- Home/
- Maharashtra State Exams (MPSC)/
- Article
Carbon Compounds for MPSC Study Notes, MPSC Science Notes, Download PDF
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 25th, 2023

Carbon compounds are an important component in chemistry. Questions are asked on this topic in all MPSC exams. In today’s article, we will look at carbon compounds in detail.
Download BYJU’S Exam Prep App and prepare General Knowledge for Maharashtra State exams.
Table of content
Carbon Compounds
Introduction
- A compound is a substance formed when two or more elements are chemically joined.
- The compounds are classified into the following two groups:
-
Organic Compounds
- Organic compounds are compounds obtained directly or indirectly from animals as well as plants.
- g. Carbohydrates, Proteins, Fats, etc.
-
Inorganic Compounds
- Compounds derived from minerals, not living organisms, are called inorganic compounds.
- g. Fe, Na, Cl, Mg, etc.
- It was said that only nature could produce organic compounds, but in 1820, scientist Friedrich Wöhler developed urea from an inorganic compound called ammonium cyanate in a laboratory.
- In 1845, Acetic Acid was produced in a laboratory by Hermann Kolbe.
- This changed the definition of organic compounds after some time. In the definition, it is said that carbon compounds are called organic compounds. This is because carbon is the main component of organic compounds.
Carbon
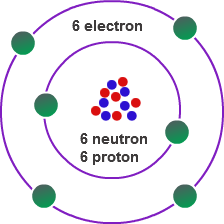
- Carbon has 6 protons, 6 neutrons and 6 electrons.
- The outermost orbitals of carbon have 4 electrons, which share with the electrons of another element.
- The bond formed by sharing with another atom is called a covalent bond.
- Carbon molecules form different compounds by forming covalent bonds.
Hydrocarbons
- All carbon compounds having carbon and hydrogen are known as hydrocarbons.
- There are two main types of carbon compounds:
Saturated Hydrocarbon
- In a hydrocarbon molecule in which all the carbon atoms are connected to another carbon atom by a single bond. They are the simplest class of hydrocarbons. They are called saturated because each carbon atom is bonded to as many hydrogen atoms as possible.
- The group of hydrocarbons that are produced naturally as well as synthetically is known as Alkane.
Alkane group:
Formula: C_n H_(2n+2)
E.g. Methane
Found
- Methane is found naturally as well as synthetically.
- Natural Gas contains 97-98% methane.
- Methane is found naturally in swamps, paddy fields, and biogas. Archaebacteria that produce methane in this area
- Methane is synthetically produced from Sodium Acetate, Soda-lime, Aluminium Carbide.
Properties
- It is in a gaseous state.
- Methane is colourless.
- Dissolves to some extent in water.
- Is flammable and generates heat.
Usage
- Used as fuel.
- It is used for the production of acetylene.
Unsaturated Hydrocarbon
- Not found naturally.
- These are only artificially created in the laboratory.
- When double or triple bonds are formed in carbon-carbon, the compound is called unsaturated hydrocarbon.
- Unsaturated Hydrocarbon falls into two groups:
1. Alkene group
- Alkene can only be prepared artificially. It is not found naturally.
- The compound in Alkene should have at least one Carbon-Carbon double bond.
E.g.: Ethylene C_2 H_4
Found
- Ethylene is produced in the laboratory with the help of alcohol.
Properties
- It is in a gaseous state.
- It is colourless.
- Does not dissolve in water
- It is flammable.
- More active than methane
Usage
- For the manufacture of polythene
- To ripen the fruits
2. Alkyne group
- This is Unsaturated Hydrocarbon.
- Can only be created artificially.
- Carbon-Carbon has a triple bond.
E.g.: Acetylene 〖 C〗_2 H_2
Found
- Can only be created artificially.
- Acetylene is produced from coal, limestone, and water.
- Acetylene can be produced from methane.
Properties
- It is in a gaseous state.
- Is colourless.
- Does not dissolve in water.
- Is flammable.
- Methane is more active than ethylene
Usage
- Used in welding work.
Structural types of hydrocarbons
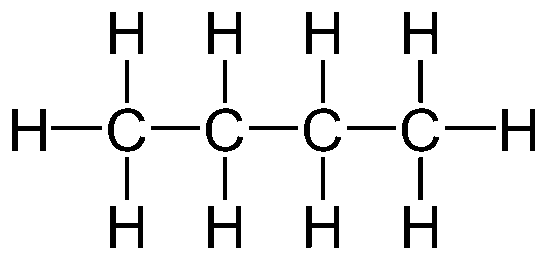
Aliphatic Hydrocarbon
Structure: Plain and simple
E.g. Alkane, Alkene, Alkyne, etc.
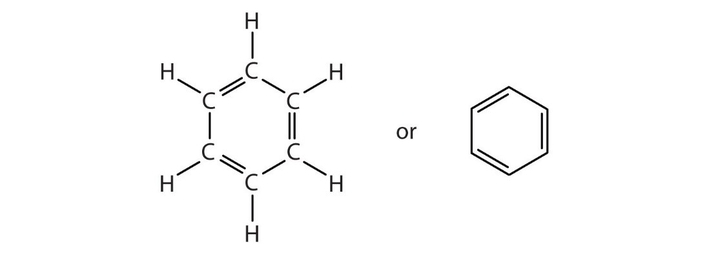
Aromatic Hydrocarbon
Structure: Ring
E.g. Benzene, Methylbenzene, Naphthalene, etc.
Allotropes of Carbon
- When the same elements from different substances by combined in different ways, then those substances are allotropes of those elements.
Graphite
- It has 3 Carbons attached to one Carbon.
- Shape: Graphite is hexagonal in shape.
- Graphite is composed of layers.
- The bond between the two layers of graphite is very weak, so the graphite is soft.
- The structure of graphite is 2D.
- Graphite has a free electron, so graphite can conduct electricity.
- Usage: in pencil, as an electrode, etc.
Diamond
- Diamond consists of 4 Carbons attached to one Carbon.
- Shape – Square
- The structure of a diamond is Network or 3D.
- It is harder than graphite.
- There is no free Electron, so the current cannot flow.
- Uses: for cutting glass, as or in jewellery, etc.
Fullerene (C-60) – Buckminsterfullerene
- C60 is a molecule consisting of 60 carbon atoms, composed of 12 pentagons and 20 hexagons.
- 3 Carbons are attached to one Carbon.
- The shape is similar to a soccer ball.
- The structure of a Fullerene is 3D.
- There are free electrons in Fullerene, thus allowing the conduction of electricity.
To know more about this topic, download the PDF, click here
Carbon Compounds, Download PDF in English
To access the content in Marathi, click here
कार्बन संयुगे
Related Important Articles:
| संख्या मालिकेची मूलभूत माहिती | |
| भारतातील क्षेपणास्त्र तंत्रज्ञान | |
| भौतिकशात्रातील काही मूलभूत संज्ञा | |
| भारतीय राज्यघटनेची निर्मिती |
More From Us:
Maharashtra Static GK
MPSC Current Affairs 2022: Download in Marathi & English
Important Government Schemes For MPSC
NCERT Books for MPSC State Exam 2022
Maharashtra State Board Books PDF
MPSC GK Study Material: Complete Notes for MPSC Exam [Free]
Download BYJU’S Exam Prep App
 Daily, Monthly, Yearly Current Affairs Digest, Daily Editorial Analysis, Free PDF’s & more, Join our Telegram Group Join Now
Daily, Monthly, Yearly Current Affairs Digest, Daily Editorial Analysis, Free PDF’s & more, Join our Telegram Group Join Now





