- Home/
- CDS & Defence/
- Article
Design an experiment to Demonstrate Hydrotropism.
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 25th, 2023
The experiment to demonstrate hydrotropism is mentioned below. It is a plant growth response where growth is regulated by a water concentration gradient. Hydrotropism is a similar response to a water stimulus, whereas hydrotropic movements relate to a plant’s movement or development in response to a water stimulation. As a result of this movement, roots move and expand in the direction of the water, exhibiting a favorable hydrotropic response. Hydrotropism is the term for the movement or growth of roots in the direction of a water supply.
Table of content
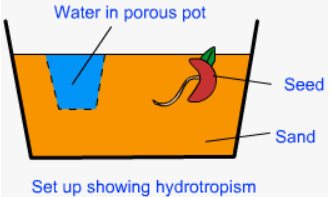
Experiment to Prove Hydrotropism
Procedure:
- Beakers 1 and 2 are seized.
- The seeds are sown in the wet soil found in Beaker 1.
- Seeds are sown in one section of beaker 2 with dry soil added, and another section with moist soil.
- Add a mini water beaker right next to it.
- Keep it for a while so the plants can grow and prosper.
Result:
- It was shown that the presence of moist soil in Beaker 1 causes plants to develop regularly and have straight roots.
- As seen in the above example, the plant in beaker 2 grows in the direction of the water when the water beaker is present next to it.
Conclusion:
- Hydrotropism is demonstrated by the plant’s roots bending in the direction of the porous water-holding vessel.
- A water concentration gradient stimulus controls the direction of development in hydrotropism, a particular sort of plant growth response.
Summary:
Design an experiment to Demonstrate Hydrotropism.
The above-mentioned experiment served to illustrate hydrotropism. It is a reaction to plant development where a gradient in water concentration controls growth. It is indicated by bending the roots of plants in the direction of water-holding vessels.
