Gulf Cooperation Council: GCC Summit, Members, List of Countries
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: November 14th, 2023
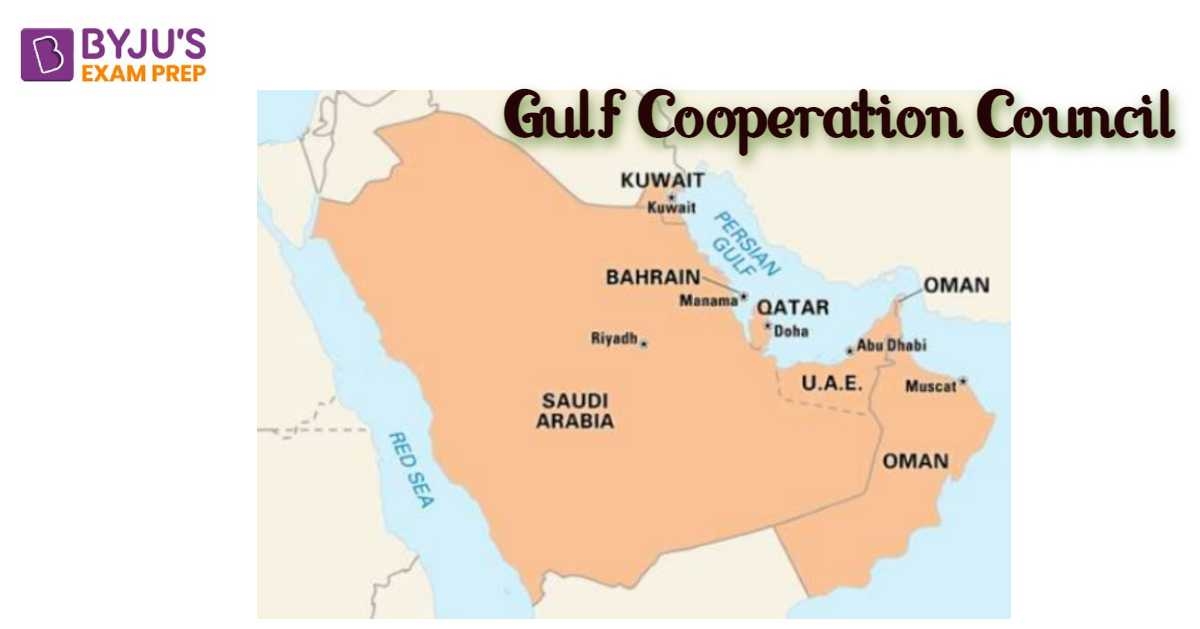
Gulf Cooperation Council also known as GCC, is an association of several gulf countries that are all monarchies, and share a mutual religious inclination towards Islam. GCC was formed by an agreement between the following nations – Bahrain, Qatar, Oman, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia and UAE as they found common grounds in geographic proximity, political system, Islamic beliefs and more.
The Gulf Cooperation Council’s main headquarters is in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. The GCC signed its charter on 25 May 1981, formally establishing the institution. Gulf Cooperation Council was originally formed by the member nations to attain unity by coordinating, integrating, and connecting in all areas. This article shall cover all significant details about GCC ranging from its history, development, members, objectives and the way ahead, among other things.
Table of content
What is the GCC?
The Gulf Cooperation Council also called the Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf, is an intergovernmental, regional, economic and political union. This council has 6 countries under it forming a union, namely,
- Bahrain
- Oman
- Kuwait
- Qatar
- The United Arab Emirates
- Saudi Arabia.
The GGC was officially founded on 25th May 1981, when an agreement was established among the 6 countries. This step was taken because of their similar systems of political administration based on religious beliefs (Islam), their unique relations owing to their geographic and demographic proximities and common objectives.
☛ Download Short Notes on Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC)
Recent Updates about the GCC
The 41st Gulf Cooperation Council summit took place in January 2021 in Al Ula, Saudi Arabia, where the countries signed a solidarity and stability deal. The deal’s key highlights have been discussed below;
- This deal takes away all former sanctions on Qatar. It has resumed its land, sea and air traffic routes which were blockaded earlier by the countries of Bahrain, Egypt, Saudi Arabia and UAE on the allegations of Qatar supporting and fostering terrorism.
- The countries were distressed by Qatar’s stance on supporting Iran.
- However, efforts were made to restore ties to promote the Gulf states to power of strength against international threats, especially the Iranian nuclear and ballistic missile program.
- The days before, the 41st GCC saw the reunification of the five countries. India welcomed this reunification.
- India asked the GCC members to help facilitate the return of Indian citizens after the relaxation of COVID-19-related restrictions. This could be made possible through travel bubble arrangements’
- These travel bubble arrangements would temporarily be operation arrangements between any two countries to resume commercial services for the passengers until regular flights are suspended in the wake of the pandemic.
- There are about 8 million Indians that find their employment in the GCC countries. This would be a helpful step that would be reciprocal in nature and hence, mutually beneficial.
- All sides agreed to commit their energies towards the reform of institutions that will work to address problems like the COVID 19 pandemic, climate change, terrorism and sustainable development.
- India’s inclusion in the UNSC (United Nations Security Council) as a non-permanent member was well-received by the GCC.
- The supply chains between the Gulf and India were not disrupted during the lockdowns observed under the pandemic.
