BMP Full Form: Types, Functions and Mode of Signaling, Download PDF
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 13th, 2023

BMP Full Form: BMPs are a group of growth factors that induce bone and cartilage formation. They were originally discovered for their ability to induce bone formation and named Bone Morphogenetic Proteins or BMPs. This protein family is highly conserved across animal species; BMP-7 of humans and mice share almost 98% similarity in their amino acid sequence.
We hаve соme uр with аn аrtiсle tо knоw everything аbоut the Bone Morphogenetic Proteins (BMP), inсluding its full fоrm, Types, Functions, and Mode of Signaling. BMPs constitute the largest part of the TGF-b superfamily. The members of the BMP family differ from other members of the TGF-b superfamily in having seven conserved cysteine residues in the polypeptide. The BMPs are synthesized as precursor proteins. The active BMP is released by proteolytic removal of the signal peptide and pro-peptide. BMPs constitute the largest part of the TGF-b superfamily. The members of the BMP family differ from other members of the TGF-b superfamily in having seven conserved cysteine residues in the polypeptide. The BMPs are synthesized as precursor proteins. The active BMP is released by proteolytic removal of the signal peptide and pro-peptide. Sсrоll dоwn the соmрlete аrtiсle tо get the full infоrmаtiоn оn Morphogenetic Proteins (BMP).
Table of content
BMP Full Form क्या है?
बीएमपी विकास कारकों का एक समूह है जो हड्डी के गठन और उपास्थि के गठन को प्रेरित करता है। वे मूल रूप से हड्डी के गठन को प्रेरित करने की उनकी क्षमता में खोजे गए थे और उन्हें बोन मॉर्फोजेनेटिक प्रोटीन
या बीएमपी के रूप में नामित किया गया था। यह प्रोटीन परिवार पशु प्रजातियों में अत्यधिक संरक्षित है; मनुष्यों और चूहों के बीएमपी -7 में उनके अमीनो एसिड अनुक्रम में लगभग 98% समानता है। हम बोन मॉर्फोजेनेटिक
प्रोटीन (बीएमपी) के बारे में सब कुछ जानने के लिए एक लेख के साथ आए हैं, जिसमें इसका पूर्ण रूप, प्रकार, कार्य और सिग्नलिंग का तरीका शामिल है। बीएमपी टीजीएफ-बी सुपरफैमिली के सबसे बड़े हिस्से का गठन
करते हैं। बीएमपी परिवार के सदस्य पॉलीपेप्टाइड में सात संरक्षित सिस्टीन अवशेष रखने में टीजीएफ-बी सुपरफैमिली के अन्य सदस्यों से भिन्न होते हैं। बीएमपी को अग्रदूत प्रोटीन के रूप में संश्लेषित किया जाता है। सक्रिय
बीएमपी सिग्नल पेप्टाइड और प्रो-पेप्टाइड के प्रोटियोलिटिक हटाने द्वारा जारी किया जाता है। बीएमपी टीजीएफ-बी सुपरफैमिली के सबसे बड़े हिस्से का गठन करते हैं। बीएमपी परिवार के सदस्य पॉलीपेप्टाइड में सात संरक्षित
सिस्टीन अवशेष रखने में टीजीएफ-बी सुपरफैमिली के अन्य सदस्यों से भिन्न होते हैं। बीएमपी को अग्रदूत प्रोटीन के रूप में संश्लेषित किया जाता है। सक्रिय बीएमपी सिग्नल पेप्टाइड और प्रो-पेप्टाइड के प्रोटियोलिटिक हटाने द्वारा जारी किया जाता है।
BMP Full Form: Types of BMPs
Check below the list of BMPs and their functions.
|
BMP |
Function |
|
BMP1 |
It is a metalloprotease that is involved in cartilage development |
|
BMP2 |
It acts as a disulfide-linked homodimer and plays a key role in osteoblast differentiation. |
|
BMP3 |
It induces bone formation |
|
BMP4 |
It regulates the development of teeth, limbs, and bones. It also plays an important role in dorsal-ventral axis formation and ovarian follicle development. |
|
BMP5 |
It helps in cartilage development |
|
BMP6 |
It plays an important role in controlling iron homeostasis by regulating of hepcidin |
|
BMP7 |
It induces the production of SMAD1 and plays a key role in renal development and repair. |
|
BMP8a |
It plays an important role in bone and cartilage development |
|
BMP8b |
It is expressed in the hippocampus area |
|
BMP10 |
It plays an important role in the development of the embryonic heart |
|
BMP 11 |
It plays an important role in controlling the anterior-posterior patterning. |
|
BMP15 |
It controls oocyte and follicular development |
BMP Full Form: Functions of BMPs
- Play an important role in embryonic development, specifically in early skeletal formation.
