- Home/
- GATE ELECTRONICS/
- GATE EC/
- Article
What is Ideal Diode?
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 25th, 2023

During forward bias, an Ideal Diode acts like a perfect conductor, while when reverse-biased, it acts like an ideal insulator. The ideal diode properties are resistance, threshold voltage, breakdown voltage, and current magnitude.
In this article, we will look into the characteristics curve of an ideal diode and see its behavior for forward and reverse biased conditions. We will also discuss the properties an ideal diode offers in its different modes of biasing and to conclude our discussion, we will look into the difference between an ideal and a conventional diode.
Download Complete Analog Circuit Formula Notes PDF
Download Formulas for GATE Electronics & Communication Engineering – Control System
Table of content
What is an Ideal Diode?
As the name suggests, an ideal diode is a diode that has all of its properties perfectly without any flaws. Diodes may operate either forwardly or reversely biased. Thus, these two modes of operation can be analyzed separately to determine the characteristics of the ideal diode.
Modes of Operation of Ideal Diode
The two modes of operation of the ideal diode are-
- Forward Bias
- Reverse Bias
Formulas for GATE Electronics & Communication Engineering – Digital Circuits
Ideal Diode Circuit Symbol
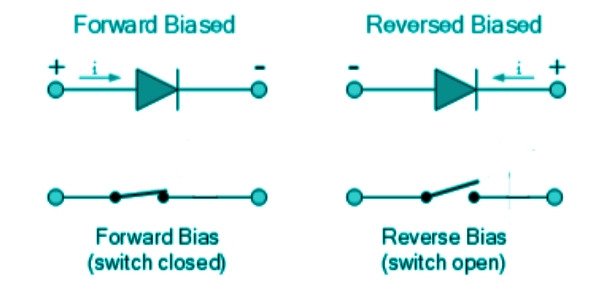
The circuit symbol of an ideal diode is the simple representation of a diode by a triangle device. This symbol becomes a short or open circuit when forward and reverse-biased, respectively.
In forward bias, the current flows from p to n side, and in reverse bias, there is supposed to be a small current from n to p, but since we are dealing with an ideal diode, the reverse current would be zero.
Ideal Diode PDF
This ideal behaviour and its respective symbol representation are shown below.
Ideal Diode V-I Curve
An ideal diode has the same characteristics curve as an ideal switch, which conducts when applied potential and is open-circuited when there is no supply. This means that the ideal diode offers zero resistance in forward bias and infinite resistance in reverse bias. Hence no current flows in reverse bias and maximum current flows in forward bias.
The characteristics curve of an ideal diode is shown below.
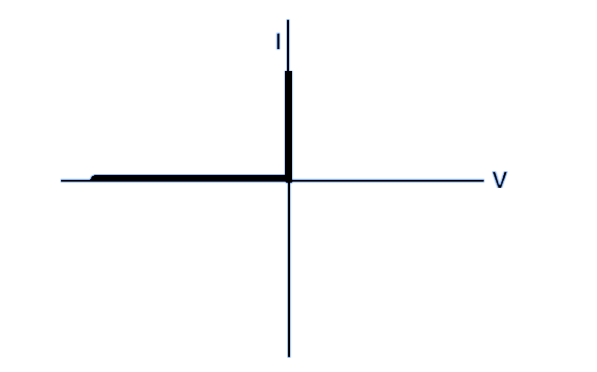
Formulas for GATE Electronics & Communication Engineering – Electronic Devices
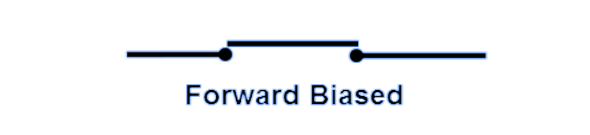
Characteristics of Ideal Diode When Forward Biased
An ideal diode in forward bias offers zero resistance, zero threshold voltage, no depletion barrier, and infinite current. In addition, an ideal diode in forward bias is expected to act as a short circuit, as shown below.
Zero Resistance
When forward-biased, an ideal diode will not resist the flow of current, which means it will be a perfect conductor. As a perfect conductor, it offers zero resistance to the flow of charge carriers.
Infinite Amount of Current
To explain why the ideal diodes offer infinite current when forward-biased, we can see the above property of zero resistance. From ohms law, we can say that
I=V/R,
and therefore,
for R=0,
we will get I=infinite.
Zero Threshold Voltage
This property of the ideal diode, under the forward bias, is also directly related to its first property, which is zero resistance. A threshold voltage is a minimum voltage needed to overcome a diode’s barrier potential and enable it to conduct; since there is zero resistance, there would not be any need for a threshold voltage for the diode to conduct.
