Analysis of Trusses
Trusses are used commonly in Steel buildings and bridges.

Definition: A truss is a structure that consists of
- All straight members
- Connected together with pin joints
- Connected only at the ends of the members
- All external forces (loads & reactions) must be applied only at the joints.
- Trusses are assumed to be of negligible weight (compared to the loads they carry)
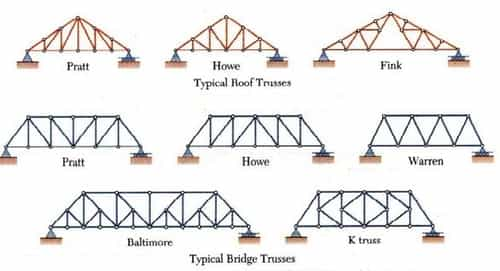
Types of Trusses
Degree of Static Indeterminacy
- DS = m+re – 2j where, DS = Degree of static indeterminacy m = Number of members, re = Total external reactions, j = Total number of joints
- DS = 0 ⇒ Truss is determinate
If Dse = + 1 & Dsi = –1 then DS = 0 at specified point. - DS > 0 ⇒ Truss is indeterminate or dedundant.
Truss Analysis: Method of Joints
- Conditions of equilibrium are satisfied for the forces at each joint
- Equilibrium of concurrent forces at each joint
- Only two independent equilibrium equations are involved
Steps of Analysis
- Draw Free Body Diagram of Truss
- Determine external reactions by applying equilibrium equations to the whole truss
- Perform the force analysis of the remainder of the truss by Method of Joints
Example 1
Determine the force in each member of the loaded truss by Method of Joints

Solution


Truss Member Carrying Zero forces
(i) M1, M2, M3 meet at a joint M1 & M2 are collinear ⇒ M3 carries zero force where M1, M2, M3 represents member.

(ii) M1 & M2 are non collinear and Fext = 0 ⇒ M1 & M2 carries zero force.

- If only two non-collinear members form a truss joint and no external load or support reaction is applied to the joint, the two members must be zero force members
- If three members form a truss joint for which two of the members are collinear, the third member is a zero-force member provided no external force or support reaction is applied to the joint.

Method of Section
- It can be used to determine three unknown member forces per FBD since all three equilibrium equations can be used
- Equilibrium under non-concurrent force system
- Not more than 3 members whose forces are unknown should be cut in a single section since we have only 3 independent equilibrium equations

Principle:
- If a body is in equilibrium, then any part of the body is also in equilibrium.
- Forces in few particular member can be directly found out quickly without solving each joint of the truss sequentially
- Method of Sections and Method of Joints can be conveniently combined
- A section need not be straight.
- More than one section can be used to solve a given problem
Example 2
The truss in Fig given below is pinned to the wall at point F, and supported by a roller at point C. Calculate the force (tension or compression) in members BC, BE, and DE.

Solution

ΣME=0
5FBC=6(80)+2(60)
FBC=120 kN compression
ΣMB=0
5FDE=4(80)
FDE=64 kN Tension
Indeterminate Truss
(i) Final force in the truss member

sign convn → +ve for tension, –ve for compression
where,
S = Final force in the truss member
K = Force in the member when unit load is applied in the redundant member
L = Length of the member
A = Area of the member
E = Modulus of elasticity
P = Force in the member when truss become determinate after removing one of the member.
P = Zero for redundant member.
Lack of Fit in Truss
![]()
Q = Force induce in the member due to that member which is 'Δ' too short or 'Δ' too long is pulled by force 'X'.
Deflection of Truss

Where, yC = Deflection of truss due to effect of loading & temp. both.
If effect of temperature is neglected then
![]()
α = Coefficient of thermal expansion
T = Change in temperature
T = +ve it temperature is increased
T = -ve it temperature is decreased
P & K have same meaning as mentioned above.
You can avail of BYJU’S Exam Prep Online classroom program for all AE & JE Exams:
BYJU’S Exam Prep Online Classroom Program for AE & JE Exams (12+ Structured LIVE Courses)
You can avail of BYJU’S Exam Prep Test series specially designed for all AE & JE Exams:
BYJU’S Exam Prep Test Series AE & JE Get Unlimited Access to all (160+ Mock Tests)
Thanks
Team BYJU’S Exam Prep
Download BYJU’S Exam Prep APP, for the best Exam Preparation, Free Mock tests, Live Classes.





Comments
write a comment