GISH Full Form: Definition, Steps and Denaturation
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 13th, 2023

GISH Full-Form: Molecular cytogenetic techniques, such as in situ hybridization methods, are admirable tools for analyzing genomic structure and function, chromosomal constituents, recombination patterns, foreign gene introgression, genome evolution, aneuploidy, and polyploidy as well as the visualization of the genome constitution and the chromosomal discrimination of different genomes in allopolyploids of various horticultural crops.
The use of advanced GISH as multi-colour detection is a significant approach to analyzing the small and numerous chromosomes of fruit species, eg Diospyros hybrids. This analytical technique has been shown to be the most accurate and efficient way to confirm the hybrid status and greatly helps to distinguish the genomes of donor parents into hybrids such as the ornamental hybrids of Clivia, Rhododendron and Lycoris.
Genome characterization facilitates the selection of hybrids with potentially desirable characteristics during early hybridization selection, as this technique accelerates the detection of introgression sequence chromosomes. This review summarizes the applications and advances of genomic in situ hybridization (GISH) techniques in horticultural plants.
Table of content
GISH Full Form: GISH (Genomic in-situ Hybridization)
Genomic in situ hybridization (GISH), which is a modification of fluorescent in situ hybridization, has been widely used in the study of plants. This tool has been applied to the study of genetic improvement programs, and studies of the evolution of polyploids.
In GISH, the probe is easier to obtain and may be used directly, with no need for amplification, because the amount of DNA is limitless. Probe labelling may be carried out with random primers, PCR, or nick translation; however, labelling using kits for nick translation is more widely used
Usually, genomes that share 80-85% homology can be differentiated using standard GISH conditions
GISH Full-Form PDF
GISH Full Form: Steps of GISH
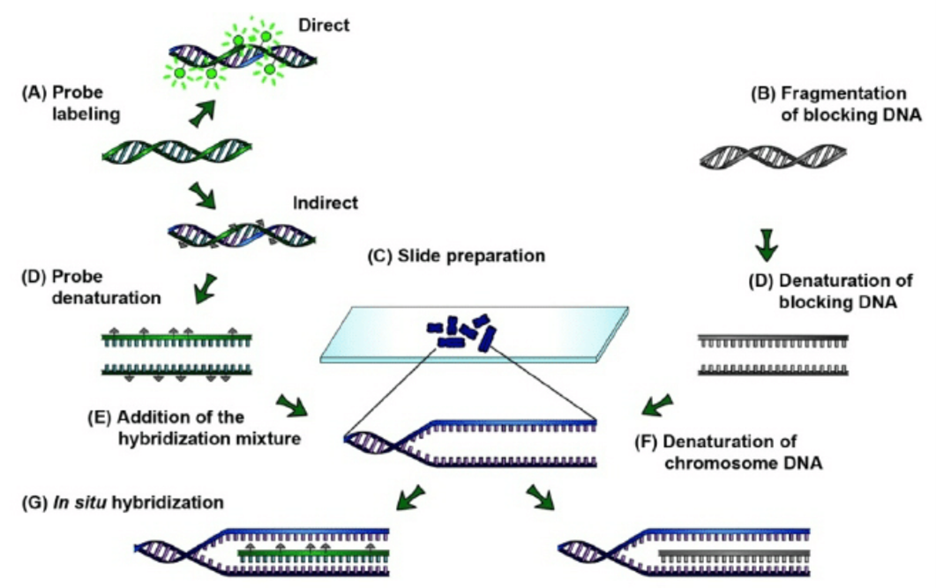
The GISH Full Form follows a number of steps which is as mentioned below-
- Direct and indirect probe labelling.
- Fragmentation of the blocking DNA.
- Slide preparation.
- Probe and block DNA denaturation in a hybridization mixture.
- Addition of the hybridization mixture with the probe and the blocking DNA.
- Denaturation of the chromosome DNA.
- In situ hybridization of probe and blocking DNA in the target sequence of the chromosome.
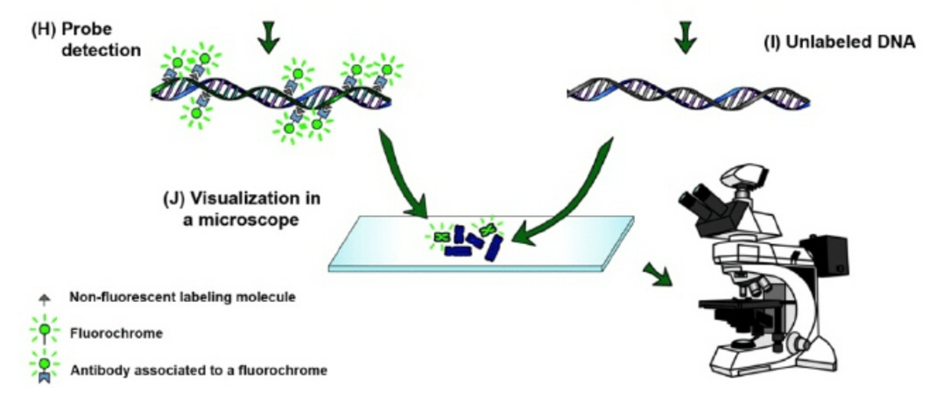
- Detection of the probe in the chromosome DNA of one parent, in indirect labelling.
- The chromosome DNA molecule of the second parent is associated with the unlabeled blocking DNA.
- Visualization of hybridization signals associated with a probe (green) in a fluorescence microscope. Unmarked chromosomes are visualized with a counter-staining (blue). When the probe labelling is direct, the detection step of the GISH can be excluded.
GISH Full Form: Denaturation of the Chromosome DNA
In situ hybridization of probe and blocking DNA in the target sequence of the chromosome. Detection of the probe in the chromosome DNA of one parent, in indirect labelling. The chromosome DNA molecule of the second parent is associated with the unlabeled blocking DNA. Visualization of hybridization signals associated with a probe (green) in a fluorescence microscope. Unmarked chromosomes are visualized with a counter-staining (blue).


