We always use the + sign for a male.
We always use – sign for female.
To show the relation from one generation to another (Mother/Father to Son/Daughter), we use a single arrowhead vertically.
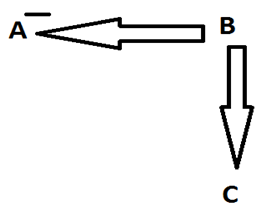
- To show the relationships within the same generation (siblings/cousins), we use a single arrowhead horizontally.
- To show the relation between husband & wife, we use a double arrowhead horizontally.
Let us see the symbolic representation of various blood relations:
1. A is the father of B: Here we know the gender of A only. B can either be a son or a daughter.
2. A is the mother of B: Here we know the gender of A only. B can either be a son or a daughter.
3. B is the son of A: Here we know the gender of B only. A can either be a father or a mother.
4. B is the daughter of A: Here we know the gender of B only. A can either be a father or a mother.
5. B is the wife of A: Here we know the gender of both A and B.
6. A is the husband of B: Here we know the gender of both A and B.
7. A is the uncle of C: Here we know the gender of A only. B & C can be either male or female.
8. A is the aunt of C: Here we know the gender of A only. B & C can be either male or female.
9. C is the nephew of A: Here we know the gender of C only. A & B can be either male or female.
10. C is the niece of A: Here we know the gender of C only. A & B can be either male or female.
11. A is the paternal grand-father of C: Here we know the gender of A and B both.
12. A is the paternal grandmother of C: Here we know the gender of A and B both.
13. A is the maternal grandfather of C: Here we know the gender of A and B both.
14. A is the maternal grandmother of C: Here we know the gender of A and B both.
Blood relation questions can be asked in two different ways.
Type I: Basic Blood Relation Questions
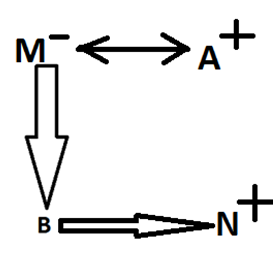
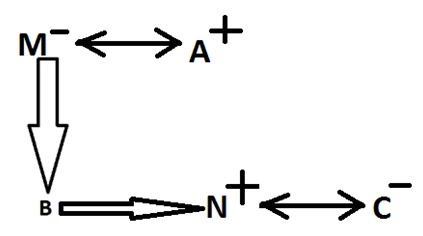
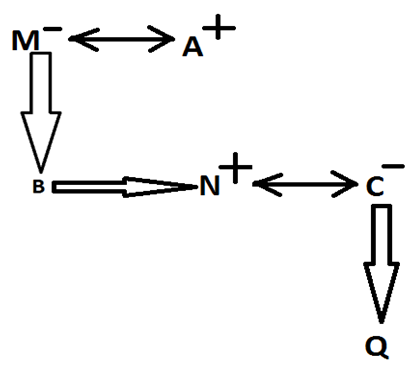
Direction: M is the mother of B. A is the husband of M. N is the only brother of B. C is married to N. Q is the only child of C. N does not have any sister. J is the father of A.
Solution:
M is the mother of B.
A is the husband of M.
N is the only brother of B.
C is married to N.
Q is the only child of C.
N does not have any sister (Which means B is definitely his brother).
J is the father of A.
Q.1) If A doesn’t have any grandson, then how is Q related to B?
Solution: We can see that Q is either the grandson or granddaughter of A. But as per the question, A doesn’t have any grandson which definitely assures that Q is A’s granddaughter. So Q is B’s niece.
Q.2) How is A related to C?
Solution: A is N’s father and C is N’s wife. So A is the father-in-law of C.
Q.3) How is B related to J?
Solution: B is the son of J’s son. So B is the grandson of J.
Type II: Blood relation Puzzle
Direction: Study the information given below and answer the question based on it. Seven people P, Q, R, S, T, U, and V belong to the same family. It’s a three-generation family and two couples are there in the family. P is the father of T who is the mother of R. V has only one son and V is not married to T. Q is the sister of T. U is not the father of R. Detailed Solution:
P is the father of T who is the mother of R. Q is the sister of T. V has only one son and V is not married to T. So it means U or S is married to T but U is not the father of R so S must be married to T. V has only one son so V must be the wife of P and U must be the brother of Q and T. R is son or daughter of T and S.  Q.1) How is R related to Q? Solution: R is either nephew or niece of Q.
Q.1) How is R related to Q? Solution: R is either nephew or niece of Q.
Q.2) How is Q related to V? Solution: Q is the daughter of V.
Type III: Coded Blood Relation
Direction: Study the information given below and answer the questions based on it.
- A+B means A is the mother of B
- A-B means A is the sister of B
- A*B means A is the father of B
- A÷B means A is the son of B
- A=B means A is the brother of B
- A≠B means A is the daughter of B.
Q.1) Which of the following means P is the aunt of Q?
- P ≠ R * Q
- P + R * Q
- P – R + Q
- P – R ÷ Q
- P *R = Q
Solution:
P - R + Q means P is the sister of R, R is the mother of Q. P is the aunt of Q
Q.2) Which of the following means, S is the son of T’s daughter?
T * M + S + N T * M + S = N T + M * S – N S ÷ M ÷ T – N T * M ÷ S ≠ N
(A) T * M + S + N means T is the father of M and M is the mother of S who is the mother of N. That is S is the daughter of T.
(B) T * M + S = N means T is the father of M, M is the mother of S and S is the brother of N.
Therefore S is the son of T daughter.
Type IV: Blood Relation with Circular Arrangement
Direction: Study the information given below and answer the questions based on it.
There are eight persons Rajan, Sanjana, Sushant, Deepa, Abhishek, Riya, Bipasha, and Harman seating around a circular table such that four of them are facing the center and the remaining are facing outside the center. There are two married couples and three generations in the family. Abhishek’s sister is seating to the immediate left of Rajan. Deepa, who faces the center, is Abhishek’s niece and she is seating opposite her grandfather. Sanjana is third to the right of her husband. Harman is Rajan’s son and is seating second to the left of his grandmother. Harman is second to the left of his father. Bipasha, who has only one daughter, is to the immediate right of her granddaughter. Abhishek is seated to the immediate left of his sister-in-law. Abhishek and Riya are not seating together and also they are not facing in the same direction which is faced by Rajan.
Solution:
Let’s arrange the jumbled pieces of information systematically and find out the required solution. There are three generations in the family, looking deeply; we get some results from the given information-
⇒Deepa is a female and she stands in the third generation.
⇒Sanjana is a female.
⇒Harman is a male and stands in the third generation.
⇒Bipasha is a female and stands in the first generation. Also, she has only one daughter.
To solve such types of questions try to make both, the family tree and the seating arrangements simultaneously.
⇒Names of the persons enclosed in rectangles and circles are males and females respectively.
⇒Persons connected with two parallel lines are spouses and similarly, persons connected with a single straight horizontal line are siblings. 

