UGC NET Study Notes on Foreign Exchange Exposure || Commerce || Management || Economics
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 13th, 2023

Table of content
With the growth of international markets, all the leading companies are establishing their operating units in the developing countries along with the developed countries. The company has to transact between the two countries which have different foreign exchange rates. In this case, the company will have foreign exchange risk.
- This can be understood with an example. Let us consider a company ABC that has its headquarters in the USA. The domestic currency of the company is the US dollar. It decided to invest one hundred million dollars in expanding its operations in India.
- At the time of estimation of costs, the exchange rate of the dollar with the Indian rupee was seventy rupees. After a period of one year, the company started to execute its plan of expansion. But the exchange rate at the time of execution was sixty-five rupees.
- The company had prepared all the expenditures by keeping the exchange rate of seventy rupees into consideration. But there is a contraction in the exchange rate, and it has now become sixty-five rupees.
- The company has to spend more than the estimated amount on the same units. This is called foreign exchange risk or a foreign exchange exposure.
- Foreign exchange exposure refers to the fluctuations or risks that affect the company while doing financial transactions in foreign currencies.
Types of financial exposure
When a company is dealing with financial transactions in foreign currencies, it may be subjected to any one of the following foreign exchange financial exposure.
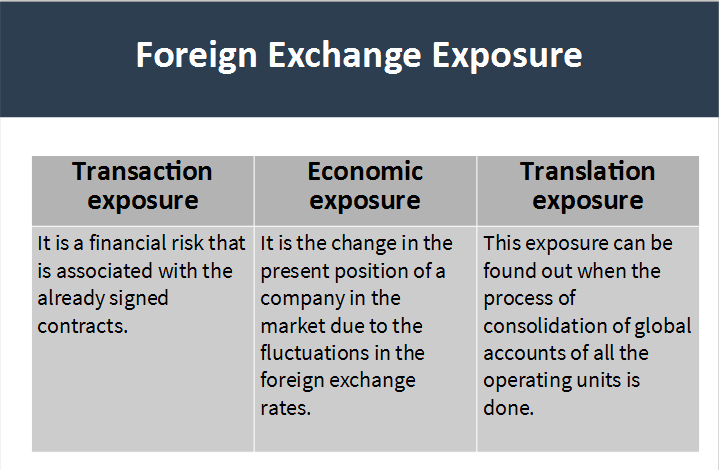
1. Transaction exposure: It refers to the financial risk that is associated with the already signed contracts for a specific period of time.
- Let us consider an American company that had decided to purchase spare parts for various electrical equipment from an Indian company for a period of five years.
- In the third year, there was a decrease in the dollar rate from seventy rupees per dollar to sixty-six rupees per dollar. The American company should pay an additional amount to the Indian company.
- It is a short term financial exposure.
- Due to the fluctuations in the foreign exchange currency rates, there will be a change in the entire value of the contract over a specific period of time.
- Companies use many hedging techniques (risk management or techniques to minimize the losses) like currency swaps and currency futures to minimize transaction exposure.
- Currency swaps involve the agreement between two parties agreeing on exchanging the cash flows at a particular date in the future.
- A futures contract involves an agreement between the buyer and a seller to sell a specific asset, on a predetermined date and price.
2. Economic exposure: It refers to the long term effects of transaction exposure. It is the change in the present position of a company in the market when compared with its competitors due to the fluctuations in the foreign exchange rates.
- It has a direct impact on the future cash flows of a company.
- When a competitor to the company is getting benefited due to the fluctuations in the exchange rates, it may affect the market share of the company.
- Let us suppose two companies A and B which supply raw materials to the manufacturing industries. Company A is operating in India and the USA. Company B is operating only in India and is the major competitor to A.
- With the appreciation of the rupee, the profits of company A have increased drastically. It reinvested the profits in India to beat company B.
- To sustain in the competition, the company has to offer competitive pricing and marketing strategies which will increase the expenditure in the long run.
- Like transaction exposure, this will not be controlled by hedging techniques. There should be a continuous restructuring of the operating costs to sustain the market.
3. Translation exposure: It refers to foreign exchange exposure, which occurs during the finalization of accounts.
- This exposure can be found out when the process of consolidation of global accounts of all the operating units is done.
- The process involves the conversion of all the assets and liabilities of the company in many countries and in different currencies into the currency of the domestic country.
- This is done by taking the present exchange rates of the domestic currency with foreign currencies. It gives the present picture of the company to all the stakeholders.
- This can be understood with an example. Let us consider a company ABC which has its headquarters in the USA and operating units in India and Japan.
- On the day of consolidation of accounts, the appreciation of rupee and yen has happened due to the market fluctuations.
- The company has to report the entire transactions in the US dollar as it is the domestic currency of the company. Due to the depreciation of the dollar, the company posted a small number of losses after consolidating the accounts.
Summary
- When operating in different countries, the company will have foreign exchange exposure.
- The fluctuations in the foreign exchange rates will lead to foreign exchange exposure.
- The home currency of the company is known as domestic currency, and the currencies of the other countries will be treated as foreign countries.
- Risk management techniques are known as Hedging techniques.
- Transaction exposure refers to the short term financial risk that is associated with the already signed contracts for a specific period of time.
- Companies use many hedging techniques like currency swaps and currency futures, to minimize transaction exposure.
- Currency swaps involve the agreement between two parties agreeing on exchanging the cash flows at a particular date in the future.
- A futures contract involves an agreement between the buyer and a seller to sell a specific asset, on a predetermined date and price.
- Economic exposure refers to the long term effects of transaction exposure. It is the change in the present position of a company due to the fluctuations in the foreign exchange rates.
- The companies work on decreasing operational costs to control economic exposure.
- Translation exposure refers to foreign exchange exposure, which occurs during the consolidation of accounts into domestic currency.
- Translation exposure states the present position of the company globally as it benefits the stakeholders of the company.
Mock tests for UGC NET Exam
UGC NET Online Coaching
Thanks
Keep Learning. Go BYJU'S Exam Prep.


