- Home/
- Regulatory Bodies/
- RBI Grade B/
- Article
Reserve Bank of India Functions, Power and Subsidiaries
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 11th, 2023

Reserve Bank of India possesses ample power with respect to the financial system of our nation. In this article, we have come up with the functions, powers, and subsidiaries of RBI in detail. Go through the full article to know everything about our nation’s Central Bank.
Table of content
RBI is India’s central bank and regulatory body, which is responsible for the issue and supply of the Indian rupee and the regulation of the Indian banking system. It also manages the country’s main payment systems and works to promote its economic development.
RBI also performs functions such as ‘Banker to Banks’ and ‘Banker to Government’. Other functions of RBI include overviewing the Indian Financial System, Currency circulation and management, Foreign Exchange Reserve Management, consumer education, and protection, etc.
This is part 2 of the 3 article series on RBI, in which we are going to discuss the powers and functions of the central bank of India. In part 1 of the article series, we discussed the history and structure of RBI.
|
There are going to be three articles in this series. They are; 1. History and Structure of RBI 2. Functions and Power of RBI |
Now, let’s discuss the RBI’s Function and Powers in detail.
Functions of RBI
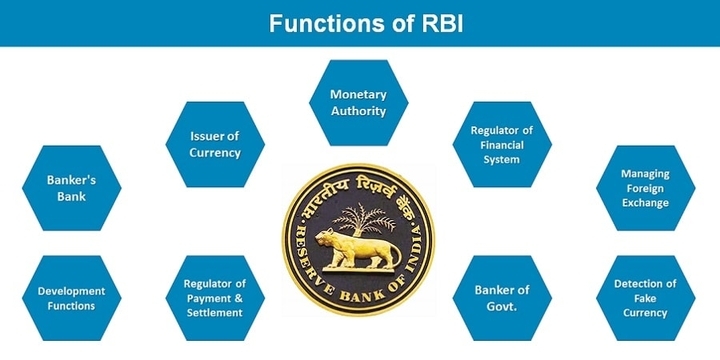
1. Monetary Authority of India:
- RBI Formulates, implements and monitors the monetary policy of India.
- The objective of the monetary policy is to maintain price stability while keeping in mind the objective of growth.
- RBI uses various direct and indirect instruments for implementing monetary policy are;
- Repo Rate
- Reserve Repo Rate
- Marginal Standing Facility
- Liquidity Adjustment Facility
- Bank Rate
- Cash Reserve Ratio
- Open Market Operations
- Market Stabilization Scheme
2. Regulates and supervise the financial system
- RBI regulates the commercial banks, co-operative banks and certain categories of Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs).
- RBi guides broad parameters of banking operations within which India’s banking and financial system functions.
- The objective behind the maintain public confidence in the financial system, protect depositors’ concerns and provide cost-effective banking services to the public.
3. Manager of India’s Foreign Exchange:
- RBI manages the Foreign Exchange of India under the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (FEMA).
- RBI facilitates external trade and payment and promotes the development and maintenance of the foreign exchange market.
4. Issuer of Indian currency:
- RBI is the central bank of India and is responsible for issuing, exchanging or destroying currency and coins not fit for circulation.
- RBI make sure to provide the public with an adequate quantity of supplies of fit currency notes and coins.
5. Developmental role in the Indian Economy:
- RBI performs a wide spectrum of promotional functions to support the national objectives of India.
6. Regulates and Supervises Payment and Settlement System of India:
- It is RBI’s responsibility to propose and promotes safe and efficient modes of payment systems in the country.
- RBI makes certain to maintain the public confidence in the payment and settlement system of India.
7. Other Functions:
- Banker to the Government:
- RBI performs all the banking functions for the central and the state governments of India. In other words, RBI acts as their banker.
- Banker to banks:
- RBI maintains banking accounts of all scheduled commercial banks of India.
Powers of Reserve Bank of India
Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934 and the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 have given the RBI wide powers of Supervision and Control over commercial Banks relating to
- licensing and establishments,
- branch expansion,
- liquidity of their assets,
- management and methods of working,
- amalgamation (merger)
- reconstruction and liquidation.
Important Acts of RBI
Following are the acts administered by the RBI:
- Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934
- Government Securities Regulations, 2007
- Banking Regulation Act, 1949
- Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999
- Securitisation and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest Act, 2002 (SERFESI Act)
- Credit Information Companies(Regulation) Act, 2005
Subsidiaries of RBI
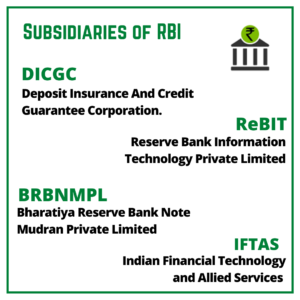
A subsidiary company is an organization that is owned or controlled by any other company. Following are the Fully Owned subsidiaries of RBI:
- Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation of India (DICGC)
- Bharatiya Reserve Bank Note Mudran Private Limited (BRBNMPL)
- Reserve Bank Information Technology Private Limited (ReBIT)
- Indian Financial Technology and Allied Services (IFTAS)
1. Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation of India (DICGC)
- Establishment: 15th July 1978.
- Headquarters: Mumbai
- DICGC was formed by merging Deposit Insurance Corporation (DIC) and Credit Guarantee Corporation of India Ltd. (CGCI)
- The functions of the DICGC are governed by the provisions of the DICGC Act 1961 framed by the Reserve Bank of India.DICGC was established for providing insurance of deposits and guaranteeing credit facilities.
2. Bharatiya Reserve Bank Note Mudran Private Limited (BRBNMPL)
- Establishment: 3rd February 1995
- Headquarters: Bengaluru
- The company manages 2 Presses:
- Mysore in Karnataka
- Salboni in West Bengal.
- Apart from this, RBI has two more printing presses both owned by the Government of India: Nasik (Maharashtra) and Dewas (Madhya Pradesh)
- Coins are minted in four mints owned by the Government of India. The mints are located in Mumbai, Hyderabad, Calcutta and NOIDA.
3. Reserve Bank Information Technology Private Limited (ReBIT)
- Established: 2016
- ReBIT delivers and manages IT projects of RBI.
4. Indian Financial Technology and Allied Services (IFTAS)
- It is a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Reserve Bank of India.
- The IFTAS has taken over the Indian Financial Network (INFINITE), Structured Financial Messaging System (SFMS) and the Indian Banking Community Cloud (IBCC) from the IDRBT (from April 01, 2016).
| Related Articles for Preparation: | |
| SIDBI Full Form | SBI Full Form |
| SWIFT Full Form | ADR Full Form |
| ICRA Full Form | GPF Full Form |
| NHB Full Form | IIFL Full Form |
| MCLR Full Form | RBL Full Form |
Why BYJU’S Exam Prep Test Series?
- Unlimited access to 18+ Bank and Insurance Exam mock tests
- Mock Tests designed by Exam Experts.
- Detailed Performance Analysis.
Download the BYJU’S Exam Prep App Now.
The most comprehensive exam prep app.
#DreamStriveSucceed
