Conditions for Deadlock in Operating System
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 25th, 2023

Conditions for Deadlock in Operating System is a scenario known as a deadlock that includes the interaction of multiple resources and processes. A deadlock condition occurs in the system when a process cannot proceed because it needs to obtain a resource that is held by another process, but it itself is holding a resource that the other process needs.
Deadlock may be defined as a permanent blocking of processes in a multi-programming operating system when a set of processes either compete for the same system resources or communicate with each other and wait for each other to complete their task first. Generally, a deadlock problem involves conflicting needs of the same resources by two or more processes. Here, we will see all the necessary conditions for Deadlock in Operating System.
Table of content
What is the Condition for Deadlock?
In the system, the deadlock occurs when the system has these four conditions simultaneously that are as follows:
- Mutual Exclusion
- No-preemption
- Hold & wait
- Circular wait
For a deadlock to occur, all four conditions must be met. The impasse is broken if any one of them is averted or resolved.
Mutual Exclusion
When two people meet on the landings, they cannot just stroll through since there is only enough room for one person. The first prerequisite for the occurrence of the deadlock is to enable only one person (or process) to utilize the step between them (or the resource).
- The resource has to be allocated to only one process, which is freely available.
- There should be a one-to-one relationship between the resource and process.
No-preemption
To overcome the deadlock, just cancel one of the processes and let the others continue. However, the Operating System does not. It provides resources to the processors for as long as the job requires till it is accomplished. As a result, there is no need for a temporary reallocation of resources. It’s the third deadlock condition.
- The resource has to be voluntarily released by the process after completing the execution.
- It is not allowed to preempt the resource from the process forcefully.
Hold & wait
Holding occurs when two individuals refuse to retreat and defend their territory. This is the next condition that must be met in order to break the deadlock.
- A process acquires resources piecemeal. While it awaits allocation and assignment of other resources, it holds on to its acquired resources.
- In other words, a process waits for some resources while holding another resource simultaneously.
Circular wait
Circular wait occurs when two persons refuse to retreat and wait for each other to recede so that they can finish their work. It’s the final thing that can cause a deadlock. Processes waiting for resources from the others form a circular chain. In that chain, each process holds at least one unit resource, which is demanded by the next process in the chain.
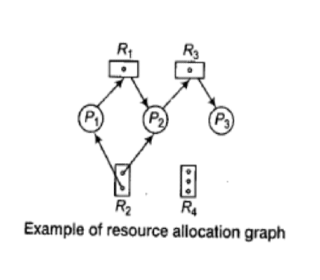
Suppose there exists a set {P0, P1,…, P0} of waiting processes such that the process P0 is waiting for a resource that P1 holds, and the process P1 is waiting for a resource that P2 holds. The resource allocation graph is:
Symbol and Representation of Condition for Deadlock
The circle will represent the process as
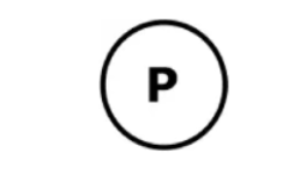
Resources will be represented with rectangle blocks as

If the process P1 is requested a resource, then it is represented as
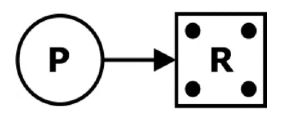
If the process P1 is holding an instance, then it is represented as
Condition for Deadlock Prevention
- The Ostrich Approach: Just ignore the deadlock problem altogether.
- Deadlock Prevention: Prevent deadlock by resource scheduling so as to negate at least one of the four conditions.
- Deadlock Avoidance: Avoid deadlock by careful resource scheduling.
- Deadlock Detection and Recovery: Detect deadlock and, when it occurs, take steps to recover.
Deadlock Prevention
- Elimination of “Mutual Exclusion” Condition
- Elimination of “Hold and Wait” Condition
- Elimination of “No-preemption” Condition
- Elimination of “Circular Wait” Condition
Deadlock Avoidance
- Max n x m matrix. If max [i, j] = k, then process Pi may request at most k instances of resource type Rj.
- Allocation n x m matrix. If allocation [i, j] = k, then Pi is currently allocated k instances of Rj.
- Need n x m matrix. If need [i, j] = k, then Pi may need k more instances of Rj to complete its task.
Need [i, j] = max [i, j] – allocation [i, j]
Safety Algorithm
- Step 1: Let ‘work’ and ‘finish’ be vectors of length m and n, respectively. Initialize
Work = Available
Finish [i] = False (for i = 1, 2, … ; n)
- Step 2:Find i such that both
- Finish [i] = False
- Need<= Work
If no such i exists, go to step 4.
- Step 3:Work = Work + Allocation Finish [i] = True Go to step 2.
- Step 4: Finish [i] = True (for all i) Then, the system is in a safe system
Deadlock Detection
- Maintain wait-for graph.
- Nodes are processes.
- Pi → Pj if Pi is waiting Pj
- Periodically invoke an algorithm that searches for a cycle in the graph.
- An algorithm to detect a cycle in a graph requires an order of n2 operations, where n is the number of vertices in the graph.
Recovery Scheme
- Temporarily prevent resources from deadlocked processes.
- Back off a process to some checkpoint allowing preemption of a needed resource and restarting the process at the checkpoint later.
- Successively kill processes until the system is deadlock-free.
Condition for Deadlock Example
The examples of deadlock conditions are mentioned below.
- The system has 2 tape drives. P1 and P2 each hold one tape drive, and each needs another one.
- Semaphores A and B, initialized to 1. P0 and P1 are in deadlock as follows:
(a) P0 executes wait (A) and preempts.
(b) P1 executes wait (B).
(c) Now, P0 and P1 enter in deadlock.
|
P0 |
P1 |
|
wait(A); |
wait(B); |
|
wait(B); |
wait(A); |
- Assume the space is available for allocation of 200Kbytes, and the following sequence of events occurs.
|
P0 |
P1 |
|
… Request 80KB; …; Request 60KB; |
… Request 70KB; … Request 80KB; |
Deadlock occurs if both processes progress to their second request.
| Important Topics for Gate Exam | |
| Brittle Material | Capacitors in Parallel |
| Capacitors in Series | Carnot Cycle |
| Cement Test | Clamping Circuit |
| Clipping Circuit | CMOS Fabrication |
| CMOS Converter | Column Base |
Download Byjus Exam Prep App for the best Preparation