So we have seen two different ways in which blood relation questions can be asked. Sometimes blood relation concept is used in seating arrangements as well to make those questions tougher. The application of blood relations will be discussed in the basics of seating arrangement.
Type IV: Blood Relation with Linear Arrangement
Direction: Read the information carefully and answer the following questions.
There are eight members A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H in a family. They sit in a straight line, some facing north while others facing south. There are three generations in the family with three couples. Four of them are male while others are female.
C faces South. F is a male and he sits on one of the extreme ends. F faces the opposite direction of his wife. A is the sister-in-law of H and the daughter-in-law of C. A sits third to the right of her daughter.
G is the son of H and he sits second to the right of his cousin. C has two children, one male, and one female. B is the mother-in-law of D and sits to his immediate right. F sits to the immediate left of his brother-in-law, D. C does not sit near his grandson. No two person seating together face the same.
Solution: A is the sister-in-law of H and daughter-in-law of C. C has two children, one male, and one female. B is the mother-in-law of D. F is the brother-in-law of D. A is the sister-in-law of H and daughter-in-law of C. G is the son of H. C has two children, one male, and one female. B is the mother-in-law of D F sits to the immediate left of his brother-in-law, D.
These lines give us the family tree. 
Now we have to arrange them in a linear form. No two person seating together face the same direction. This means that the direction will be alternate.
F is a male and he sits on one of the extreme ends. F sits to the immediate left of his brother-in-law, D. B is the mother-in-law of D and sits to his immediate right.
There are two possible cases. 
F faces the opposite direction of his wife. A sits third to the right of her daughter. A’s daughter is E.
In both cases, the directions of A and F will be the opposite. Only one possible case is there in both cases. 
G sits second to the right of his cousin. E is the cousin of G.
C faces South. C does not sit near his grandson. G is the grandson of C.
In Case I, C will face North so this case can be eliminated. Case II is correct. ![]()
This is the final arrangement.
Key points related to blood relations:
- Never assume any person to be male or female if not specified in the question.
- Step by step approach can always give the solution for blood relation questions, doesn't matter the question is a coded or simple one.
To boost the preparation of all our users, we have come up with some free video (Live Class) series, free quizzes, and previous papers.
Here are the links:
- Daily Free Video Series - Click Here
- Daily Free Quizzes - Click Here
- Attempt CSIR-NET Previous Papers - Click Here
More from us:
- Get Unlimited access to Structured Live Courses and Mock Tests- Online Classroom Program.
- Get Unlimited access to 20+ Mock Tests-BYJU'S Exam Prep Test Series.

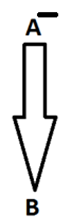







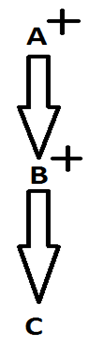










Comments
write a comment