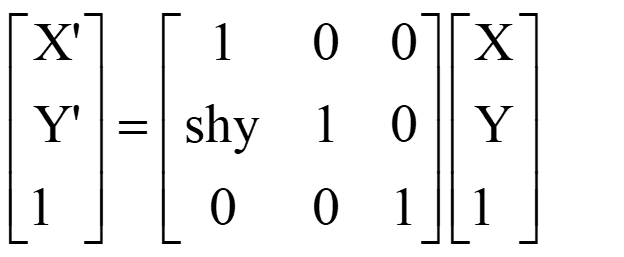What is 2D Transformation in Computer Graphics?
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 25th, 2023

2D Transformation in computer graphics is a process of modifying and re-positioning the existing graphics in 2 dimensions. Transformations help change the object’s position, size, orientation, shape, etc.; there are three basic rigid transformations: reflections, rotations, and translations. 2D Transformations in computer graphics take place in a two-dimensional plane. There is a fourth common transformation called dilation.
In this article, we will learn about the transformation in computer graphics, various types of transformation, and their examples.
Download Formulas for GATE Computer Science Engineering – Programming & Data Structures
Table of content
What is 2D Transformation in Computer Graphics?
Transformation means a change in the object’s orientation, size, and shape. They position the object, change its shape, and even change how something is viewed. Transformation plays a major role in computer graphics, repositioning the graphics on the screen and changing their size or orientation. The basic geometrical 2D Transformation in Computer Graphics are:
- Translation
- Rotation
- Scaling
The derived geometrical transformation is:
- Reflection
- Shearing
Download Formulas for GATE Computer Science Engineering – Algorithms
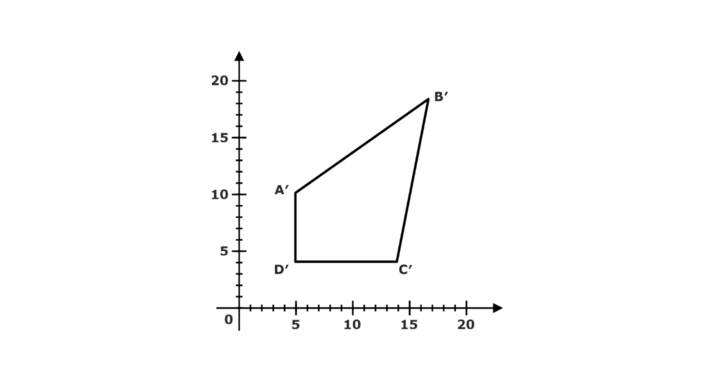
2D Translation in Computer Graphics
The translation is repositioning an object along a straight-line path from one coordinate location to another coordinate location.
The translation is the rigid body transformation that saves an object without deformation. A translation moves to a different position on the screen.
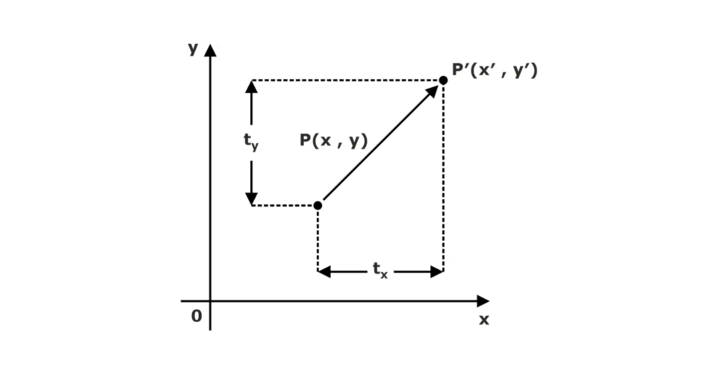
From the above figure, we can write that:
X’ = X + tx
Y’ = Y + ty
The pair (tx, ty) is called the shift vector or translation vector. The above equations may be represented using the column vectors.
>P=[X]/[Y] p’ = [X′]/[Y′] T = [tx]/[ty]
We can also write it as:
P’ = P + T
Download Formulas for GATE Computer Science Engineering – Discrete Mathematics
2D Rotation in Computer Graphics
It is the transformation that is used to reposition one object along the circular path in the XY plane. We specify a rotation angle θ and the portion of the rotation point(pivot point) A and B about which the object is being rotated to generate a rotation.
Suppose you want to rotate it at the angle θ. After rotating it to the new location, you will get a new point P’ A′, B′.
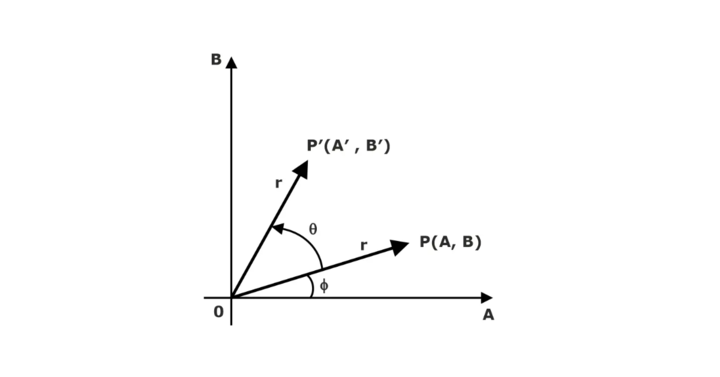
Using standard trigonometric, the original coordinate of points P A and B can be represented as −
A=rcosϕ…(i)
B=rsinϕ…(ii)
Similarly we can represent point P’ A′,B′ as −
A′ = rcos(ϕ+θ) = rcosϕcosθ−rsinϕsinθ…(iii)
B′ = rsin(ϕ+θ) = rcosϕsinθ+rsinϕcosθ…(iv)
Substituting equations (i) & (ii) in equations (iii) & (iv), respectively, we will get
A′ = xcosθ−ysinθ
B′ = xsinθ+ycosθ
Representing the above equation in matrix form,
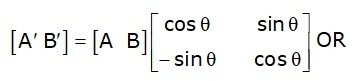
P′ = P . R
Where R is the rotation matrix

The rotation angle will be positive or negative. For the positive rotation angle, we may use the above rotation matrix. However, for negative angle rotation, the matrix will change as shown below:
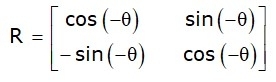
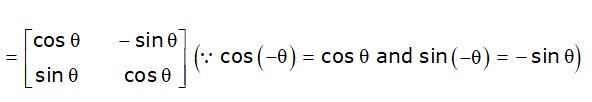
2D Scaling in Computer Graphics
Scaling is the transformation that is used to change the object’s size. The operation is carried out by multiplying the coordinate value(X, Y) with Sx and Sy scaling factors.
