Landforms: Fluvial, Glacial, Karst, Coastal & Arid
River Landforms
The river sculptures the land in the upper stage through the process of erosion and in the lower stage through the process of deposition.
Process | Upper or Youth Stage | Middle or Mature Stage | Lower or Senile Stage |
Erosion | Vertical Erosion | Vertical and lateral erosion | Later deposition |
Gradient | Steep valley sides – V-Shaped valley | U-Shaped valley | Almost base level |
Deposition | Active erosion with very little deposition | Erosion equals deposition | Lot of deposition. Formation of Deltas near river mouth |
Landforms | Rapids and waterfalls, V-shaped valleys, gorges, river capture | Meanders formation, ox-bow lakes, interlocking spurs, river cliffs and slip-off slopes | Floodplains, deltas, estuary, meanders and oxbow lakes |
Glacial Landforms
Landforms of Highland Glaciation
- Corrie, Cirque or Cwm: A steep horseshoe-shaped basin.
- Aretes or Pyramidal Peaks: When two corries cut back on opposite sides of a mountain, knife-edged ridges are formed called Aretes.
- Bergschrund: a deep crack at the head of the glacier.
- U-Shaped glacial troughs: Valley formed due to the downward movement of glaciers.
- Hanging valleys: A tributary valley ‘hangs’ above the main valley so that its stream plunges down as a waterfall.
- Rock basins and rock steps: Excavation of bedrock due to the glacial erosion process
- Moraines: Pieces of rock fragments which becomes stationary after the glacier melts. They may be lateral moraine, median moraine, terminal moraine etc.
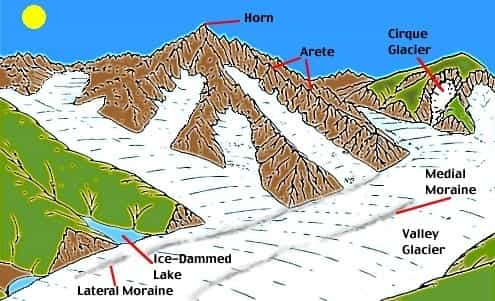
Landforms of Glaciated Lowlands
- Roche moutonnee: a resistant residual rock hummock.
- Crag and Tail: a mass of rock with precipitous slope on the upstream side and softer leeward slope.
- Boulder clay or Glacial till: an unsorted glacial deposit comprising a range of eroded materials forming a monotonous and featureless landform.
- Erratics: Boulders of varying size transported by the ice and composed of materials entirely different from those of the region.
- Drumlins: Oval, elongated whale-back hummocks. It is known as the Basket of Eggs topography.
- Eskers: they are long, narrow, sinuous ridges composed of sand and gravel which mark the former sites of sub-glacial meltwater stream.
- Terminal moraines: Coarse debris deposited at the edge of the ice sheet.
- Outwash plains: fluvioglacial deposits washed out from the terminal moraines. They are called Knob and kettle topography.

Arid or Desert Landforms
Desert Landscape
- Hamada or Rocky desert
- Reg or stony desert
- Erg or sandy desert
- Badlands: Hills are eroded into gullies and ravines.
- Mountain deserts: Dissected desert highlands due to erosion.
Erosional Landforms
- Deflation hollows: Winds lower the ground by blowing away the unconsolidated materials.
- Mushroom rocks: A mushroom rock, also called rock pedestal, or a pedestal rock, is a naturally occurring rock whose shape, as its name implies, resembles a mushroom.
- Inselbergs: isolated residual hills rising abruptly from the level ground.
- Demoiselles: These are rock pillars which stand as resistant rocks above soft rocks as a result of differential erosion of hard and soft rocks
- Zeugens: A table-shaped area of rock found in arid and semi-arid areas formed when more resistant rock is reduced at a slower rate than softer rocks around it under the effects of wind erosion
- Yardangs: Yardang, a large area of soft, poorly consolidated rock and bedrock surfaces that have been extensively grooved, fluted, and pitted by wind erosion. The rock is eroded into alternating ridges and furrows essentially parallel to the dominant wind direction.
- Ventifacts or dreikanter: these are pebbles faceted by sand-blasting.

