- Home/
- GATE MECHANICAL/
- GATE ME/
- Article
Cycloidal Gear
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 25th, 2023
A cycloidal gear is a type of gear characterized by teeth shaped like a portion of a cycloid curve. Cycloidal gears are typically used in systems that require precise and smooth motion, as the cycloidal tooth profile allows for low-friction and low-noise operation. Cycloidal gears are often used in high-precision applications, such as in scientific instruments, robotics, and aerospace systems. They are also used in some transmission systems, such as cycloidal drives, which transmit power between rotating shafts.
Cycloidal Gear PDF [GATE Notes]
Cycloidal gears are known for their high accuracy, smooth operation, and low wear, making them well-suited for use in various applications. One of the main advantages of cycloidal gears is their ability to transmit torque smoothly and with minimal noise. This is due to the unique shape of the teeth, which allows for low-friction and low-impact engagement between the gears. They are often used in conjunction with other gears, such as bevel gears or worm gears, to create complex transmission systems with a wide range of torque and speed ratios.
Table of content
What is a Cycloidal Gear?
The cycloidal gear profile, as opposed to the involute gear form used for most other gears, is a type of toothed gear used in mechanical clocks. The epicycloid and hypocycloid curves, generated by a circle rolling around the outside and inside of another circle, respectively, serve as the foundation for the gear tooth profile.
When two toothed gears mesh, an imaginary circle, known as the pitch circle, can be formed around the center of each gear where their teeth make contact. The addenda are the curves of the teeth outside the pitch circle, and the dedendum is the curves of the tooth gaps inside the pitch circle. One gear’s addendum sits inside the other gear’s dedendum.
The addenda of the wheel teeth in cycloidal gears are convex epi-cycloidal curves created by the same generating circle as the dedendum of the pinion. This ensures that the motion of one gear is transferred at a locally constant angular velocity to the other.
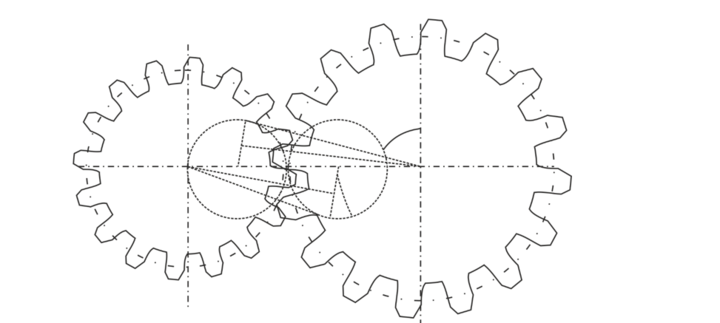
Construction of a Cycloid
A cycloid is a curve generated by the path of a point on the circumference of a circle as it rolls along a straight line. The construction of a cycloid involves drawing a circle with a radius
and tracing the path of a point on the circumference of the circle as it rolls along a straight line.
To construct a cycloid, follow these steps:
-
Draw a circle with a radius
and a point P on the circle’s circumference. -
Place the circle so that it touches the straight line at point A, and roll the circle along the line until point P reaches point B.
-
As the circle rolls, point P traces out a curve. This curve is the cycloid.
-
To complete the cycloid, draw a line connecting points A and B. This line is the base of the cycloid.
-
To draw the cusps of the cycloid, draw a line perpendicular to the baseline at points A and B. These lines will intersect the cycloid at the cusps.
The resulting curve is a cycloid, and its shape is determined by the radius of the circle and the distance that the circle rolls along the straight line. Cycloids are often used in engineering and physics to study objects’ motion and design mechanical systems. They are also used in mathematics to study geometric and mathematical concepts.
Download Formulas for GATE Mechanical Engineering – Machine Design
Cycloidal Gear Construction
Constructing cycloidal gears requires precision machining techniques and careful attention to detail. It is important to ensure that the gears are accurately machined and properly aligned to ensure smooth and efficient operation. Cycloidal gears are often used in high-precision applications, such as in scientific instruments, robotics, and aerospace systems, where smooth and accurate motion is critical. To construct cycloidal gears, follow these steps:
-
Determine the size and number of teeth on the gears. Cycloidal gears are typically made with a small number of teeth, typically between 8 and 20, to ensure a precise and smooth motion.
-
Create a drawing of the gear profile using a mathematical formula or software to generate the cycloidal shape of the teeth.
-
Cut the gear blank to the appropriate size and shape using a milling machine or other machining equipment.