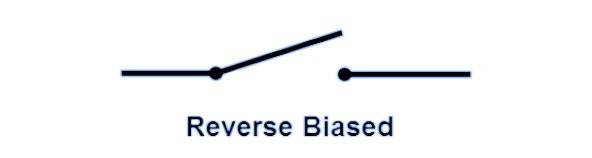
Characteristics of Ideal Diode When Reverse Biased
An ideal diode in reverse bias offers characteristics such as infinite resistance, zero reverse leakage current, and no reverse breakdown.
Considering an ideal case, an ideal diode in the forward bias is expected to act as a short circuit, as shown below.
Infinite Resistance
When reverse-biased, an ideal diode should completely inhibit current flow. When reverse-biased, the ideal diode mimics a perfect insulator and offers infinite resistance to the flow of charge carriers.
Zero Reverse Leakage Current
This property can be justified with the property that the ideal diode offers infinite resistance when reverse-biased. Since there is infinite resistance, there can not be any current flow.
No Reverse Breakdown Voltage
When a reverse bias diode fails and starts to conduct heavy currents, it is said to have reverse breakdown voltage. Still, since there can be no current with the presence of infinite resistance, there would be no breakdown and hence no reverse breakdown voltage. Irrespective of the voltage magnitude, the diode will behave like an insulator.
Comparison Between Conventional and Ideal Diode
Below, we will distinguish between an ideal’s and conventional diode’s properties and characteristics.
| Characteristics | Ideal Diode | Conventional Diode |
| Threshold Voltage | The junctions of an ideal diode do not have a threshold voltage, so they conduct current when you apply a forward voltage across them. | A threshold voltage is present in conventional diodes before conducting forward currents. For silicon diodes, this voltage is approximately 0.7V, while for germanium diodes, it is approximately 0.3V. |
|
Forward Current |
A diode would have zero internal resistance in an ideal condition, resulting in an infinite forward current when a forward voltage is applied across its terminals. | A diode would have zero internal resistance in an ideal condition, resulting in an infinite forward current when a forward voltage is applied across its terminals. |
| Breakdown Voltage | Due to their infinite resistance to reverse voltage, ideal diodes do not have a breakdown voltage. | When a reverse bias is applied to conventional diodes, the junctions will break down and conduct a large amount of current. |
| Reverse Leakage Current | As an ideal diode has no breakdown point, it never conducts reverse current, also known as leakage current. | There will be some leakage current on conventional diodes even with reverse voltage. |
| Characteristics Curve | 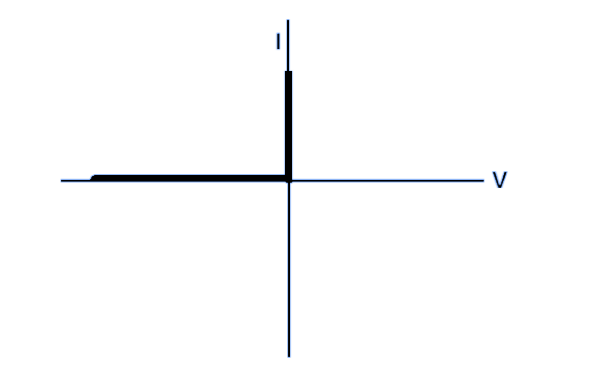 |
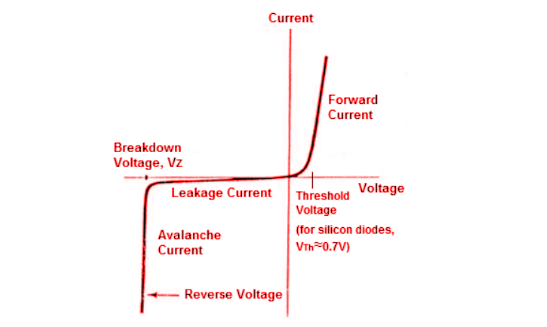 |
| Biasing Circuit | 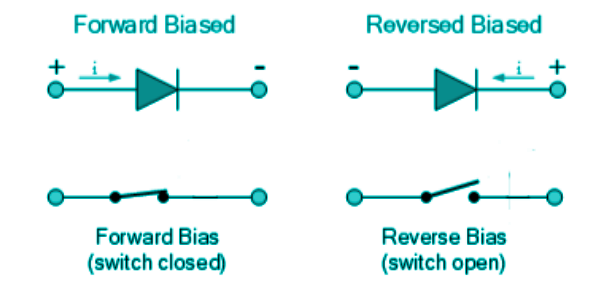 |
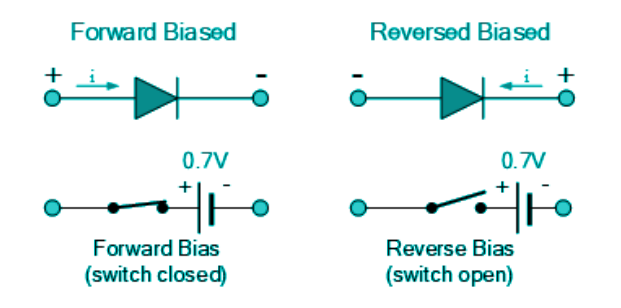 |


