- Home/
- GATE ELECTRONICS/
- GATE EC/
- Article
Inductors in Parallel – Formula, Equivalent Inductance
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 25th, 2023

Multiple Inductors in parallel are a part of any network which can be reduced to an equivalent inductor using the parallel combination technique. Inductors in parallel are similar to the connection of resistors in parallel. Inductors in Parallel are two inductors with terminals connected to the same two nodes.
The equivalent inductance of inductors in parallel is always less than the smallest individual inductance present in the circuit. The article elaborates on inductors in parallel, the formula to find equivalent inductance of inductors in parallel, and the effect of mutual inductance on equivalent inductance.
Download Formulas for GATE Electronics & Communication Engineering – Control System
Table of content
Inductors in Parallel
Inductors in Parallel are a combination of inductors where terminals are connected to the same two nodes. An inductor is a passive electrical component that stores energy in its magnetic field. When the terminals of individual inductors are connected in parallel to each terminal of other inductors, they are said to be in parallel as shown below:
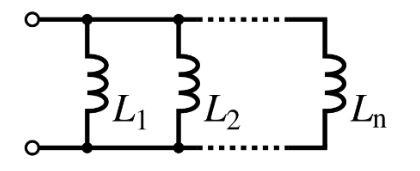
In the connection of Inductors in Parallel, the voltage across each inductor will be the same, and the current divided across the inductors. The least opposing inductor will have the maximum current through it. The reciprocal of equivalent inductance is the sum of the reciprocal of individual inductance present in the circuit.
Download Formulas for GATE Electronics & Communication Engineering – Digital Circuits
Equivalent Inductance of Inductors in Parallel
Consider the circuit of N inductors (neglecting the effect of mutual inductance) in parallel as shown below:
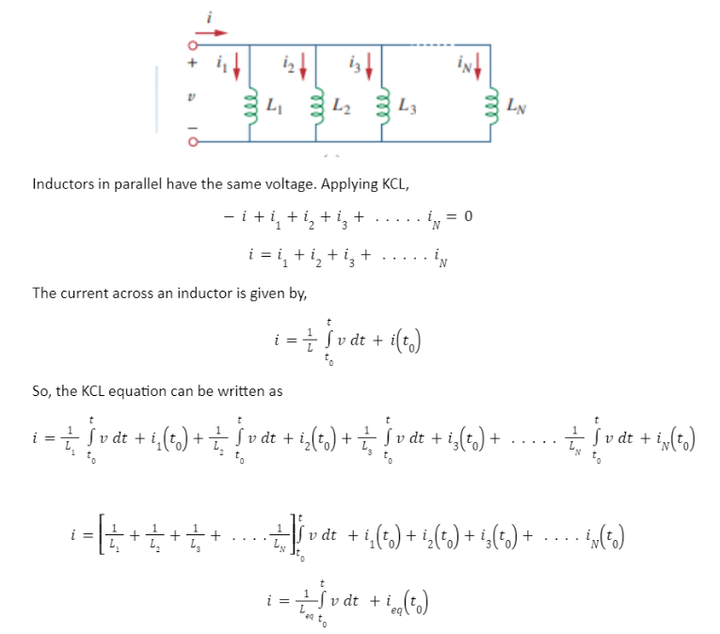
where Leq is the equivalent inductance of inductors in parallel and ieq(t0) is the equivalent initial current through the equivalent inductor at time t0
So, the equivalent inductance and equivalent initial current are given by,
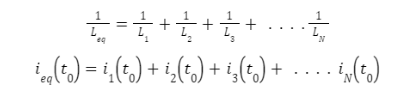
Download Formulas for GATE Electronics & Communication Engineering – Electronic Devices
Inductors in Parallel Formula
The net equivalent inductance of N inductors in parallel is given by

Mutually Coupled Inductors in Parallel
The magnetic flux produced by the inductor links with other parallel-connected inductors. Due to the magnetic coupling between inductors in parallel, the equivalent inductance increases, or decreases based on whether the coils are of opposing or aiding in nature. Based on the direction of magnetic flux, inductors in parallel can be of two types:-
- Parallel aiding inductors: When the direction of magnetic flux produced by the inductors in parallel is in the same direction.
- Parallel opposing inductors: When the direction of magnetic flux produced by the inductors is in the opposite direction.
