Type of Cheque in Indian Banking System: Cheque Related Terms, Types & Quizzes
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 25th, 2023

Cheque is one type of negotiable instrument signed by the drawer that orders the bank to pay a certain sum of money to a specified person. Read the article and attempt quiz given in the end of the article to check your understanding of this topic.
Cheque is a negotiable instrument that contains an order to the bank, signed by the drawer (the person whose name the cheque has been issued), to pay a certain sum of money to a specified person. As per the Negotiable Instrument Act 1881, “cheque is a bill of exchange drawn on a specified banker and not expressed to be payable otherwise than on demand”.
The Type of Cheque topic takes place under the General Awareness Section asked in the following bank exams.
| SBI PO | SBI Clerk |
| IBPS PO | IBPS Clerk |
| RBI Assistant | SBI Apprentice |
| IDBI Executive | IDBI Assistant Manager |
| IBPS RRB PO/Clerk | RBI Grade B |
Cheque Related Terms
- Drawer: Person who issue the cheque or hold the account with bank.
- Drawee: Person who is directed to make the payment against cheque. In case of cheque, it is bank.
- Payee: A person whose name is mentioned in the cheque or to whom the drawee makes payment. If drawer has drawn the cheque in favour of self, then drawer is payee.
- Validity: 3 months from the date of issue of cheque.
- MICR (Magnetic Ink Character Recognition) code is a character recognition technology used mainly by the banks to ease the processing and clearance of cheques. This code is printed at the bottom of cheques and includes the document type indicator, bank code, bank account number, cheque number, cheque amount, and a control indicator. MICR code is a 9-digit code that uniquely identifies a bank and a branch participating in an Electronic Clearing System (ECS).
Types of Cheques
Order Cheque
- Order cheque is a type of cheque that cannot be endorsed, i.e., only the payee, whose name has been mentioned in the cheque is liable to get cash for that amount.
- This is a cheque in which, the printed word ‘Bearer’ on the cheque is cancelled.
- The cancellation of the word “Bearer” automatically makes the cheque an “order” cheque.
- An order cheque can be paid to the named payee across the bank’s account if so presented.
- Identification must be insisted on by the bank when encashing the order cheque for the presenter.
- The ID number and the named payee’s signature will be asked for on the back of the cheque.
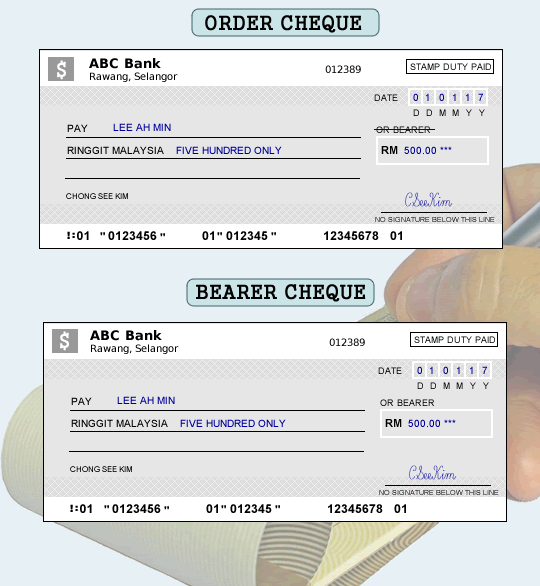
Open / Bearer Cheque
- This type of Cheques are risky in nature for drawer. When the word “Bearer” on the cheque is not crossed or cancelled, the cheque is called a bearer cheque.
- Open / Bearer Cheques are payable to person specified in the instrument or any person who posses it and present for payment over the counter.
- In case of cheque is lost, person who find it can collect payment from the bank.
Blank Cheque
- A cheque on which the drawer puts his signature and leaves all other columns blank is called a blank cheque.
- A check that is signed by the payer but with no specific amount indicated, leaving this determination up to the drawee.
- More generally, a term used for any situation in which an usually high level of trust is afforded by one party to another.
Counter cheque
- Blank cheque was also commonly used as a synonym for counter cheque. It was fairly common for banks, especially in small towns, to issue cheque to customers which were not personalized other than the name of the bank.
- Businesses would have pads of counter cheque which did not even have the bank specified on them – the customer had to not only fill in the value of the cheque, the date, and their signature, but also had to designate the bank on which funds were to be drawn.
Post Dated Cheque
- If a cheque bears a date later than the date of issue, it is termed as post- dated cheque.
