- Home/
- GATE ELECTRONICS/
- GATE EC/
- Article
Breakdown Diode
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 25th, 2023

The breakdown of a diode happens when you apply a reverse bias across the diode. The breakdown of a diode happens when you apply a reverse bias across the diode. There are two types of breakdowns in p-n junctions, which are Avalanche and Zener breakdowns. When a diode is designed for a specific breakdown voltage, it is called a breakdown diode. The reverse-bias breakdown voltage of a junction can be varied by choice of junction doping concentrations. The Zener effect (tunneling) for abrupt junctions with extremely heavy doping is the breakdown mechanism. However, the more common breakdown is avalanche (impact ionization) for lightly doped or graded junctions.
By varying the doping, we can fabricate diodes with specific breakdown voltages ranging from less than one to several hundred volts. This article will give you an overview of the types of breakdown diodes: Zener Diode and Avalanche Diode. You will learn about their properties, breakdown mechanisms, and applications.
Download Complete Analog Circuit Formula Notes PDF
Download Formulas for GATE Electronics & Communication Engineering – Control System
Table of content
What is a Breakdown Diode?
When a diode is designed for a specific breakdown voltage, it is called a breakdown diode. The reverse-bias breakdown voltage of a junction can be varied by choice of junction doping concentrations. The Zener effect (tunneling) for abrupt junctions with extremely heavy doping is the breakdown mechanism.
However, the more common breakdown is avalanche (impact ionization) for lightly doped or graded junctions. The avalanche breakdown is uniform across the whole junction; the breakdown voltage is nearly constant with changing current. The breakdown mechanism involves impact ionization. At the same time, the Zener diode is a PN junction diode with a thin junction and heavy doping.
Formulas for GATE Electronics & Communication Engineering – Electronic Devices
Zener Breakdown Diode
A Zener breakdown diode is a rectifying diode that handles breakdown due to reverse breakdown voltage without failing. When a heavily doped junction is reverse biased, the energy bands cross at relatively low voltages; due to the crossing of the bands, empty states align in the n-side conduction band opposite to the many filled states of the p-side valence band. Suppose the barrier separating these two bands is quite narrow. In that case, the tunneling of electrons occurs, and the tunneling of electrons from the p-side valence band to the n-side conduction band constitutes a reverse current from n to p; this is the Zener effect. Finally, net current develops and increases with an increase in the electric field.
The Zener effect is the field ionization of the host atoms at the junction. The reverse bias of a heavily doped junction causes a large electric field within the depletion region; at a critical field strength, electrons participating in covalent bonds are torn from the bonds by an electric field and accelerated to the n side of the junction.
In reverse bias, Zener breakdown diodes; initially, the current is less. A leakage current is a small current that will flow through the diode. The moment it hits the breakdown voltage, the current increases suddenly. This is used in the application of voltage regulation. Once the voltage across a Zener reaches the breakdown voltage, it is said to be Zener voltage. The VI characteristic curve is shown below.
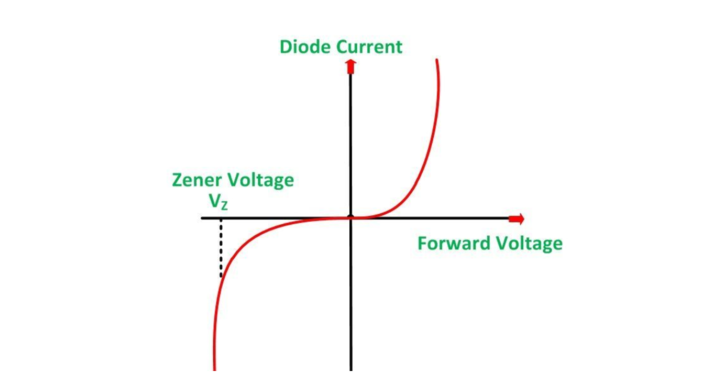
Avalanche Breakdown Diode
An avalanche diode is a semiconductor device that operates in a reverse breakdown region. Avalanche diodes are lightly doped, and the width of the depletion layer in the avalanche diode is very wide compared to the Zener diode; because of this wide depletion region, reverse breakdown occurs at higher voltages in avalanche diodes. The breakdown voltage of avalanche diodes is carefully set by controlling the doping level. Avalanche diodes are used to protect electrical systems from excess voltages.
The avalanche breakdown occurs due to minority carriers accelerated enough to create ionization in the crystal lattice, producing more carriers which in turn create more ionization. The VI characteristic curve of the Avalanche diode in comparison with the Zener diode is shown below. In the graph reverse breakdown voltage for the avalanche diode is more than the Zener diode.
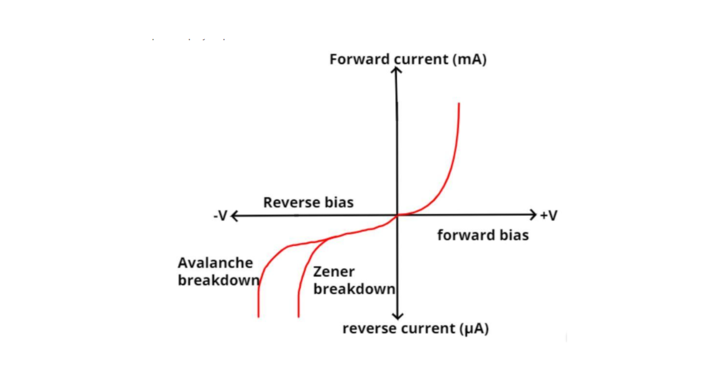
Formulas for GATE Electronics & Communication Engineering – Signals Systems
Differences between Zener and Avalanche Breakdown Diode
Two types of breakdowns occur in PN junction diodes. Below given table shows the difference between those breakdowns, which are Zener breakdown and avalanche breakdown:
|
Avalanche Breakdown |
Zener Breakdown |
|
The avalanche breakdown occurs in lightly doped junctions with wide depletion widths. |
The Zener breakdown occurs in heavily doped junctions with narrow depletion widths. |
|
The high reverse potential is required |
The low reverse potential is required |
|
An increase in temperature increases the breakdown voltage. |
An increase in temperature decreases the breakdown voltage. |
|
Impact ionization occurs. |
Field ionization occurs |


