- Home/
- Maharashtra State Exams (MPSC)/
- Article
Forest Fires: Types, Causes and Effects, Preventive Measures
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 25th, 2023

Forest Fires: Uttarakhand has been battling with the recurring events of forest fires. Nearly 1000 incidents of forest fires reported, with 45 in the last 24 hours in 1st week of April. Uttarakhand sought help from the central govt for helicopters and personnel from the National Disaster Response Force (NDRF).
Download BYJU’S Exam Prep App and prepare General Knowledge for Maharashtra State exams.
Table of content
-
1.
Forest Fires: Types, Causes and Effects, Preventive Measures
-
2.
What are Forest Fires?
-
3.
Causes of Forest Fire
-
4.
Types of forest fires
-
5.
Indian regions vulnerable to forest fires?
-
6.
Why forest fires occur frequently in Uttarakhand?
-
7.
Reasons for rising severity in mitigating forest fires
-
8.
Preventive measures
-
9.
Way forward
Forest Fires: Types, Causes and Effects, Preventive Measures
Uttarakhand became a separate state in 2000, and due to the climate change impacts, the state is battling with one of the worst episodes of forest fires. Normally, forest fires occur in the third week of May when the temperature in the north starts to reach its peak. But this year it is occurring from April onwards.
State Forest Department Highlights
- 989 fire incidents reported between Oct 1 2020 and April 4, 2021.
- Around 1297.43 hectares of rich, biodiverse forests have been destroyed.
- India’s State of Forest Report 2019 highlights that over 30,000 incidents of forest fires were reported in the country in 2019.
What are Forest Fires?
- It is a common hazard in the forests that occur due to uncontrolled burning leading to loss of biodiversity. Forest fires pose severe threat to fauna and flora disturbing the ecology and environment of a region.
Causes of Forest Fire
1. Natural Causes
- High atmospheric temperature and dryness (low humidity)
- Littering of leaves and twigs burst into flames ignited by the slightest spark.
2. Man-made Causes
- When forests catch hold of naked flame due to sheer carelessness such as cigarette or bidi, electric spark or any other source of fires.
Types of forest fires
1. Natural or controlled forest fire
- A controlled burn is a wildfire that are set intentionally for a specific purpose.
- It is also called back-burning, all the flammable material is burnt up and extinguished.
- Well planned and well-managed controlled burns are beneficial for forest management, the excess littering when cleared helps avert wildfires.
2. Surface fires
- Occur due to surface litters resulted from shedding of leaves on the forest floors.
3. Underground fire
- Low intensity fire
- Occurs due to organic matter burning in the dense forests.
- Usually, these fires spread entirely underground and burn for some meters below the surface.
- Fire spreads very slowly and continues up to months destroying vegetative cover of the soil.
4. Crown fires
- A crown fire is the one in which the crown of trees and shrubs burn.
- Crown fires are dangerous in a coniferous forest, as the logs burn profusely.
- If the fire starts downhill, chances are that it spreads up as per the upward air flow, spreading the fire.
Indian regions vulnerable to forest fires?
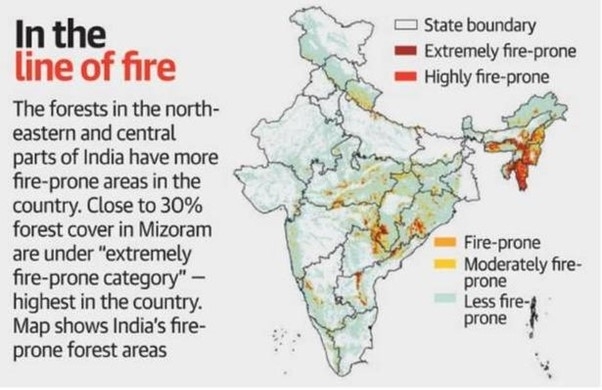
- Youngest fold mountain ranges of Himalayas
- Western Himalayas are more prone to forest fires than the Eastern Himalayas.
- Eastern Himalaya have high humidity and dense forest cover due to intense rains.
- Chirr (Pine) forests are more susceptible for forest fires and their expansion has resulted more incidents of forest fires in recent years.
Why forest fires occur frequently in Uttarakhand?
- Forest fires are not uncommon in Uttarakhand.
- During spring season mid-February onwards, the trees shed dry leaves and soil loses moisture and temperature increases. Uttarakhand normally witnesses forest fires after the spring season, and it continues up till mid-June.
- The year 2021 is different for two reasons:
- Lack of adequate rainfall in the winter resulting in dry soil.
- Higher temperature in March and April compared to previous years.
- The impact of the climate crisis is not only linked with change in weather pattern but also the anthropogenic activities such as clearing land for farming related activities, or sometimes sheer carelessness.
- A study by Forest Survey of India nearly 95% of fire incidents are of anthropogenic origin.
Reasons for rising severity in mitigating forest fires
- India’s firefighting capacities are not adequate
- Lack of modern equipment
- Poor rapid response system lacking requisite field staff and number of vehicles
Impact of Forest Fire
- Loss of valuable timer resources
- Catchment area degradation
- Loss of flora and fauna endemic to the region
- Wildlife habitat loss
- Natural regeneration is disturbed leading to the reduction of forest
- Loss of carbon sink
- Microclimate of the region is impacted
- Soil productivity is impacted, and soil erosion increases
- Livelihood of tribal people or the forest dwellers affects severely as many are dependent on non-timber forest produce
- Measures
- Successive Five-Year Plans have provided funds for forests maintenance.
- During the British period, fire was prevented in the summer by removingforest litter all along the forest boundary. This was called Forest Fire Line
- This line used to prevent fire breaking into the forest from one compartment to another.
- The collected litter was burnt in isolation. Generally, the fire spreads only if there is continuous supply of fuel (Dry vegetation) along its path.
Govt. measures
- Successive Five-Year Plans have provided funds for forests fighting.
- During the British period, fire was prevented in the summer through removal of forest litter all along the forest boundary. This was called Forest Fire Line
- This line used to prevent fire breaking into the forest from one compartment to another.
- The collected litter was burnt in isolation. Generally, the fire spreads only if there is continuous supply of fuel (Dry vegetation) along its path.
Preventive measures
- Clearing of the combustible and inflammable material on regular intervals
- Vigilance drive to keep fire incidents under the watch
- Adaption of safety practices near forests i.e., in factories, oil stores, coalmines, chemical plants and in local community household kitchens.
- Incorporation of fire fighting and fire reducing equipment
Way forward
- Forest fires are usually seasonal, and they usually start in the dry season. Fire and can be prevented by adequate precautions. The best way to control a forest fire is to prevent it from spreading. It can be done by creating firebreaks in the shape of small clearings of ditches in the forests.
- Uttarakhand’s Forest fire is a warning of the challenges that lie ahead in preserving India’s fragile natural ecosystems. To retain the precious carbon sinks, which is depleting with every passing year, there is need to involve local communities’ participation for timely report or averting the incidents.
Read the article in Marathi, click here: जंगलातील आग
More From Us:
MPSC Current Affairs 2022: Download in Marathi & English
Important Government Schemes For MPSC
NCERT Books for MPSC State Exam 2022
Maharashtra State Board Books PDF
MPSC GK Study Material: Complete Notes for MPSC Exam [Free]
 Daily, Monthly, Yearly Current Affairs Digest, Daily Editorial Analysis, Free PDF’s & more, Join our Telegram Group Join Now
Daily, Monthly, Yearly Current Affairs Digest, Daily Editorial Analysis, Free PDF’s & more, Join our Telegram Group Join Now


