What is a TCP Header?
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 25th, 2023

The TCP header in the Transmission Control Protocol segment can range from 20 to 60 bytes. The acronym of TCP is Transmission Control Protocol. It is a protocol, practice, and regulations that control online communication between computers. The TCP(Transmission Control Protocol) has two protocols: TCP and UDP. In TCP, UDP headers are limited to 8 bytes in size, while the TCP Header is larger at 20 bytes with an option for additional data.
The 20 bytes in TCP Header are for the compulsory fields and 40 bytes for the optional field. If there is no optional field, a header is 20 bytes. Else, it can be of at most 60 bytes. Candidates are advised to go through the study notes on the TCP header while preparing for GATE and other related engineering examinations.
Table of content
What is Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)?
Before studying the TCP header in detail, let us first discuss the TCP. The TCP provides a connection-oriented, full-duplex, reliable, streamed delivery service using IP to transport messages between two processes.
Reliability is ensured by:
- Connection-oriented service
- Flow control using sliding window protocol
- Error detection using checksum
- Error control using go-back-N ARQ technique
- Congestion avoidance algorithms; multiplicative decrease and slow-start
Formulas for GATE Computer Science Engineering – Databases
What is TCP Header?
The Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) header is the first 24 bytes of a TCP segment that contains the parameters and state of an end-to-end TCP socket. The TCP header tracks the state of communication between two TCP endpoints.
TCP Header Diagram
The diagram of TCP Header is shown below:
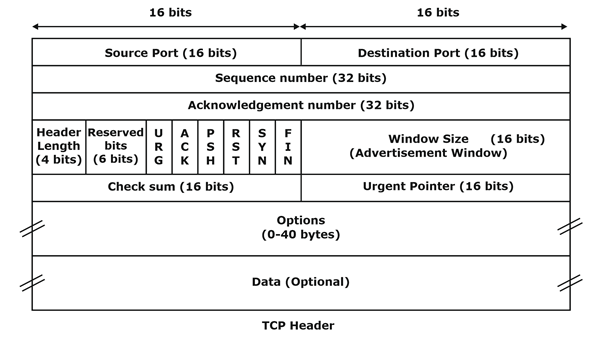
TCP Header Format
The TCP header format is classified into various fields that are as follows:
- Source port
- Destination port
- Sequence number
- Acknowledgement number
- HLEN
- Control Flag Bits
- Window size
- Checksum
- Options
Formulas for GATE Computer Science Engineering – Theory of Computation
Source Port
It defines the port number of the application program in the sender’s host. The source port is 16 bits in size.
Destination Port
It defines the port number of the application program in the receiver’s host. The destination port is 16 bits in size.
Sequence Nnmber
It conveys to the receiving host which octet in this sequence comprises the first byte in the segment. The sequence number is a 32-bit field. TCP assigns a unique sequence number to each byte of data contained in the TCP segment.
Acknowledgement Number
The acknowledgement number specifies the sequence number of the next octet that the receiver expects to receive. The acknowledgement number is a 32bit field. During the three-way handshake, the request segment is sent for connection establishment.
HLEN
This field specifies the number of 32-bit words present in the TCP header. This field helps the receiver to know from where the actual data begins. The HLEN field is of 4 bits, and it ranges from 20 bytes to 60 bytes in tcp header size.
Control Flag Bits
The control flag bit is 6 bits. The control flag field is basically divided into the following felids that are as follows:
- If the URG(Urgent pointer)=1, then the urgent pointer is in use otherwise, it is not in use.
- IF ACK = 1 means the acknowledgement number is valid, and if ACK = 0 means the segment does not contain acknowledgement.
- If PSH(Push the data without buffering) = 1 means the request to forward the data to the application layer without buffering it.
- If RST = 1 means it abruptly resets the connection whenever there is a host crash or is sometimes used to reject a segment.
- SYN: Synchronize sequence numbers during connection establishment
Connection request: SYN=1,ACK=0
Reply: SYN=1,ACK=1
FIN: Terminate the connection
Window Size
It tells how many bytes may be sent, starting at the acknowledged byte. It advertises how much data (in bytes) the sender can receive without acknowledgement. Thus, the window size is used for Flow Control.
Checksum
The checksum is used for error detection. It checksums the data, header, and pseudo-header. The sender adds CRC checksum to the checksum field before sending the data. The receiver rejects the data that fails the CRC check.
Options
The options field is used for several purposes. The options field contains 40 bytes of information. Some widely used options are:
- MSS(maximum segment size)
- Window scale
- Time Stamp