-
Use a hobbing machine or a gear shaper to cut the teeth into the gear blank, following the profile created in step 2.
-
Check the gear for accuracy using a gear tester or other measurement equipment.
-
Repeat the process to create the mating gear, ensuring that the size and number of teeth match those of the first gear.
-
Assemble the gears into a transmission or other mechanical system, ensuring that the gears are aligned correctly and that the transmission operates smoothly.
Advantages of Cycloidal Gears
Cycloidal gears are a type of gear system that use involute cycloid curves to transmit torque between two rotating shafts. They offer several advantages over other types of gears, including:
-
High accuracy: Cycloidal gears have a very high degree of accuracy due to the precise nature of the cycloidal tooth profile. This makes them ideal for applications that require precise positioning or motion control.
-
Low noise: Cycloidal gears operate quietly due to smooth tooth engagement and low contact stresses.
-
High efficiency: Cycloidal gears have a high transmission efficiency, resulting in less heat generation and reduced power loss.
-
Compact size: Cycloidal gears can be made smaller and more compact than other gears, making them ideal for use in tight spaces or where size is a limiting factor.
-
Smooth operation: Cycloidal gears have a smooth, continuous motion due to the rolling contact between the teeth, resulting in low vibration and wear.
Download Formulas for GATE Mechanical Engineering – Strength of Materials
Disadvantages of Cycloidal Gears
Cycloidal gears are highly efficient, as they have a high tooth contact ratio, which helps to reduce power loss due to sliding and wear. In addition to their use in transmission systems, cycloidal gears are also used in other mechanical systems, such as in robotics, where they transmit power and motion between moving parts. However, there are also some disadvantages to using cycloidal gears:
-
Cost: Cycloidal gears can be more expensive to manufacture than other gears due to the precision required in the manufacturing process.
-
Limited load capacity: Due to the lower contact stresses, cycloidal gears have a lower load capacity than other types of gears, such as spur or helical gears.
-
Limited speed range: Cycloidal gears are not well suited for high-speed applications due to the rolling contact between the teeth.
-
Complex design: Cycloidal gears are more complex to design and manufacture than other gears due to the involute cycloid tooth profile.
Overall, the decision to use cycloidal gears should be based on the specific requirements of the application and the trade-offs between the advantages and disadvantages of this type of gear system.
Cycloidal Gears Applications
Cycloidal gears are typically used in applications that require precise positioning or motion control, such as:
-
Robotics: Cycloidal gears are often used in robotic applications due to their high accuracy, smooth operation, and compact size.
-
Aerospace: Cycloidal gears are used in aircraft control systems, such as flight control surfaces, due to their high accuracy and smooth operation.
-
Medical equipment: Cycloidal gears are used in medical equipment, such as CT scanners and MRI machines, due to their precise positioning capabilities and low noise.
-
Machine tools: Cycloidal gears are used in machine tools, such as lathes and milling machines, due to their high accuracy and smooth operation.
-
Printing press: Cycloidal gears are used in printing press machines to ensure precise and accurate movement of the printing plates.
-
Elevators: Cycloidal gears are used in elevator systems to provide precise and smooth movement of the elevator car.
-
Food processing: Cycloidal gears are used in food processing equipment, such as mixers and grinders, due to their high efficiency and smooth operation.
-
Textile machinery: Cycloidal gears are used in textile machineries, such as spinning and weaving machines, due to their high efficiency and smooth operation.
Overall, cycloidal gears are well-suited for applications that require precise positioning or motion control and have limited space for the gear system.
Cycloidal Gear vs. Planetary Gear
Cycloidal gears and planetary gears are two types of gears used in various mechanical systems. While they have some similarities, some key differences exist between these two gears.
Some key differences between cycloidal gears and planetary gears include the following:
-
Tooth profile: Cycloidal gears have teeth that are shaped like a portion of a cycloid curve, while planetary gears have teeth that are shaped like a portion of a circle.
-
Precision: Cycloidal gears are known for their high precision and smooth operation, while planetary gears are known for transmitting high torque and power.
-
Several teeth: Cycloidal gears typically have a small number of teeth, typically between 8 and 20, while planetary gears can have larger teeth.
-
Applications: Cycloidal gears are often used in high-precision applications, such as in scientific instruments, robotics, and aerospace systems, while planetary gears are used in a wider range of applications, including in transmission systems, pumps, and motors.
Overall, cycloidal and planetary gears are useful tools for transmitting power and motion in mechanical systems. The choice between these two types of gear will depend on the specific requirements of the application and the desired performance characteristics.


