- Home/
- SSC & Railways/
- SSC CGL/
- Article
Foreign Invasions in India: Railways & SSC GK History Notes
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 25th, 2023

Natural resources abound in India, which is one of the reasons it has attracted empires from different civilizations. There is a lengthy list of Indian invaders who came with the intention of capturing the land of riches. The Greek and Persian invasions, among others, were the most important in ancient Indian history.
In this Blog, we will discuss the Invaders of India in detail. Furthermore, we will discuss foreign invasions in India in chronological order, as well as their effect on Indian society and culture. The Invaders of India is a significant subject in the Ancient History section of the SSC History Syllabus, and this article will aid in its preparation.
Table of content
Here we have discussed SSC GK History Notes based on Foreign Invasions in India. We have covered all important points related to Foreign Invasion in India which are asked in SSC, Railways & other competitive exams.
Foreign Invasions in India
India is a country of abundance and virtues, which has resulted in numerous foreign invasions. Almost 200 times, foreign conquerors attempted to rob India. Some foreign invasions in India continued for years, while others were brief. The following are the most well-known foreign invasions in India-
- Persian Invasion
- Iranian Invasion
- Greek Invasion
- Mahmud of Ghazni
- Invasion by Muhammad Ghori
- Timur Invasion in India
- Mughal Empire Invasion
- British East India Company Invasion
Foreign Invasions: Timeline
| Invasion | Timeline |
|
Aryan Invasion |
1800-1500 BCE |
|
Persian invasions |
535 BC |
|
Alexander’s Invasion |
336 BC -323 BC |
|
Invasion of Seleucid |
305 -303 BC |
|
Indo-Greek Invasion |
180 BC |
|
Huna Invasion |
458 AD |
|
Arab Invasion by Mohammed Bin Kasim |
712 AD |
|
Turkish Invasion by Mahmud of Ghazni |
1001 AD |
|
Turkish Invasion by Muhammed of Ghur |
1175 AD |
|
Mongol Invasion |
1206-1368 AD |
|
The Invasion of Mughals |
1526-1761 AD |
|
The Invasion of Nadir Shah |
1736 -1747 AD |
|
The European Invasions |
till 1947 AD |
Aryan Invasion
For the first time, Aryans are believed to have invaded India. They are a group of nomadic Indo-European clans. The Indus Valley Civilization flourished in the Indo-Gangetic Plains as the Aryans conquered and settled in the Indus River Valley. They ultimately colonized the Deccan region and moved southward in India. Each of these events, according to legend, occurred between 1800 and 1500 B.C.
Persian Invasion
Cyrus the Great, the empire’s founder, launched the first of two major invasions in 535 BCE, annexing the regions west of the Indus River that formed the Achaemenid Empire’s eastern border. Darius the Great I attacked Sindh and Punjab after Cyrus died. The son of Darius, who was engaged in a war with the Greeks, is also included on the list of Persian Invaders of India.
Iranian Invasion
Iranian rules Darius penetrated into NW India in 516 BC and annexed Punjab, West of Indus and Sindh. This was 20th province of Iran and contributed 1/3rd of the total revenue of Iran due to fertile lands. Xerxes, the successor of Darius, employed a large number of Indians in the war against Greeks.
Results of the contacts
- The impetus to trade and commerce.