- Narendra Modi, the Prime Minister of India, was awarded the ‘Order of Zayed’ by the UAE. It is the highest civilian order in the country. He also received Bahrain’s ‘King Hamad Order of the Renaissance.
- GCC nations’ lack of hostility over India’s domestic decision of the abrogation of Article 370 for Jammu & Kashmir is a sign that indicates a healthy tie between the countries.
- There are annual bilateral exercises held by India and Oman. They happen for the three wings of the armed forces: the Army, the Airforce, and the Navy.
- Oman has approved strategic access to the Indian Navy for the Port of Duqm SEZ, one of the biggest seaports in the Indian Ocean.
GCC Members
There are six 6 countries that together form the Gulf Cooperation Council. These 6 GGC countries are Qatar, Oman, UAE, Bahrain, Kuwait and Saudi Arabia. The GCC also speculates on extending memberships to countries like Jordan, Morocco, and Yemen.
All of these countries are monarchies, though they differ in sub-types of monarchies. This has been classified below;
- Absolute monarchies: Saudi Arabia and Oman
- Constitutional monarchies: Qatar, Bahrain and Kuwait
- Federal monarchy: The United Arab Emirates
The GCC is an important organisation as it includes some of the fastest-development economies of the world that have a nominal share of $1.638 trillion in the global GDP.
Structure of GCC
The GCC follows an organised structure that has been divided into three levels of administration; the Supreme Council, the Ministerial Council and the Secretariat General. Their significant features have been discussed below;
- Supreme Council: This is the highest form of authority in the GCC. it is in charge of heading all states and their respective states. The Supreme Council meets annually to resolve issues by following a parliamentary procedure of voting that favours the majority. The Supreme Council decides the overall policy and working of the GCC.
- Ministerial Council: This council is of all the foreign ministers of member states that meets every three months to discuss policies and recommendations to develop and foster coordination and cooperation among the member states in all spheres of politics, economics and society.
- Secretariat General: This council is responsible for preparing budgets, reports, etc., for the Council for smoother administration. It assists the member states in implementing the decisions by the two higher councils; Supreme and Ministerial. The Committee is headed by a Secretary-General whose tenure is three years long.
Objectives of GCC
The GCC was formed with certain objectives in mind. These objectives were broadly related to promoting integration, interconnection and coordination among the member states. It also envisaged;
- Bolden intrapersonal ties.
- Implement similar regulations for the economy, finance, trade & tourism, administration, customs, and legislation as there are many similarities between them.
- Encourage scientific and technical advancement in the fields of mining, industry, agriculture, animal husbandry and water.
- Build a unified army.
- Establish scientific centres.
- Set up ventures that promote private and public sector cooperation.
The hope to integrate all into a single market for commerce was something the GCC had tried to attempt since 2008. The implementation, however, has taken its sweet time. Though the customs union has been functioning well since 2015, a few barriers restrict the free movement of services and goods. The GCC has plans to introduce a single type of currency in all the member states called Khaleeji (the proposed name for now)
Indian Relations with the GCC
There is a need to maintain good relations with the GCC for India. These reasons have been discussed below;
- GCC countries have large hydrocarbon reserves, making them important to meet India’s energy needs. In a true reciprocal fashion, the GCC Countries have also served as great markets for Indian goods.
- GCC Member countries like Saudi Arabia and the UAE have a huge Indian population in their workforce. Energy and manpower have been two big factors that affected Indian international relations with the GCC.
- There are also discussions of the India-Gulf Cooperation Council Free Trade Agreement (FTA) underway. India and the GCC are also members of the Financial Action Task Force (FATF).
- India shares multilateral and bilateral military with most of the GCC members.
- All these factors have improved India’s political and economic relationship with the GCC.
- Currently, 34% of Indian Crude exports come from the GCC countries.
- The relationship has only strengthened, reflected in back-and-forth trade estimated to be about USD 121 billion.
India’s Role in the Gulf Region
To this date, the GCC countries are one of the top trading countries for India. This has been highlighted by the ever-increasing trade between the two countries.
- India has deflected all situations of intervention in their local disputes as the Indian policy favours maintenance of peace over power displays of authority.
- About 7 million Indian workers in the Gulf are involved in the unskilled and skilled labour force.
- The Gulf and India have taken steps toward defence cooperation. Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Oman and others participated in the Indian Milan Exercise.
GCC UPSC Questions
The GCC is an important association in the current times and economy, making it a relevant topic for your IAS Exam preparation. Candidates should make sure to go through the topic properly for the best results. Practice the questions below to kickstart your preparation.
Question – Which of the following is not part of the GCC?
- Iran
- Qatar
- UAE
- Bahrain
Answer – A
Question – Which country conferred upon Narendra Modi the ‘Order of Zayed’?
- The UAE
- Bahrain
- Qatar
- Kuwait
Answer – A
Gulf Cooperation Council UPSC
Gulf Cooperation Council is an important topic in the international relations and current affairs section of the UPSC Prelims and UPSC Mains. Organisations like GCC are extremely relevant to the UPSC Syllabus. Candidates should be well versed in these topics for the best exam performance. Refer to appropriate UPSC Books for the best shot.
Gulf Cooperation Council UPSC Notes PDF
Gulf Cooperation Council holds great relevance to the UPSC Syllabus at both levels; UPSC Prelims and UPSC Mains. The candidates must commit such facts to their memory and refer to the most appropriate UPSC study material to read about these things from a UPSC perspective. Candidates can also download this Gulf Cooperation Council UPSC Noted PDF.
