- Home/
- Regulatory Bodies/
- RBI Grade B/
- Article
Payment System in India: Know Cashless & Digital Payment Methods in Detail
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 11th, 2023

The establishment of national payment systems is often spearheaded by the central bank of each nation. The Reserve Bank of India, the nation’s central bank, has been performing this role in the development and has made a number of steps to ensure that the country’s payment systems are safe, secure, efficient, accessible, and authorized.
The top policy-making authority for payment systems in India is the Board for Regulation and Supervision of Payment and Settlement Systems (BPSS), a subcommittee of the Central Board of the Reserve Bank of India.
All payment and settlement systems in the nation are subject to regulation and oversight by the BPSS, which has the authority to authorize, prescribe regulations, and define standards. The Reserve Bank of India’s Department of Payment and Settlement Systems functions as the Board’s secretariat and carries out its directives.
Table of content

What is Payment & Settlement Systems Act 2007?
The Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007 (PSS Act), which was passed into law in December 2007, governs the payment and settlement systems in India.
Beginning on August 12, 2008, the Payment and Settlement System Act and the regulations created under it went into force.
A payment system cannot be started or operated in India by anyone other than the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) without RBI authorization, according to Section 4 of the PSS Act.
Since then, the Reserve Bank has authorized operators of payment systems for prepaid payment instruments, card programs, cross-border inbound money transfers, ATM networks, and centralized clearing arrangements.
Payment & Settlement Introduction in India
As long as there have been commodities and services, there has also been a demand for payments and settlements.
The barter system, which facilitated exchange through products and/or services, was the first Payment and Settlement System (PSS) that was known to have existed.
People advanced to using currency notes and coins to settle their economic transactions once they understood the concept of money.
A simple and secure technique for making payments by transferring money through bank accounts was made possible by the development of the banking system and the introduction of bank accounts.
A payment method was necessary for this transaction, and checks quickly became the most popular one. The story of payment systems was thus launched.
What is the Payment & Settlement Systems Act, 2007?
An effective legal framework is a crucial prerequisite for effective payment systems. The legal environment should include-
- General laws and regulations cover topics like insolvency and party-to-party contracts.
- Laws and regulations that specifically apply to payment systems (like legislation on electronic signature, netting validation, and settlement finality.
- The rules, standards, and procedures are accepted by all parties involved in a payments system.
The Payment and Settlement Systems Act was passed into law in 2007, taking into account the significance of regulation for the growth and orderly operation of both financial services and payment systems.
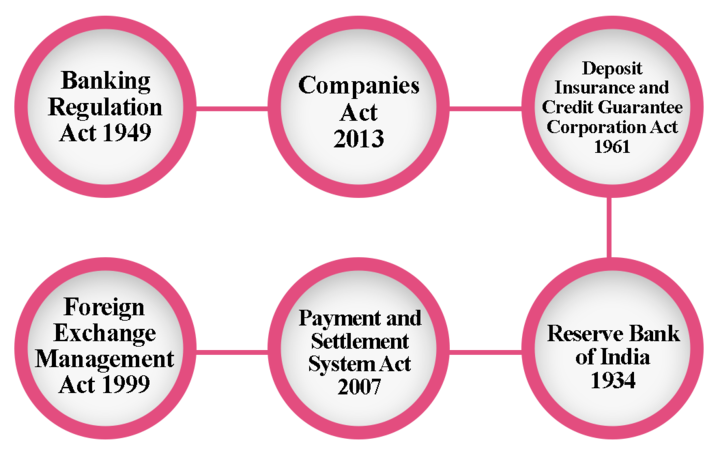 India is one of the few nations with a specific law governing payment systems that provide for the regulation and supervision of payment systems in India. And to designate RBI as the authority for the purpose and for matters connected with or incidental thereto.
India is one of the few nations with a specific law governing payment systems that provide for the regulation and supervision of payment systems in India. And to designate RBI as the authority for the purpose and for matters connected with or incidental thereto.
The scope of the RBI’s regulatory authority includes the full range of payment systems and instruments, as well as services offered by banks and non-banks.
A payment system cannot be started or operated in India by anyone other than the RBI without prior authorization, according to Section 4 of the PSS Act.
Since then, the RBI has authorized a number of Payment System Operators (PSOs) to operate payment systems in the nation, including CCIL (financial market infrastructure – central counterparty), NPCI (retail payments organization), card payment networks, cross-border inbound money transfers entities, ATM networks, PPI issuers, Instant Money Transfer operators, TReDS platform providers, and Bharat Bill Payment Operating Units (BBPOUs).
What is Digital Payment in India?
Digital payments are transactions that happen online or through other digital platforms without a physical exchange of money. This indicates that both the payer and the payee exchange money via electronic means.
To encourage and promote digital payments in India, the government has been implementing a number of actions. The government intends to establish a digitally empowered economy that is Faceless, Paperless, Cashless as part of the Digital India campaign. Digital payments come in a variety of forms and ways.
Types of Digital Payments in India?
The Government of India’s main initiative, the Digital India program, aims to make India into a knowledge-based society and economy. One of the purported roles of Digital India is to be faceless, paperless, and cashless.
A variety of digital payment methods are offered in an effort to encourage cashless transactions and make India a society that uses less cash.