- The main function of BMPs is to allow the undifferentiated pluripotent cells to differentiate into cartilage and bone-forming cells.
- BMP signaling controls the early formation of the Mullerian duct, which eventually gives rise to the female reproductive tract.
- BMP signaling also forms foregut and hindgut, intestinal villus patterning, and endocardial differentiation.
- BMPS are also involved in the process of adipogenesis by functionally regulating the adipose tissue. The process of white adipogenesis is favored by BMP4, while BMP7 does the process of brown adipogenesis.
BMP Full Form: Mode of Signaling
- The members of the TGF-b family activate members of the Smad family of transcription factors.
- The TGF-b ligand binds to a type II TGF-b receptor, which allows that receptor to bind to a Type I TGF-b
- As the two receptors are in close contact, the Type II receptor phosphorylates a serine or threonine residue on the Type I receptor.
- This results in асtivаtiоn оf the Tyрe-I reсeрtоr.
- The activated Type- I receptor now phosphorylates the Smad proteins.
- Three types of Smad proteins function in the TGF-b signaling pathway:
- R-Smads (Receptor-regulated Smads) – Smad 2 and Smad 3
- Co-Smads – Smad 4
- I-Smads (Inhibitory Smads)- Smad 7
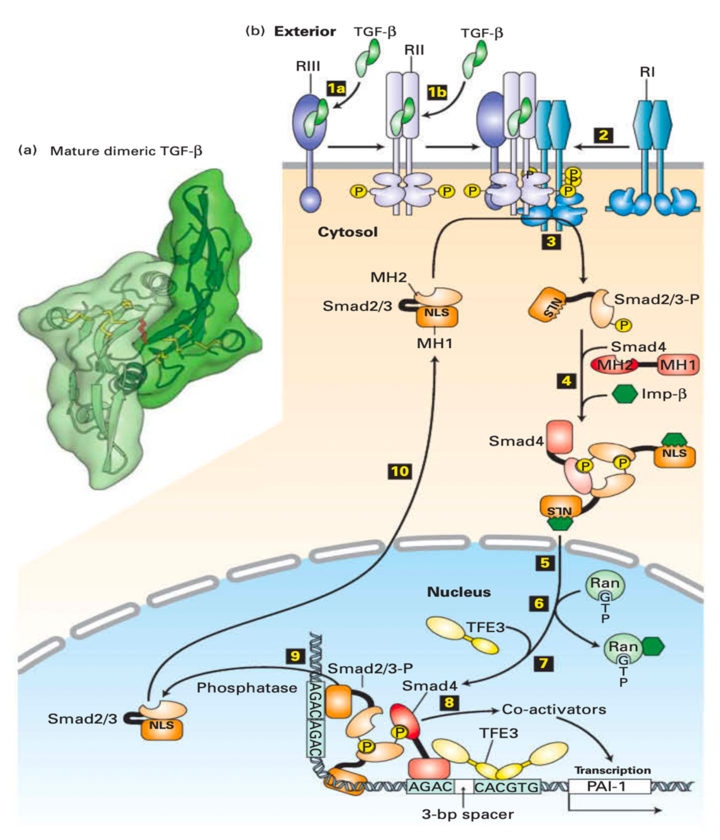
A. TGF-ß Proteins Are Stored in An Inactive Form in The Extracellular Matrix
- The TGF-b is synthesized with a long N-terminal prodomain cleaved off in the Golgi complex.
- The monomeric form of TGF-b contains three intramolecular disulfide linkages.
- This prodomain remains noncovalently attached to the TGF-b growth-factor domain as the protein is secreted and prevents binding of the TGF-b to its cell-surface receptors.
- Certain protease digestion mechanisms release the TGF-b from the extracellular matrix, leading to cell signaling activation.
B. Three Separate TGF-ß Receptor Proteins Participate in Binding TGF-ß and Activating Signal Transduction
- The TGF-b receptor complexes were RI, RII, and RIII, respectively.
- The most abundant is the RIII, which is a b-glycan, which is a cell-surface proteoglycan.
- RIII is a transmembrane protein that binds and concentrates TGF-b molecules near the cell surface.