- Kharoshthi script came into India
- Iranian influence on Ashokan sculptures is clearly seen
- Iranian invasion eventually led to Alexander’s invasion
Greek Invasion (Alexander)
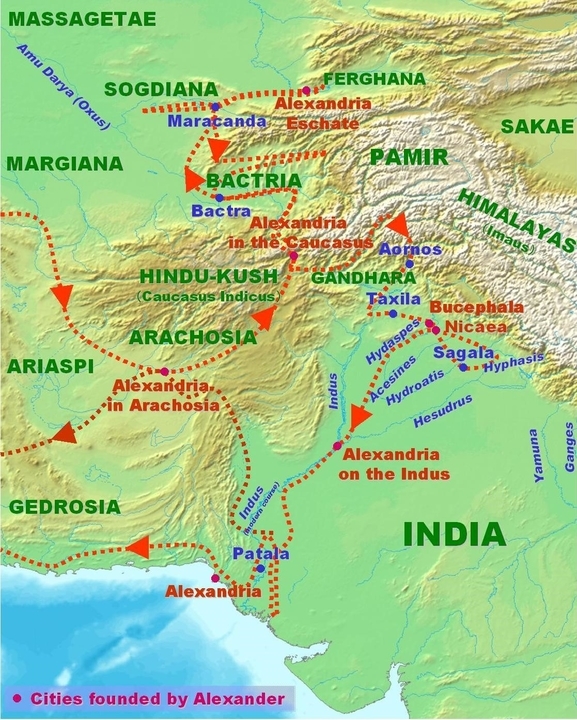
He defeated the last king of the line of Darius, Xerxes in 333 BC and 331 BC. After occupying the realm of the Persian king, Alexander crossed the Hindukush mountains in eastern Afghanistan in 327 BC.
After annexing Iran, Alexander moved into India through Khyber Pass. Ambhi, the ruler of Taxila readily submitted. He met Porus at Jhelum where he defeated him in the Battle of Hydaphes but later restored his kingdom to him. Alexander marched till the Beas river but his army refused to accompany him. He remained in India from 326-325 B.C after which he was forced to retreat.
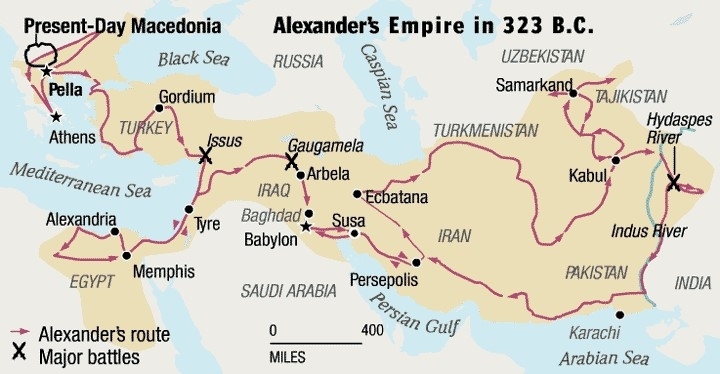
Results of the invasion
Direct contact between India and Greek was established through four distinct Land and Sea routes which led to increased trade and commerce.
Cities established: Alexandria in Kabul, Boukephala beside Jhelum, Alexandria in Sindh
Alexanders’ expeditions have given us clearly dated records of his campaign, valuable geographical accounts and information about Indian society and economy
Mahmud of Ghazni
Mahmud of Ghazni was an Invader of India who was fiercely opposed to Hinduism. He led one of India’s most famous foreign invasions in order to gain riches and spread Islam throughout the country. Mahmud of Ghazni destroyed the richest temples, such as Mathura and Somnath, 17 times and used the proceeds to construct Ghazni’s capital. Ghazni was a well-known alien invader in India. In 1001AD, Mahmud of Ghazni assaulted and invaded India, then modern-day Pakistan.
Muhammad Ghori
In 1175 A.D., Muhammad Ghori attacked India. He moved towards Delhi after capturing Multan and Punjab. His empire stretched from Herat (Afghanistan) to Western Bengal, including the Khurasan area. In 1191 A.D., the valiant Rajput chiefs of northern India led by Prithvi Raj Chauhan defeated him in the First Battle of Terrain. In 1192, he stormed again with a massive force of Turkish mounted archers, defeating the Rajputs in the Second Battle of Tarain and executing Chauhan. Later, he abandoned his plans for Indian attacks and focused his efforts on expanding in the West.
Taimur Invasion
Timur was the first Timurid emperor, and he conquered the Delhi Sultanate. It was governed by Sultan Nasir-Ud-Din Mahmud Shah at the time.
