Synthetic Materials & Chemicals
Material created by man using natural materials is known as synthetic materials. Some important synthetic materials are given below:
Cement:
- Discovered by English Mason, Joseph Aspdin, he named it Portland cement.
- Limestone, clay, and gypsum are some important raw material that is required in the manufacturing of the cement.
- When cement is mixed with water and left for some time, it becomes a hard mass. This is known as the setting of Cement, it is an exothermic process that’s why sprinkling of water is done for a few days for new construction.
- Mortar is a mixture of cement, sand, and water; it is used for plastering walls and binding bricks.
- Concrete is a mixture of cement, sand, gravel, and water. It is used for the construction of floors.
- The structure having iron rods embedded in wet concrete is known as reinforced concrete.
Glass:
- It is a supercooled liquid of silicate, it is amorphous in nature.
- The raw material used for the formation of glass is sodium carbonate, calcium carbonate, and sand.
- Sudden cooling of molten glass makes it brittle if cooled very slowly make it opaque.
- The process of slow and uniform cooling is called annealing.
- When a glass is attacked by hydrofluoric acid, it is called etching of glass.
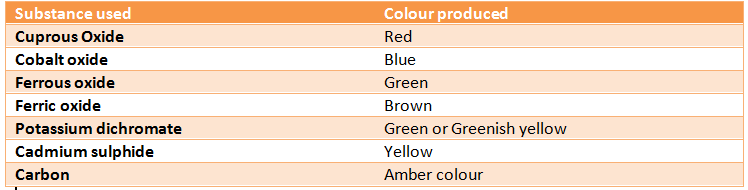
- Coloured glass is obtained by adding certain metallic oxides or salts to the molten glass.
Types of glasses and their uses
Soft glass (Soda Glass):
- The mixture of sodium or calcium silicate.
- Used in making of glass, mirrors, and common glassware, etc.
Hard Glass:
- The mixture of potassium and calcium silicates.
- Resistant to the action of acids and used for making hard glass.
Pyrex glass (Borosilicate glass) :
- Used by fusing a mixture of sand, lime, borax and alkali carbonates.
- Used in making of pharmaceuticals containers.
Glass fibre:
- Glass wool is an excellent heat insulator.
- Used in the insulating material in oven, refrigerator.
Chemicals Used in Agriculture:
Fertilizers:
- These are the chemical substances which are rich in a particular nutrient.
- They supply nitrogen phosphorus and potassium.
- Excess used of fertilizers can reduce the fertility of the soil.
- Good fertilizers are easily dissolved in water and stable so that elements are retained for a longer duration.
- It should not disturb the pH level of the soil.
- Urea is the best fertilizers.
- Calcium superphosphate, nitro phosphate, triple phosphate and phosphatic slag (Thomas slag) are some important phosphatic fertilizers.
- The mixture of nitrogenous, phosphatic and potash fertilizers in the proper ration is called NPK fertilizers.
- NP fertilizers are prepared by mixing nitrogenous and phosphatic fertilizers in a definite ratio.
Pesticides:
Pesticides are the chemicals which are used to kill pests which adversely affect the crops e.g. DDT and malathion. They can be categorized into the following category:
- Insecticides
- Fungicides
- Nematicides
- Molluscicides
- Herbicides
- Rodenticides: Zinc phosphide is used to kill rodents.
Explosives
- These are the substance which contains a great amount of stored energy that can produce an explosion.
- Chemical explosives may consist of either a chemically pure compound such as nitroglycerine or a mixture of a fuel and an oxidizer.
Types of Explosives:
Primary Explosives:
- A relatively small amount of energy is required for initiation.
- Use in detonators e.g. acetone peroxide, silver azide and ammonium permanganate.
Secondary Explosives:
- Are less sensitive and require more energy for initiation.
- RDX and TNT are some secondary explosives.
Tertiary Explosives:
- Used in large scale mining and construction operation and in terrorism.
- Nitro-glycerine is a highly unstable and sensitive liquid also called Noble’s Oil.
- Dynamite is a mixture of highly sensitive nitro-glycerine with sawdust, powdered silica.
- RDX (Research and development explosive) is a very powerful explosive.
Dyes:
- Coloured substances used for colouring wool, textiles materials, and foodstuffs.
- A material which is used as dyes must be able to fix itself to the material it is applied and must resist the action of water, acids, and alkalies.
Dyes can be classified into the following category:
Azo Dyes:
- These dyes contain the azo group (-N=N-).
- Formed during the coupling reactions, e.g. red, orange.
Indigoid Dyes:
- These dyes contain indigoid group in their molecules e.g. indigo.
Anthraquinone dyes
Phthalein Dyes
On the basis of their applications dyes can be classified into the following types:
Vat Dyes: these dyes are water-insoluble dyes and applied to fibre cotton and are obtained from indigo dyes.
Direct Dyes: these dyes can be applied to the fabric from their aqueous solution.
Acid dyes: used as their sodium salts which are soluble in water.
Basic dyes: In acidic medium, these dyes are used to dye modified nylons and polyesters e.g. aniline yellow and malachite green.
More From Us:
Good News | Good News | Good News
SSC Success Batch: A comprehensive 10 Months Foundation Course (English Batch)
SSC सफलता Batch: A comprehensive 10 Months Foundation Course (Hindi Batch)
Highlights of the New Revolutionising Course
- Launching a completely new study plan for 10+ months.
- Based on Practicing the concept regularly.
- Notes and dedicated doubt solving sessions.
- We will have a dedicated Practice day and Homework.
- Dedicated days for Study Holidays.
- Sectional, Mock and Surprise Tests.
- Concept building recorded videos.
- Dedicated lengthy individual courses for tough topics.
3 Crore+ Registered Aspirants | 2.5 Crore Downloads | 50,000+ Selections
So why wait? Update your app right away!




Comments
write a comment