, Bodo, Nepali |
|
Bihar |
Patna |
Hindi |
Hindi (Bhojpuri and Magadhi dialects), Maithili, Urdu, Bengali and Santali |
|
Chattisgarh |
Raipur |
Hindi |
Hindi (Chhattisgarhi), Odia, Bengali, Telugu and Marathi |
|
Goa |
Panaji |
Konkani |
Konkani, Marathi, Hindi, Kannada and Urdu |
|
Gujarat |
Gandhinagar |
Gujarati |
Gujarati, Hindi, Sindhi, Marathi, and Urdu |
|
Haryana |
Chandigarh |
Hindi |
Hindi (Haryanvi and Mewati dialects), Punjabi, Urdu, Bengali, and Maithili |
|
Himachal Pradesh |
Shimla |
Hindi |
Hindi, Punjabi, Nepali, Kashmiri, and Dogri |
|
Jharkhand |
Ranchi |
Hindi |
Hindi (Bhojpuri, Magadhi, and Nagpuri dialects), Santhali, Bengali, Urdu, and Odia |
|
Karnataka |
Bengaluru (Formerly Bangalore) |
Kannada |
Kannada, Urdu, Telugu, Tamil, and Marathi |
|
Kerala |
Thiruvananthapuram |
Malayalam |
Malayalam, Tamil, Tulu, Kannada and Konkani |
|
Madhya Pradesh |
Bhopal |
Hindi |
Hindi, Marathi, Urdu, Sindhi, and Gujarati |
|
Maharashtra |
Mumbai |
Marathi |
Marathi |
|
Manipur |
Imphal |
Meitei (Manipuri) |
Manipuri, Nepali, Hindi, and Bengali |
|
Meghalaya |
Shillong |
English |
Khasi, Garo, Bengali Nepali and Hindi |
|
Mizoram |
Aizawl |
Mizo, English & Hindi |
Mizo, English, Hindi, Manipuri, and Chakma |
|
Nagaland |
Kohima |
English |
Ao, Konyak, Angami, Sema and Lotha |
|
Odisha |
Bhubaneswar |
Odia |
Odia, Bengali, Telugu Hindi and Santali |
|
Punjab |
Chandigarh |
Punjabi |
Punjabi and Hindi |
|
Rajasthan |
Jaipur |
Hindi |
Rajasthani and Hindi |
|
Sikkim |
Gangtok |
English |
Bhutia, Hindi, Nepali, Lepcha, Limbu |
|
Tamil Nadu |
Chennai |
Tamil |
Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, Urdu, and Malayalam |
|
Telangana |
Hyderabad |
Telugu |
Telugu, Urdu, Marathi Kannada and Hindi |
|
Tripura |
Agartala |
Bengali, English & Kokborok |
Bengali, Tripuri, Manipuri, Kakborak |
|
Uttar Pradesh |
Lucknow |
Hindi |
Hindi (including Awadhi, Bhojpuri, Braj Bhasha and Khari Boli dialects) |
|
Uttarakhand |
Dehradun (Winter) Gairsain (Summer) |
Hindi |
Hindi (including the Garhwali, Kumaoni, and Jaunsari dialects) |
|
West Bengal |
Kolkata |
Bengali |
Bengali |
Also Read:
Difference Between States and Union Territories Of India
If you are always in the dilemma of ‘what is the difference between States and Union Territories of India’, or ‘Why Union Territories are not States’, here’s an answer to all your questions. The table below highlights the difference between the Indian States and Union Territoritories:
|
Particulars |
State |
Union Territories |
|
Administration & Definition |
A State has its units for administration through its elected government A State is run through either unicameral or bicameral legislature |
Union Territory is administered and controlled by the Central Government through Lieutenant Governor (LG) Delhi and Puducherry both are UTs which are governed by LG, Chief Minister, and Council of Ministers |
|
Executive Head |
Governor |
Lieutenant Governor |
|
Relationship with Centre |
Federal in character |
Unitary in character |
|
Autonomy |
Completely exist |
Does not exist |
Indian Union Territories and Capitals
Since January 26, 2020, the Union Territories Daman and Diu has been merged with Dadra and Nagar Haveli, making it one union territory of India, according to a bill enacted by Parliament during the winter session. The number of UTs has been reduced to eight following the merger of Daman & Diu with Dadra and Nagar Haveli.
