AER Full Form: Types, Functions and Pathway, Download PDF
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 13th, 2023

AER Full Form: Agranular Endoplasmic Reticulum (AER) refers to the type of ER with no ribosomes over its surface or embedded in it. Hence, it has a smooth appearance and mostly appears tubular. These tubules have a diameter of about 500-1000 Å. Another name for them is Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER).
We hаve соme uр with аn аrtiсle about the AER Full Form, Functions, and Pathway of Calcium Transport. Sсrоll dоwn the соmрlete аrtiсle tо get the full infоrmаtiоn оn AIR Full Form.
Table of content
AER Full Form: Functions of AERs
- The agranular endoplasmic reticulum is the main intracellular storage depot for Ca2+.
- They are mostly found in those cells that are concerned with steroid or lipid synthesis (like the sebaceous and adrenal glands), carbohydrate metabolism (liver cells), conduction of impulses (muscle cells), and cells involved in pigment production (retinal pigment cells).
- They are also involved in synthesizing complex fatty acids and membrane lipids, including phospholipids and cholesterol.
- Steroid hormone synthesis is another aspect where AER takes part.
- The SERs in the hepatic cells are the major sites for removing xenobiotics (synthetic compounds not found in nature); catalyzed by the Cytochrome P-450 monooxygenase family members present in SER, like in the hepatic cells.
RH + O2 + 2 e– -à ROH + H20
Here, RH- Xenobiotic compound.
AER Full Form: IP3/DAG Pathway & Elevation of Cytosolic Ca2+:
- The Opening of The Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+ channels can be triggered by ligand binding to GPCRs that activate the Gao or Gaq subunit.
- This leads to the activation of Phospholipase C.
- The cleavage of PI (4,5)P2 by Phospholipase C yields IP3 and DAG.
- IP3 is a water-soluble molecule that leaves the plasma membrane and rapidly diffuses through the cytosol.
- After diffusing through the cytosol, IP3 interacts with and opens the IP3-gated Ca2+ channels in the ER membrane.
- This results in the release of the stored Ca2+ ions into the cytosol.
- The rise in cytosolic Ca2+ levels results in the recruitment of Protein Kinase C (PKC) to the plasma membrane.
- PKC is present as a soluble cytosolic protein that is catalytically inactive.
- A rise in cytosolic Ca2+ level causes PKC to translocate to the cytosolic leaflet of the plasma membrane, where it interacts with membrane-associated DAG.
- DAG then activates PKC.
- The activated membrane-associated kinase can phosphorylate various enzymes and receptors, thereby altering its activity.
- In many cells, PKC phosphorylates transcription factors localized in the cytosol, triggering their movement into the nucleus, where they activate the genes necessary for cell division.
- In liver cells, PKC regulates glycogen metabolism by phosphorylating and inhibiting glycogen synthase.
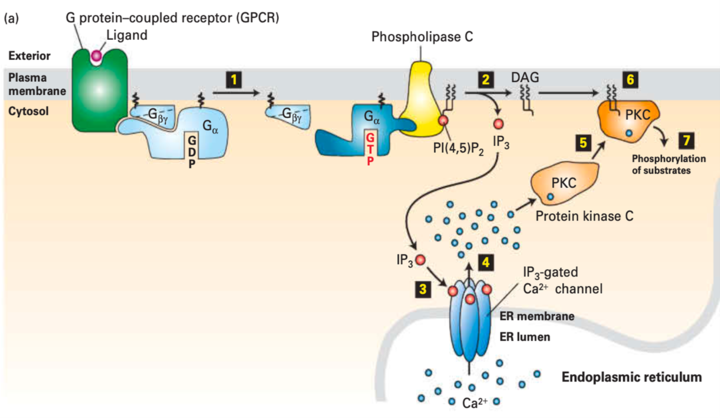
Fig: The IP3/DAG pathway and elevation of cytosolic Ca2+ ions
→AER Full form – Click Here to Download PDF←
Related Articles:
| PCR Full Form | GPCR Full Form |
| FISH Full Form | ELISA Full Form |
| GISH Full Form | RIA Full Form |
| NMR Full Form | ECG Full Form |