Timur was a renowned Indian invader who achieved great military success as a leader of nomad warriors. Timur’s greatest victory was the conquest of Delhi; he ruled over Central Asia, and the area flourished during his reign.
Mughal Invasion
Babur was also one of India’s Invaders and the creator of the Mughal Empire. His Panipat Battle was instrumental in changing India’s political past. His victory marked the commencement of the Mughal Empire and the end of the Delhi Sultanate. The Mughal Empire ruled the Indian Subcontinent until the advent of the East India Company, which marked the start of British colonization.
Nader Shah
Nader Shah was the founder of the Afsharid dynasty and the most powerful ruler in Iranian history. He conquered Ghazni, Kabul, Peshawar, Sindh, and Lahore before moving into Mughal territory. He controlled Northern India until March 1739, when he attacked Delhi. On February 13, 1739, the Mughal ruler Muhammad Shah raised a massive army to confront Nader’s troops in the Battle of Karnal. At the Battle of Karnal, his force easily defeated the Mughals, crushed the Mughal army, and brutally massacred and looted Delhi. He also took with him all of the Mughal treasury’s valuables, including the renowned Peacock Throne and the Kohinoor diamond.
British Invasion
Britishers were also Indian Invaders, and their reign is known as British India. On August 24, 1608, they arrived in India as merchants to head the foreign invasion of India. However, British expansion began with the win at the Battle of Palsset in 1757. The British Company controlled nearly every sector, including administrative and military authority. The British Crown seized complete control of India in 1857, launching the British Raj. Crown Rule continued in India until 1947.
Central Asian contacts and their results
The Indo-Greeks
The series of invasions began in 200 BC by the Bactrian Greeks who were pushed by the Scythian tribes.
- Menander (165-145 BC) was the most famous ruler who was converted to Buddhism by Nagasena. The questions of Menander were compiled as Milindapanho.
- Indo-Greeks were the first to issue Gold coins in India and they were also the first to issue coins which could be definitely attributed to Kings.
- They introduced the features of Hellenistic Art through which Gandhara style had developed.
The Shakas (1st BC – 4th AD)
- The Shakas or Scythians replaced Indo-Greeks. There were five branches of Shakas and they controlled a much larger territory.
- Vikrama Samvat started in 57 BC when a king called as Vikramaditya in Ujjain defeated the Shakas.
- Rudradaman I (AD 130-150) was a famous king who ruled over western India. He repaired the Sudarshana lake in Kathiawar.
The Parthians
- They originally belonged to Iran and they replaced the Shakas in the NW India.
- During the times of Gondophernes, St.Thomas is said to have come to India for the propagation of Christianity.
The Kushans
- They were nomadic people of Central Asia who ruled from the Oxus to the Ganges.
- The Kadaphises I and II ruled for 28 years from 50 AD. They were replaced by the Kanishka.
- Peshawar was their first capital and Mathura the second.
- Kanishka started the Shaka era in 78 AD.
- Kanishka patronized Buddhism by holding a Buddhist council in Kashmir where the doctrines of the Mahayana form of Buddhism was finalized.
Impact of the Central Asian Contacts
- Advances in building activities and pottery
- They had a better cavalry
- They identified themselves as an integral part of India
- Satrapy system of Government developed
- They appointed military governors called Strategos
- Mahayana style of Buddhism developed with Gandhara and Mathura schools of Art supporting Buddhism.
Conclusion
From the Aryan Invasion to the British Invasion, foreign invasions in India have been constant since the beginning of time. Despite being conquered and ruled by a variety of world leaders, India ultimately gained independence from all of them. We now live proud lives, reflecting on the past while labouring every day to improve our country’s standing. Foreign invasions aided the political union of the Indian subcontinent as well as the growth of trade, commerce, art, and culture.
Download PDF
All the Best
Check OUT

3 Crore+ Registered Aspirants | 2.5 Crore Downloads | 50,000+ Selections