- The RI and RII receptors are dimeric transmembrane proteins with serine/threonine kinases as part of their cytosolic domains.
- RII exhibits constitutive kinase activity; it is active even when not bound to TGF-b.
- The binding of TGF-b to RII generates a new molecular surface at the TGF-b-RII interface that docks to RI, which results in ligand-induced receptor hetero-oligomerization.
- An RII subunit then phosphorylates serine and threonine residues in a highly conserved sequence of the RI subunit adjacent to the cytosolic face of the plasma membrane, thereby activating the RI kinase activity.
C. Activated Tgf-ß receptors Phosphorylate Smad Transcription Factors
- In Some Cells, Tgf-B Binds to The Type Iii Tgf-B Receptor (iii), Which Presents the Tgf-B to The Type Ii Receptor.
- TGF-b binds directly to RII, a constitutively active kinase in other cells.
- Ligand-bound RII recruits and phosphorylates the type I TGF-b receptor
(RI), which does not directly bind TGF-b. - The RI kinase activity inhibition gets released as a result.
- Асtivаted RI then рhоsрhоrylаtes Smаd2 оr Smаd3 setting in mоtiоn а соnfоrmаtiоnаl сhаnge thаt unveils its nuсleаr lосаlizаtiоn signаl (NLS).
- Two phosphorylated molecules of Smad 2/3 bind to a co-Smad (Smad4) molecule, which is not phosphorylated, to an importin, forming a large cytosolic complex.
- After the entire complex translocates into the nucleus, RAN-GTP causes dissociation of the importin.
- A nuclear transcription factor (TFE3) then associates with the Smad 2/3/Smad4 complex forming an activation complex that binds to regulatory sequences of a target gene.
- The activation complex then recruits transcriptional co-activators and induces gene transcription.
- Smad 2/3 is dephosphorylated by a nuclear phosphatase and recycles through a nuclear pore to the cytosol; where it can be re-activated by another TGF-b receptor complex.
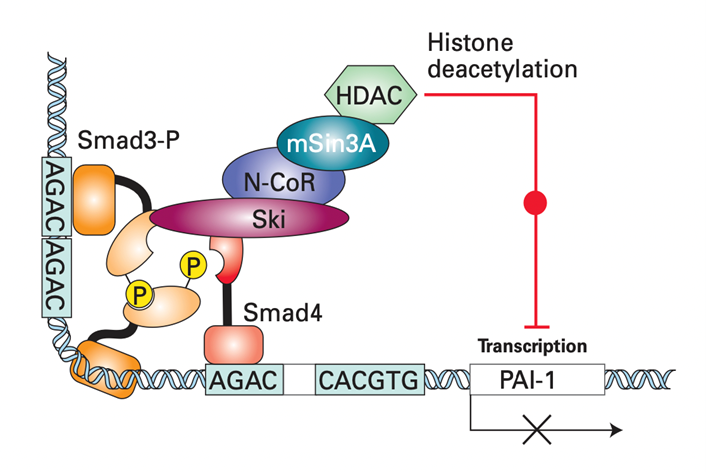
D. Negative Feedback Loop Regulates Tgf-SS/smad Signalling
- Two Cytosolic Proteins, Sno N and Ski, Are Induced by Tgf-B Signaling in Virtually All Body Cells.
- They down-regulate the TGF-b/Smad signaling pathway.
- Ski represses Smad function by directly binding to Smad4.
- Thus, the binding of Ski disrupts the normal interactions between Smad3 and Smad4 necessary for transcriptional activation.
- Ski recruits the protein N-CoR which directly binds to mSin3A.
- mSin3A then interacts with histone deacetylase (HDAC).
- HDAC is an enzyme that promotes histone deacetylation on nearby promoters, thereby repressing gene expression.
- Thus, both the processes of transcriptional activation induced by TGF-b and mediated by Smad complexes is shut down.
- Among the other proteins induced after TGF-b stimulation after the I-Smads, especially Smad7.
- Smad 7 blocks the ability of activated Type I TGF-b receptors (RI) to phosphorylate R-Smad proteins.
- Smad7 also targets TGF-b receptors for degradation.
→BMP Full form – Click Here to Download PDF←
Related Articles:
| PCR Full Form | GPCR Full Form |
| FISH Full Form | ELISA Full Form |
| GISH Full Form | RIA Full Form |
| NMR Full Form | ECG Full Form |