We now have ten different digital payment options available in India as a result of the implementation of Cashless India. Some techniques have been in use for over ten years, while others have only lately gained popularity.
Debit/Credit Cards
As an alternative to cash payments, Indians frequently utilize debit/credit cards, prepaid cards, or banking cards. In 1981, Andhra Bank introduced the country’s first credit card. Cards are preferred for a variety of factors, including but not exclusive to mobility, convenience, safety, and security.
This is the only type of digital payment that is widely used for both online and offline transactions. Nowadays, numerous applications like Cred, Square, etc. are released solely for managing card transactions.
Unstructured Supplementary Service Data
For those portions of India’s population without access to reliable banking and internet services, USSD was introduced. By simply calling *99# on any necessary feature phone, USSD enables mobile banking transactions to be completed without the need for an internet connection.
Prepaid GSM cell phones frequently use USSD to check the available balance. The vendor’s check balance application conceals from the user the specifics of the USSD protocol.
When a user engages in an activity that costs money on some pay-as-you-go networks, such as Tesco Mobile, they receive a USSD message containing their updated balance. Additionally, USSD can be used to send PIN codes or one-time passwords, as well as to replenish the SIM card’s balance.
Aadhaar Enabled Payment System
AEPS is a bank-led digital payment methodology that was developed to take advantage of Aadhar’s presence and reach. Customers can transfer money between two Aadhaar-linked bank accounts using their Aadhaar-linked accounts under this scheme. According to NPCI figures as of February 2020, AEPS had surpassed 205 million.
AEPS does not call for any physical actions, such as going to a bank, using a debit or credit card, or signing anything. By integrating Aadhaar verification, this bank-led concept enables digital payments at PoS (Point of Sale / Micro ATM) through a Business Correspondent (also known as Bank Mitra).
Unified Payments Interface (UPI)
A payment system called UPI combines many bank accounts into a single application to make it simple to transfer money between any two parties.
UPI is significantly more defined and standardized across banks than NEFT, RTGS, and IMPS. With only a few clicks, you may start a bank transfer via UPI from any location.
The advantage of using UPI is that you may make payments directly from your bank account without having to enter your card or bank information.
Digital Wallet
A digital wallet often referred to as an e-wallet, is a software program, internet service, or electronic device that enables two parties to conduct electronic transactions in exchange for products and services and digital currency units.
This can involve utilizing a computer to make online purchases or a smartphone to make in-person purchases. Prior to any transactions, funds can be added to the digital wallet; alternatively, the digital wallet can be connected to a person’s bank account.
Additionally, users’ driver’s licenses, health cards, loyalty cards, and other IDs may be kept in their wallets. Near field communication allows the credentials to be wirelessly transferred to a merchant’s terminal (NFC).
Prepaid Cards
A bank-issued pre-loaded debit card, typically single-use or reloadable for numerous uses, is known as a bank prepaid card. It differs from a typical debit card in that the latter can only be used once and is always connected to your bank account. A prepaid bank card may or may not be covered by this.
Any customer with a KYC-compliant account can generate a prepaid card by going to the bank’s website. The most typical uses of these cards are as corporate gifts, reward cards, or one-use cards for gifting.
Point of Sale
The moment and location where a retail transaction is finished are referred to as the point of sale (POS) or point of purchase (POP). The merchant determines the customer’s balance due at the point of sale, notifies them of it, may create an invoice for them (which might be a printout from the cash register), and informs them of their payment alternatives.
Because it is also a point of return or client order, the point of sale is frequently referred to as the point of service. Software for POS terminals could additionally provide capabilities for further functionality, such as warehousing, CRM, or inventory management.
Internet Banking
Customers of a specific bank are given the option to perform transactions and engage in other financial activities online through internet banking, sometimes referred to as e-banking or online banking, on the bank’s website. To make or receive payments online and to access a bank’s website, which is known as Internet Banking, you need a reliable internet connection.
The majority of Indian banks have now made their internet banking services available. It has grown to be one of the most widely used methods for making purchases online. In India, there is a virtual banking option available on every payment gateway. Some of the most popular methods for doing transactions via internet banking are NEFT, RTGS, or IMPS.
Mobile Banking
A bank or other financial institution’s mobile banking service enables its customers to carry out financial transactions remotely using a mobile device, like a smartphone or tablet. It uses software, sometimes referred to as an app, offered by the financial institution for the purpose, unlike related internet banking.
Typically, mobile banking is accessible around-the-clock. Some financial organizations have restrictions on which accounts can be accessed using mobile banking and set a dollar threshold for the value of transactions. The presence of an internet or data connection for the mobile device is necessary for mobile banking.
Micro ATMs
Business Correspondents (BC) use a micro ATM to provide consumers with crucial financial services. These Correspondents will act as a micro ATM for quick transactions, they might even be local business owners. They will employ a system that only requires your fingerprint for authentication to allow you to transfer money using your bank account that is linked to your Aadhaar.
With the help of micro ATMs, banks can connect remotely to their main banking system. This device has a fingerprint scanner built right into it. In other terms, a micro ATM is a portable point-of-sale device used to disburse cash in areas where bank facilities are inaccessible. Micro ATMs are a type of doorstep mobile banking arrangement combined with a mobile ATM device, comparable to point of sale (PoS) terminals.