Source: Revision world
Depositional landforms
- Dunes: Dunes are hills of sand formed by the accumulation of sand and shaped by the movement of winds.
- Barchans: Crescent-shaped dunes occurring transversely to the wind direction.
- Seifs: Longitudinal dunes, which are long, narrow ridges of sand, often over a hundred miles long lying parallel to the direction of prevailing winds.
- Loess: the fine dust blown beyond the desert limits is deposited on neighbouring lands as loess.
- Bolsons: It is a semiarid, flat-floored desert valley or depression, usually centred on a playa or salt pan and entirely surrounded by hills or mountains. It is a type of basin characteristic of basin-and-range terrain
- Playas: an alkali flat or sabkha, a desert basin with no outlet which periodically fills with water to form a temporary lake.
- Pediments: a broad, gently sloping expanse of rock debris extending outwards from the foot of a mountain slope, especially in a desert.
- Bajadas: A bajada consists of a series of coalescing alluvial fans along a mountain front. These fan-shaped deposits form from the deposition of sediment within a stream onto flat land at the base of a mountain
Karst Topography
Karst is a topography formed from the dissolution of soluble rocks such as limestone, dolomite, and gypsum. It is characterized by underground drainage systems with sinkholes and caves.

- Grykes/Clints: Clints are the blocks of limestone that constitute the paving, their area and shape are directly dependent upon the frequency and pattern of grykes. Grykes, or scailps, are the fissures that isolate the individual clints
- Swallow holes/Sink Holes (Dolines or Uvalas): A sinkhole is a depression or hole in the ground caused by some form of collapse of the surface layer.
- Stalactites/Stalagmites: A stalactite is an icicle-shaped formation that hangs from the ceiling of a cave, and is produced by the precipitation of minerals from water dripping through the cave ceiling. A stalagmite is an upward-growing mound of mineral deposits that have precipitated from water dripping onto the floor of a cave.
- Caverns: Large-scale features where caves are formed due to the dissolution of limestones. May include Poljies.
Coastal Landforms

Erosional Features

- Capes and Bays: On exposed coasts, softer rocks are worn back into inlets, coves or bays due to erosion while the harder rocks persist as headlands, promontories or capes.
- Cliffs and wave-cut platforms:
 3. Cave, arch, stack and slump
3. Cave, arch, stack and slump
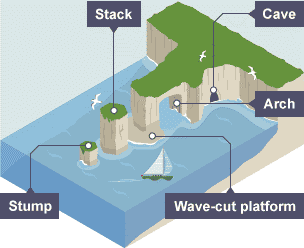
Source: BBC
4. Geos and gloups: Where a cave roof collapses, a narrow inlet or geo is formed.
Depositional Features
- Beaches: Sands and gravels loosened from the land are moved by waves to be deposited along the shore as beaches.
- Spits and bars: Deposition of material piling up into a ridge forming a spit with one end attached to the land and the other end projecting into the sea. When the ridge of shingle is formed across the mouth of a river, it is called a bar.

3. Marine dunes and dune belts: Due to on-shore wind’s force, a large amount of coastal sand is driven landwards forming marine dunes.
- Coastline of Submergence
- Ria coasts: Formed in upland coastal regions where the mountains run in right angles to the sea where the lower valley is submerged due to deglaciation.
- Fiord coasts: Submerged U-shaped glacial troughs.
- Dalmatian coasts: Longitudinal coasts where mountains run parallel to the coast.
- Estuarine coasts: In submerged lowlands, the mouths of rivers are drowned so those funnel-shaped estuaries are formed.
- Coastline of Emergence
- Uplifted lowland coast: Smooth, gently sloping coastal lowland is formed with shallow lagoons, salt-marshes and mudflats.
- Emergent upland coast: Faulting or earth movement thrust up coastal plateau so that whole region is raised, with consequent emergent features such as a steep cliff, deep off-shore waters etc.

To boost the preparation of all our users, we have come up with some free video (Live Class) series.
Here are the links
MP राज्य परीक्षाओं के लिए करंट अफेयर्स
मध्य प्रदेश राज्य परीक्षाओं के लिए 2000 सबसे महत्वपूर्ण प्रश्न
More from us
Get Unlimited access to 45+ Mock Tests-BYJU'S Exam Prep Test Series




Comments
write a comment