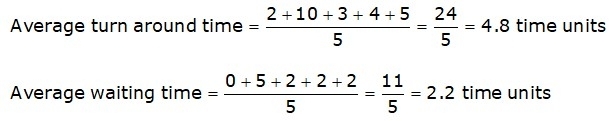Round Robin Scheduling
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 25th, 2023

Round Robin Scheduling is one of the CPU scheduling algorithms in which every process will get an equal amount of time or time quantum of the CPU to execute the process. Each process in the ready state gets the CPU for a fixed time quantum. As the time quantum increases in the round robin scheduling, the number of context switches decreases, and response time increases for the round robin algorithm. Similarly, as the time quantum decreases, the number of context switches increases, and response time decreases.
Round robin scheduling falls under the category of Pre-emptive scheduling. This algorithm got its name from the round robin principle. In the round robin principle, each person takes turns sharing something evenly. This article discusses round-robin scheduling’s algorithm advantages, disadvantages, and examples.
Download Formulas for GATE Computer Science Engineering – Programming & Data Structures
Table of content
What is Round Robin Scheduling?
The round robin scheduling is a preemptive FCFS based on a timeout interval (quantum or time slice). A running process is preempted (interrupted) by the clock, and the process will be kept in the ready state and then submits a process from the ready queue into the CPU.
In the round robin scheduling algorithm, if the time quantum of the process is shorter, it leads to more context switches (overhead). If the time quantum of the process is substantial (time quantum greater than every process service time), then the round robin scheduling algorithm will work the same as FCFS.
Flowchart of Round Robin Scheduling Algorithm
The flowchart of the round robin scheduling algorithm is given below. In this, all the processes are in the ready queue. The burst time of every process is compared to the time quantum.
If the burst time of the process is less than the time quantum in the round robin scheduling algorithm, the process is executed to its burst time. Else, the process is executed upto the time quantum, and when the time quantum expires, it checks if the process is executed completely and then terminates. Else, it goes again to the ready queue.
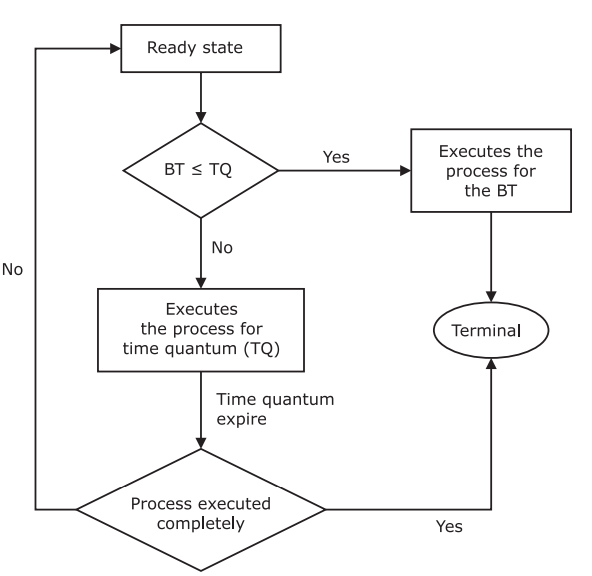
Figure: Flowchart of Round Robin Scheduling Algorithm
Advantages of Round Robin Scheduling
The advantage of the round robin scheduling algorithm is fairness since every process in the ready state or queue gets an equal time quantum or the CPU share.
The round robin scheduling algorithm is simple to implement. The newly created process is added to the end of the ready queue, and the round robin scheduling algorithm does not suffer starvation.
Download Formulas for GATE Computer Science Engineering – Discrete Mathematics
Disadvantages of Round Robin Scheduling
The disadvantage of the round robin scheduling is that this algorithm gives a larger waiting time for the process and the response time of the process is also very large compared to other scheduling algorithms.
The round robin scheduling algorithm provides a low throughput of the system because there are more context switches in the round robin scheduling algorithm, which increase the overhead of the CPU.
Download Formulas for GATE Computer Science Engineering – Algorithms
Round Robin Scheduling Example
Consider the following 5 processes: A, B, C, D, and E, with arrival time and burst time as given below:
|
Process |
Arrival time |
Burst time |
|
A |
0 |
2 |
|
B |
1 |
3 |
|
C |
2 |
1 |
|
D |
3 |
2 |
|
E |
4 |
2 |
What are the average waiting and turnaround times for the round robin scheduling algorithm(RR) with a time quantum of 2?
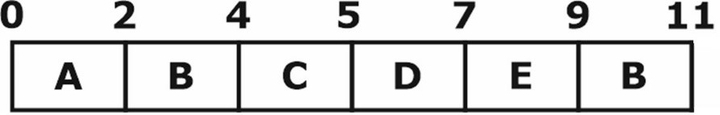
For the round-robin scheduling algorithm, we have the ready queue as:
A, B, C, D, E, B, E, B
The Gantt chart using the RR algorithm is as follows.
Now, we know
- Turnaround time = Completion time – Arrival time
- Waiting time = Turnaround time – Burst time
|
Process Id |
Arrival time |
Burst time |
Completion time |
Turnaround time |
Waiting time |
|
A |
0 |
2 |
2 |
2 – 0 = 2 |
2 – 2 = 0 |
|
B |
1 |
3 |
11 |
11 – 1 = 10 |
10 – 5 = 5 |
|
C |
2 |
1 |
5 |
5 – 2 = 3 |
3 – 1 = 2 |
|
D |
3 |
2 |
7 |
7 – 3 = 4 |
4 – 2 = 2 |
|
E |
4 |
2 |
9 |
9 – 4 = 5 |
5 – 3 = 2 |
Now,