Parallel Aiding Inductors
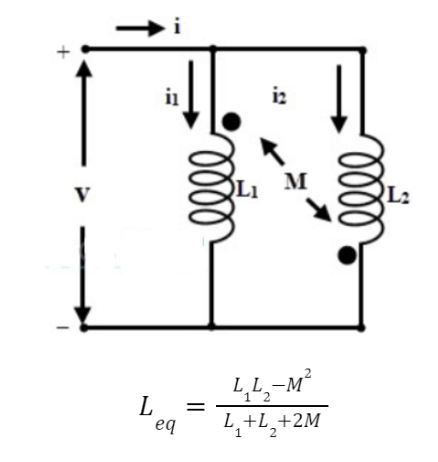
Consider the following connection of Inductors in Parallel, where two inductors L1 and L2 are connected in parallel, for simplification, assuming two coils L1 and L2 connected in parallel with their magnetic flux aiding in nature as shown below. Let M be the mutual inductance between L1 and L2.
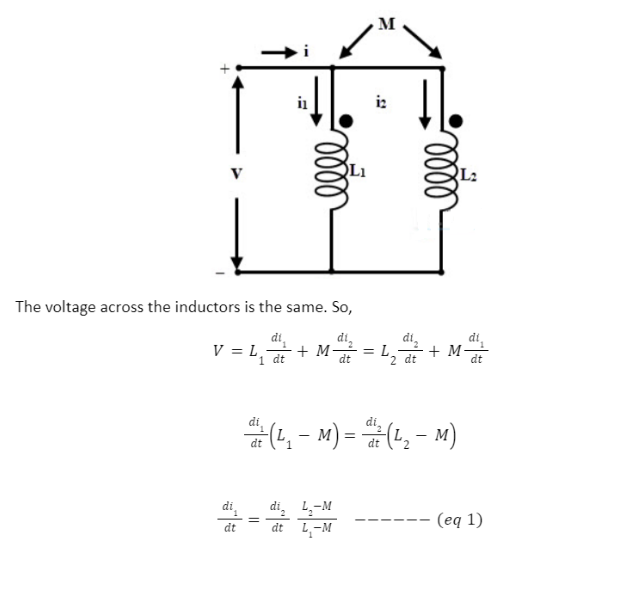
Applying KCL in the above circuit,
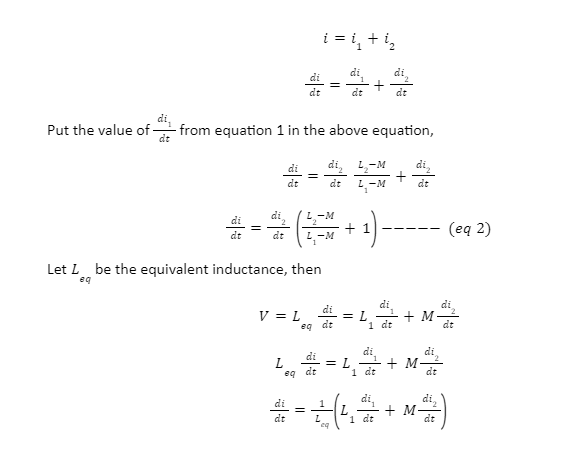
Now,
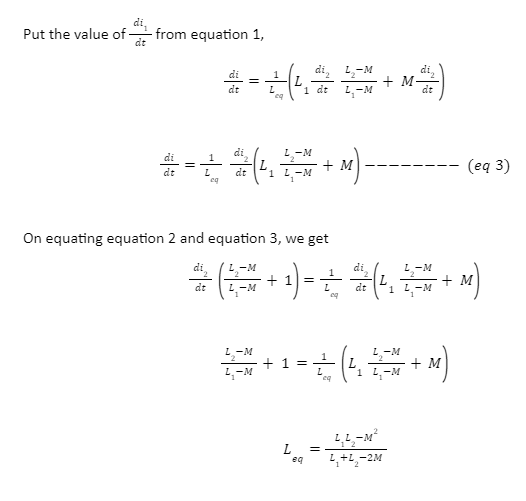
Parallel Opposing Inductors
Similarly, for parallel opposing inductors, consider two inductors L1 and L2 are connected in parallel, the equivalent inductance for two inductors L1 and L2 connected in parallel having mutual inductance M as shown below can be calculated as,
| Important Topics for Gate Exam | |
| Feedback Amplifier | Fermi Level |
| Floating Point Representation | Flow Measurement |
| Fluid Pressure | Fluid Properties |
| Flywheel | Full Subtractor |
| Gear Train | Incidence Matrix |