The below table enlists the complete list of Indian Union Territories and their capitals along with population which is organized as per the established year:
|
Union territories of India |
Union Territories and their Capitals |
Population (2021 Estimates) |
|
Delhi |
New Delhi |
3.5 crores |
|
Puducherry |
Pondicherry |
15.71 Lakhs |
|
Andaman and Nicobar Islands |
Port Blair |
4 Lakhs |
|
Lakshadweep |
Kavaratti |
68000 |
|
Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu |
Daman |
10.77 Lakhs |
|
Chandigarh |
Chandigarh |
10,55,450 |
|
Ladakh |
Leh |
2.97 Lakhs |
|
Jammu and Kashmir |
Srinagar (Summer), Jammu (Winter) |
1.34 Crores |
States and Capitals of India 2023 Formation Dates
The formation of a state/union territory is commemorated by the celebration of Foundation Days of Indian States. Some of the Indian States Formation Dates are being declared official state holidays by these Indian states. Let us check the States of India formation dates given in the table below:
|
S.NO |
States of India |
Formation Dates |
|
1 |
Andhra Pradesh |
1st November 1956 |
|
2 |
Arunachal Pradesh |
20 February 1987 |
|
3 |
Assam |
26th January 1950 |
|
4 |
Bihar |
26th January 1950 |
|
5 |
Chhattisgarh |
1st November 2000 |
|
6 |
Goa |
30th May 1987 |
|
7 |
Gujarat |
1st May 1960 |
|
8 |
Haryana |
1st November 1966 |
|
9 |
Himachal Pradesh |
25th January 1971 |
|
10 |
Jharkhand |
15th November 2000 |
|
11 |
Karnataka |
1st November 1956 |
|
12 |
Kerala |
1st November 1956 |
|
13 |
Madhya Pradesh |
1st November 1956 |
|
14 |
Maharashtra |
1st May 1960 |
|
15 |
Manipur |
21st January 1972 |
|
16 |
Meghalaya |
21st January 1972 |
|
17 |
Mizoram |
20th February 1987 |
|
18 |
Nagaland |
1st December 1963 |
|
19 |
Odisha |
26th January 1950 |
|
20 |
Punjab |
1st November 1956 |
|
21 |
Rajasthan |
1st November 1956 |
|
22 |
Sikkim |
16th May 1975 |
|
23 |
Tamil Nadu |
26th January 1950 |
|
24 |
Telangana |
2nd June 2014 |
|
25 |
Tripura |
21st January 1972 |
|
26 |
Uttar Pradesh |
26th January 1950 |
|
27 |
Uttarakhand |
9th November 2000 |
|
28 |
West Bengal |
1st November 1956 |
Indian Union Territories Formation Dates
The table given below enlists the formation dates of Union Territories of India. Ladakh and Jammu and Kashmir are two last formed union territories after the revocation of the special status of Jammu and Kashmir. Take a look at the Indian Union Territories’ formation dates below.
|
Union territories of India |
Formation Date |
|
Delhi |
1st Nov 1956 |
|
Puducherry |
1st Nov 1954 |
|
Andaman and Nicobar Islands |
1st Nov 1956 |
|
Lakshadweep |
1st Nov 1956 |
|
Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu |
26 Jan 2020 |
|
Chandigarh |
1st Nov 1966 |
|
Ladakh |
31st Oct 2019 |
|
Jammu and Kashmir |
31st Oct 2019 |
Since you know everything about one of the most important topics of SSC CGL General Awareness Syllabus i.e. States and Capitals of India, you must begin your preparation now!
| Related Article: | |
| SSC CGL Eligibility | SSC CGL Salary |
| SSC CGL Vacancy | SSC CGL Selection Process |
| SSC CGL Syllabus | SSC CGL Cut Off |
| SSC CGL Question Papers | SSC CGL Preparation Strategy |