- Any check or draft that has a future date written upon it by the user.
- The amount of the check will not be drawn from the account until the date written on the check. For example, a check written on the 14th of the month but dated for the 28th will not be cashed for another two weeks.
Open Cheque
- A cheque that is not a crossed cheque. The person whose name appears on the cheque can write the name of another person on it, and the money will be paid to them.
- An open cheque is a cheque that is not crossed on the left corner and payable at the drawee bank on presentation of the cheque.
- The words ‘OPEN’ should not be struck off and the person issuing the cheque should sign on the reverse of the cheque also before giving it to another person; otherwise the bank may refuse payment.
- The latter can collect the money from any branch of the bank nowadays, depending on the bank. S/he should also sign at the back of the cheque while receiving the amount.
Gift Cheques
- Gift cheque is a cheque foisted in decorative form issued for a small extra charge by the banks for use by customers who wish to give presents of money on special occasions.
- Gift cheques may be purchased in unlimited numbers from every branch of the ‘X’ Bank.
- Example: Birthday Gift, Wedding Gift, Honour Gift and EASI SMART Gift.
Outstanding Cheque
- A cheque which has been written and therefore has been entered in the company’s ledgers, but which has not been presented for payment and so has not been debited from the company’s bank account.
Account Payee Cheque
- A bearer cheque becomes an account payee cheque by writing “Account Payee” or crossing it twice with two parallel lines on the left-hand side top corner.
- It is considered the safest type of cheque and is also known as a crossed cheque.
Crossed Cheque

- A crossed cheque is one which has two short parallel lines marked across its face.
- A cheque which carries too parallel transverse lines across the face of the cheque with or without the words “I and co”, is said to be crossed.
- The advantage of crossing is that it reduces the danger of unauthorised persons getting possession of a cheque and cashing it. A crossed cheque can only be cashed through a bank of which the payee of the cheque is a customer.
Bankers Cheque
- The banker’s cheque is an instrument issued by the bank on behalf of customer containing an order to pay a certain sum to a specified person within the city.
- All banker’s cheque are pre-printed with “NOT NEGOTIABLE”.
- The validity period of the Banker’s cheque is 3 months however it can be re-validated subject to some legal formalities.
Bearer Cheque
- A Cheque which is payable to a person whosoever bears, is called bearer cheque.
- The cheque sometimes can be made payable to “Cash” or bearer or made payable to a specific name, for example, “bujji sekhar or Bearer”.
- This cheque is payable by the drawee bank over the counter to the Bearer or presenter of the cheque.
- A Bearer cheque can be negotiated or pass to another person by mere delivery.
Stale Cheque
- Check presented at the paying bank after a certain period (typically six months) of its payment date.
- A stale check is not an invalid check, but it may be deemed an ‘irregular’ bill of exchange.
- A bank may refuse to honor it unless its drawer reconfirms it payment either by inserting a new payment date or by issuing a new check. Also called stale dated check.
Self-cheques
- A self-cheque is written by the account holder as pay self to receive the money in the physical form from the branch where he holds his account. It comes under bearer cheque where instead of writing the name, the account holder writes “self” to receive money physically from the branch where he holds the account.
Mutilated Cheque
- If a cheque is torn into two or more pieces such cheque is Mutilated Cheque.
- If it presented for payment, such a cheque the bank will not make payment against such a cheque without getting confirmation of the drawer.
- In case, if a cheque is torn at the corners and no material fact is erased or cancelled, the bank may make payment against such a cheque.
Traveller’s Cheques
- It is an instrument issued by a bank for remittance of money from one place to another.
- Travelers Cheques are accepted almost everywhere and are available in many denominations.
Important Details That Should be Present on Cheque
- A cheque should be dated properly.
- Should mention the amount of money in figures and words.
- A cheque must be signed by the person issuing the cheque. The person issuing the cheque is known as Drawer.
- A cheque must be drawn upon a specified bank (drawee).
- A cheque must have the name of the recipient of the cheque. The recipient of the cheque is known as Payee.
Attempt Quiz for Types of Cheques
Click here to access Test Series
Why BYJU’S Exam Prep Test Series?
- Unlimited access to 18+ Bank and Insurance Exam mock tests
- Mock Tests designed by Exam Experts.
- Detailed Performance Analysis.
Download the BYJU’S Exam Prep App Now.
The most comprehensive exam prep app.
#DreamStriveSucceed