Scaling is performed about the origin as
if scale > 1 then enlarges the object and moves it away from the origin.
If scale = 1, then leaves the object the same.
If scale < 1, then shrink/reduce the object and move it towards its origin.
Therefore the equation for scaling is given by:
X’ = X . SX and Y’ = Y . SY
The scaling factor SX and SY scale the object in the X and Y direction, respectively. The above equations may also be represented in matrix form as below:
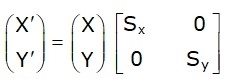
OR
P’ = P . S
The following figure shows the scaling process where S is the scaling matrix.
2D Reflection in Computer Graphics
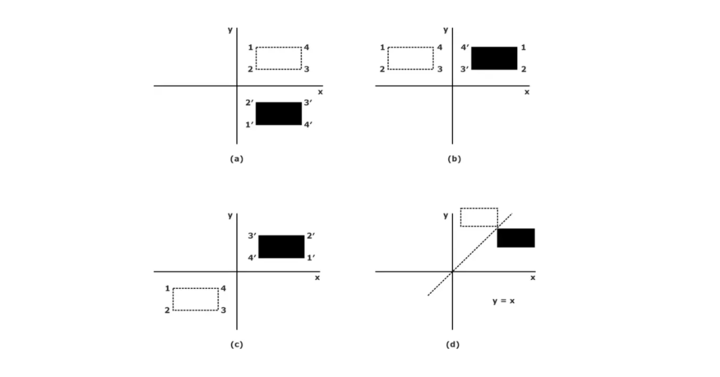
Reflection is the mirror image of the original object. In other words, we will say that it is the rotation operation with 180°. In reflection transformation, the object’s size does not change.
The following figures reflect the X and Y axes and the origin, respectively.
2D Shearing in Computer Graphics
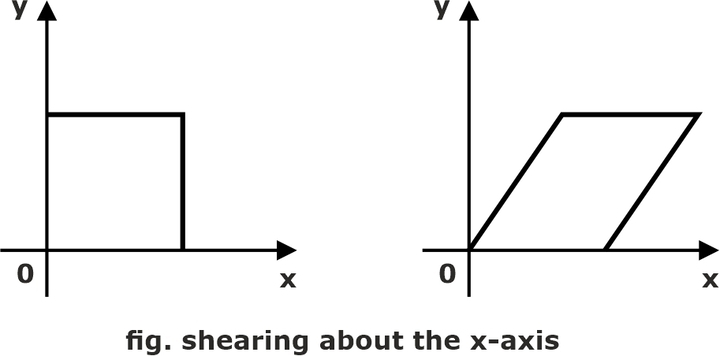
Shearing is the transformation used to change the shape of an existing object in the 2D plane. The size of the object changes along the X direction as well as the Y direction. Shearing along the X-axis is as follows:
Suppose we want to shear the below image along the x-axis with the shearing parameter shx, which is:
The equation is as follows:
X’= X + Y.shx
Y’ = X
The shearing matrix along the X-axis is as follows:
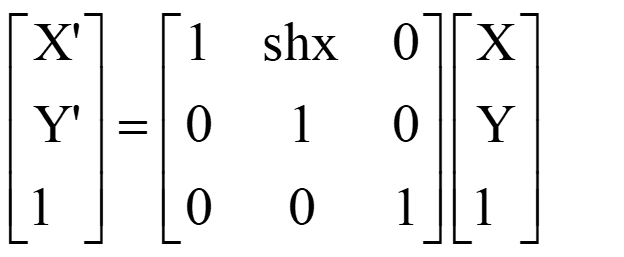
Shearing along the Y-axis is as follows:
Suppose we want to shear the below image along the Y-axis with the shearing parameter shy, which is: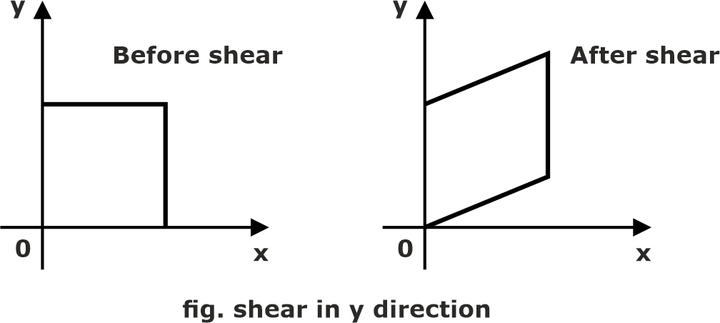
The equation is as follows:
Y’= X.shy + Y
X’ = X
The shearing matrix along the X-axis is as follows: