Genetic Engineering: Applications, Scope, and Advantages
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: November 14th, 2023
Genetic Engineering, also known as genetic modification, is the manual addition of new DNA into an organism. The process involves laboratory-based technologies to alter the DNA structure of an organism. Through genetic engineering, scientists can move desirable genes from one plant or animal to another or from a plant to an animal or vice versa. Genetic Engineering is used in various fields and has applications in agriculture, medicine, and more.
Applications of Genetic Engineering are an important topic in the Science and Technology part of the UPSC Syllabus. Genetic Engineering holds importance for both UPSC Prelims and UPSC Mains. Candidates must prepare the topic well.
Table of content
What is Genetic Engineering?
Jack Williamson first used Genetic Engineering in his science fiction novel Dragon’s Island, published in 1951. Genetic Engineering involves changing a single base pair (A-T or C-G), deleting a region of DNA, or adding a new segment of DNA. It facilitates the addition of traits not originally found in the organisms. Genetic Engineering can correct Genetic disorders in humans.
Genetic Engineering involves splicing an area of a chromosome, a gene that controls a particular characteristic of the organism. The process involves the direct manipulation of one or more genes. The first microorganism to be genetically modified is bacteria.
The biotech regulator in India is Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC). The Committee is created under the Ministry of Environment and Forests.
Applications of Genetic Engineering
Genetic Engineering is used in medicine, research, industry, and agriculture. As India aims to become a trillion-dollar economy, the research, innovation, and development in the field of Genetic Engineering can boost and lay the foundation for a well-established medical industry.
Applications of Genetic Engineering in Medicine
- Drugs Manufacturing
- Vaccines
- Monoclonal antibodies
- Gene therapy
- Antihemophilic factors
- Growth hormones of humans
- Creation of model animals
- FSH
- Human albumin
Applications of Genetic Engineering in Agriculture
With the help of Genetic Engineering, scientists can create Genetically Modified Crops, which are regarded as more beneficial. Some examples of Genetically Modified Crops include Bt Cotton, Bt Brinjal, GM Mustard, etc. GM crops are fungal and virus-resistant.
☛ What are Genetically Modified Crops?
Applications of Genetic Engineering in Industry and Research
Genetic Engineering is used widely in the food, medicines, and fuel industries. It is also used in gene coding to get a useful protein. In the field of research, organisms are genetically engineered to discover the functions of certain genes.
Advantages of Genetic Engineering
Genetic engineering can have a huge impact and revolutionize nutrition and public health. The major advantages of Genetic engineering are:
- Therapeutic Cloning: Therapeutic cloning is the transfer of nuclear material isolated from a somatic cell into an enucleated oocyte to derive embryonic cell lines with the same genome as the nuclear donor.
- Genetically Modified (GM) Crops: GM Crops have desirable traits and are regarded as more beneficial than normal crops. They are majorly drought-resistant and disease-resistant and are fortified with more nutrients.
- Treatment of diseases and disorders: Genetic Engineering has advanced much in medicine. Genetic disorders are fixed by replacing faulty genes with functional genes. Disease-carrying insects can be engineered to become sterile insects, thus helping curb the spread of certain diseases.
- Faster Growth Rate: The plants and animals produced by genetic engineering can be grown faster.
Challenges of Genetic Engineering
Though Genetic Engineering is a boon for mankind, it is also a bane. It can sometimes result adversely and produce unforeseen results. The challenges associated with Genetic Engineering are:
- GM crops can cause an allergic reaction and have adverse health effects.
- The genetically modified genes may have an irreversible effect and affect the region’s biodiversity.
- Genetic Engineering manipulates the law of nature and has many moral and ethical issues.
☛ Disadvantages of Genetically Modified Foods
Genetic Engineering UPSC
Genetic Engineering and its application is a very important topic of the UPSC Exam. The topic has weightage both in UPSC Prelims and UPSC Mains. To prepare for the topic, one can refer to the NCERT Books for UPSC and keep oneself updated with Current Affairs.
Genetic Engineering UPSC Questions
If one analyzes the UPSC Previous Year Question Papers, one can see every year, questions are asked from this section of the UPSC Syllabus.
Question: Gene is made of which chemical?
- D.N.A.
- R.N.A.
- Protein
- Enzyme
Answer: Option 1
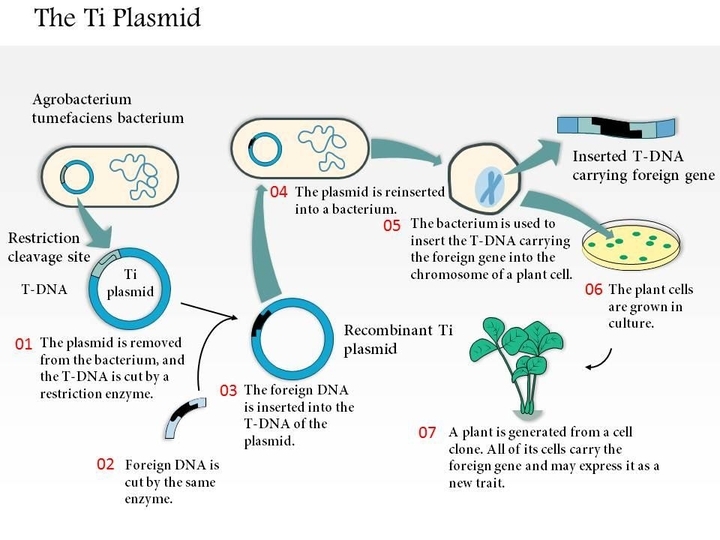
Question: The bacteria generally used for genetic engineering is
- Agrobacterium
- Bacillus
- Pseudomonas
- Clostridium
Answer: Option 1
