Power Electronics & Drives: DC to AC Converters
DEFINITION: As we have already aware from the term Inverter which is an Electrical Setup used for daily purposes. In Inverter input, DC is converted to AC power by switching the DC input voltage in a sequence so as to generate AC output. The Inverter is the power electronic circuit, which converts the DC voltage into AC voltage. The DC source is normally a battery or output of the controlled rectifier.
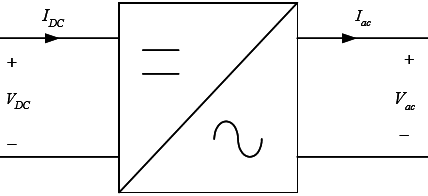
- Output voltage of the inverter may be a square wave, quasi-square wave or low distorted sine wave.
- Output Voltage of the inverter is controlled by the drives of the switches.
- Another technique to control the output of the Inverter is Pulse Width Modulation Technique,In this case the Inverter are called Pulse Width Modulated Inverter.
- Since for the inverter operation input DC is converted to AC output which may contain some harmonics,these harmonics can be reduced by using proper control schemes.
TYPICAL APPLICATIONS – Un-interruptible power supply (UPS), Industrial (induction motor) drives, Traction, HVDC.
Types of inverter
Inverters can be broadly classified into two types. They are
1. Voltage Source Inverter (VSI)
When the DC voltage remains constant, then it is called Voltage Source Inverter(VSI) or Voltage Fed Inverter (VFI).
2. Current Source Inverter (CSI)
When the input current is maintained constant, then it is called Current Source Inverter (CSI) or Current Fed Inverter (CFI).
Voltage source inverter (VSI) with variable DC link
Sometimes, the DC input voltage to the inverter is controlled to adjust the output. Such inverters are called Variable DC Link Inverters. The inverters can have a single phase or three-phase output.
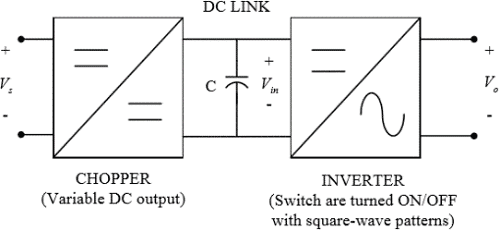
- DC link voltage is varied by a DC-to DC converter or controlled rectifier.
- Generate “square wave” output voltage.
- Output voltage amplitude is varied as DC link is varied.
- Frequency of output voltage is varied by changing the frequency of the square wave pulses.
VSI | CSI |
VSI is fed from a DC voltage source having small or negligible impedance. | CSI is fed with adjustable current from a DC voltage source of high impedance. |
Input voltage is maintained constant | The input current is constant but adjustable. |
Output voltage does not dependent on the load | The amplitude of output current is independent of the load. |
The waveform of the load current as well as its magnitude depends upon the nature of load impedance. | The magnitude of output voltage and its waveform depends upon the nature of the load impedance. |
VSI requires feedback diodes | The CSI does not require any feedback diodes. |
The commutation circuit is complicated | Commutation circuit is simple as it contains only capacitors. |
Power BJT, Power MOSFET, IGBT, GTO with self commutation can be used in the circuit. | They cannot be used as these devices have to withstand reverse voltage |
Single phase voltage source inverters




Due to symmetry along x-axis
𝑎o = 0 , 𝑎𝑛 = 0
𝑏𝑛 = 4Vs/nπ
The instantaneous output voltage

& =0, For n=2,4.....
The rms value of the fundamental output voltage




DC Supply Current
Assuming a lossless inverter, the ac power absorbed by the load must be equal to the average power supplied by the dc source.

𝑉01 =Fundamental rms output output voltage
𝐼0=rms load current
𝜃1=the load angle at the fundamental frequency
Single phase full bridge inverter


Instantaneous load current 𝑖0 for an RL load

Where θn = tan-1(nwL/R)
The rms output voltage is

The instantaneous output voltage in a Fourier series

Three Phase Voltage Source Inverter
When three single-phase inverters are connected in parallel a three phase inverter is formed.
The gating signal has to be displaced by 1200 with respect to each other so as achieve three phase balanced voltages.
A 3-phase output can be achieved from a configuration of six transistors and six diodes.

Two type of control can be applied to transistors, they are such as 180o & 120oconduction
180-degree conduction.

Here Q1Q2Q3Q4Q5 & Q6 are the positions of thyristor When 𝑄1 is switched on, terminal a is connected to the positive terminal of dc input voltage.

When Q4 is switched on terminal a is brought to negative terminal of the dc source. There are 6 modes of operation is a cycle and the duration of each mode is 60o.
The conduction sequence of thyristor or if we replace 123,234,345,456,561,612. The gating signals are shifted from each other by 60o to get 3-𝜑 balanced voltages.

Three phase 120o mode VSI

The circuit diagram is same as that for 180o mode of conduction.
Here each thyristor conducts for 120o.There are 6 steps each of 60o duration, for completing one cycle of ac output voltage.
Waveform & Harmonics of Square Wave Inverter

Filtering

- Output of the inverter is “chopped AC voltage with zero DC component”. In some, applications such as UPS, “high purity” sine wave output is required.
- An LC section low-pass filter is normally fitted at the inverter output to reduce the high frequency harmonics.
- In some applications such as AC motor drive, filtering is not required.
In square wave inverters, maximum output voltage is achievable. However there in NO control in harmonics and output voltage magnitude.
- The harmonics are always at three, five, seven etc times the fundamental frequency.
- Hence the cut-off frequency of the low pass filter is somewhat fixed. The filter size is dictated by the VA ratings of the inverter.
- To reduce filter size, the PWM switching scheme can be utilised.
- In this technique, the harmonics are “pushed” to higher frequencies. Thus the cut-off frequency of the filter is increased. Hence the filter components (I.e. L and C) sizes are reduced.
- The trade off for this flexibility is complexity in the switching waveforms.
Pulse-width modulation (PWM)
A better square wave notching is shown below -this is known as PWM technique.

Both amplitude and frequency can be controlled independently. Very flexible.
PWM-output voltage and frequency control

Output voltage harmonics
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) is a measure to determine the “quality” of a given waveform.

Study of harmonics requires understanding of wave shapes. Fourier Series is a tool to analyse wave shapes.
Harmonics of square-wave

When n is even cos nπ =1
When n is odd cos nπ = -1
bn = 4 Vdc/ nπ
- Harmonic decreases as n increases. It decreases with a factor of (1/n).
- Even harmonics are absent – Nearest harmonics is the 3rd. If fundamental is 50Hz, then nearest harmonic is 150Hz.
- Due to the small separation between the fundamental an harmonics, output low-pass filter design can be quite difficult.
Quasi-square wave

an = 0 Due to half wave symmetry.

If n is even then bn = 0
If n is odd then

In particular, amplitude of the fundamental

In General, nth Harmonics will be eliminated if ⇒ α = 90o/n




Comments
write a comment