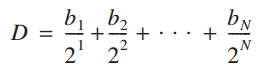- Home/
- GATE ELECTRICAL/
- GATE EE/
- Article
A/D and D/A converters Study Notes for GATE EE Exam
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 25th, 2023

A/D and D/A converters Study Notes for GATE EE Exam: In this article, you will find the Study Notes on Data Converters which will cover the topics such as DAC & ADC, Classification of DAC, Weighted Resistor and R-2R ladder circuits, Inverting Circuits, Types of ADC and CMOS Logic implementations.
Download Formulas for GATE Electrical Engineering – Electrical Machines
Table of content
ADC and DAC
It is possible to convert the analogue signal to digital and vice-versa. We can get digital from analogue through ADC and can get analogue from digital through DAC.
Digital to Analog Converter (DAC)
DAC converter (also called D/A) accepts an n-bit digital word or input and produces an analogue sample.


where, bn = 1, k = Proportionality factor; bn = 0, if nth bit of digital input is 1; if nth bit of digital input is 0.
Classification of DAC

Weighted Resistor DAC (N – bit):
- A DAC can be implemented by using a Summing Amplifier and a set of resistors R, 2R, 4R, 8R, etc as its inputs.
- The circuit consists of a reference voltage Vf, N binary-weighted resistors R, 2R, 4R, 8R, . . . , 2(N-1) R, N single-pole double-throw switches & an Op-amp together with its feedback resistance Rf = R/2.
- The switches are controlled by an N-bit digital input word D.

V0 = -Rf If = -Vf D

LSB resistance = (2N–1) MSB resistance.
- The accuracy of the DAC depends critically on the accuracy of the Reference voltage, the precision of the binary-weighted resistors, and the completeness of the switches.
- A disadvantage of the binary-weighted resistor network is that for a large number of bits (N > 4), the difference between the smallest and largest resistances becomes quite large. This denotes difficulties in maintaining accuracy in resistor values.
R – 2R Ladder DAC:
Non-Inverting OP-amp type DAC


Inverting Amplifier:



Inverted Ladder R – 2R Circuit:


![]()

Specifications for DAC
- Resolution in DAC is exchanged in analogue output corresponding to 1 LSB bit increase in the input.
- Resolution = weight of LSB =

- V= Voltage corresponding to logic
- N = Number of bits.
- Analog Output Analog output = resolution x decimal equivalent of binary data
- Maximum Analog Output Voltage (VFS) VFS is the maximum analogue output voltage of DAC.
![]()
VFS = Vr
- Percentage Resolution:
![]()
- Maximum Error Maximum error acceptable in ADC and DAC equals resolution.
- Resolution (R-2R ladder type) =

Analog to Digital Converter
- A/D converter (also called an ADC) accepts an analogue sample VA and produces an N-bit digital word.
- Examples of ADC usage are cellphone, thermocouples, digital voltmeters, and a digital oscilloscope.
- Types of A/D Converters: Dual Slope A/D Converter, Successive Approximation A/D Converter, Flash A/D Converter, Delta-Sigma A/D Converter, etc.
Counter type ADC:

- In N-bit counter type ADC:
- Maximum number of clock pulses required for conversion = 2N -1
- The maximum time required for conversion = (2N -1) TCLK
- Minimum number of clock pulses = 1
- The average number of clock pulses = 2N-1
Successive Approximation Type ADC:
- It is faster than digital ramp ADC.
- Conversion time (tc) is independent of the value of the analogue input voltage (Va).
- It has a fixed conversion time.

- Maximum number of clock pulses = N for conversion
- Maximum conversion time = N.TCLK
Flash Type ADC:
- It is also known as Parallel-comparator type ADC or Simultaneous converter.
- It is the highest speed ADC (fastest ADC)
- Functional component
- It utilizes 2N -1 comparators to compare the input signal level with each of the 2N -1 possible quantization levels.
- The output of the comparators is processed by an encoding-logic block to provide the N bits of the output digital word.
- Complete conversion can be obtained within one clock cycle.
- For N-bit comparator:
- Total number of comparators = 2N -1,
- Total number of resistors = 2N,
- Total number of priority encoders = 1 (2N × N)
2-bit Flash Converter:

Dual Slope Integrating Type ADC:
- It has the slowest conversion time but has a relatively low cost.
- The following components are present in the Dual slope A/D converter:
- Integrator
- Electronically Controlled Switches
- Counter
- Clock
- Control Logic
- Comparator


where, n = Count recorded in the counter.
Dual Slope Integrating Type ADC:
- Total number of clock pulses = 2N + n
- Maximum number of clock pulses = 2N + 2N – 1 = 2N + 1 -1== 2N + 1

CMOS: Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor
CMOS inverter


CMOS contains two types of power dissipation
- Static power dissipation During logic 0 or logic 1
- Dynamic power dissipation Occurs during transitions and it is given by
 where C is the capacitance of MOSFET
where C is the capacitance of MOSFET
Other Logic Gates by CMOS

- Power dissipation is lowest in CMOS.
- Pdiss = 0.01mW Figure of merit = 0.7 PJ
- Noise margin =VDD/2
- tpd = 70 ns Fan-out = 50
Click on the Links Below to Avail Green Card:
Click Here Avail GATE/ESE EC Green Card !!! (150+ Mock Tests)
Click Here Avail GATE/ESE EE Green Card !!! (193+ Mock Tests)
| Important Related Links | |