SAARC: Countries, Objectives, Full Form, Functions, SAARC UPSC Notes
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: November 14th, 2023
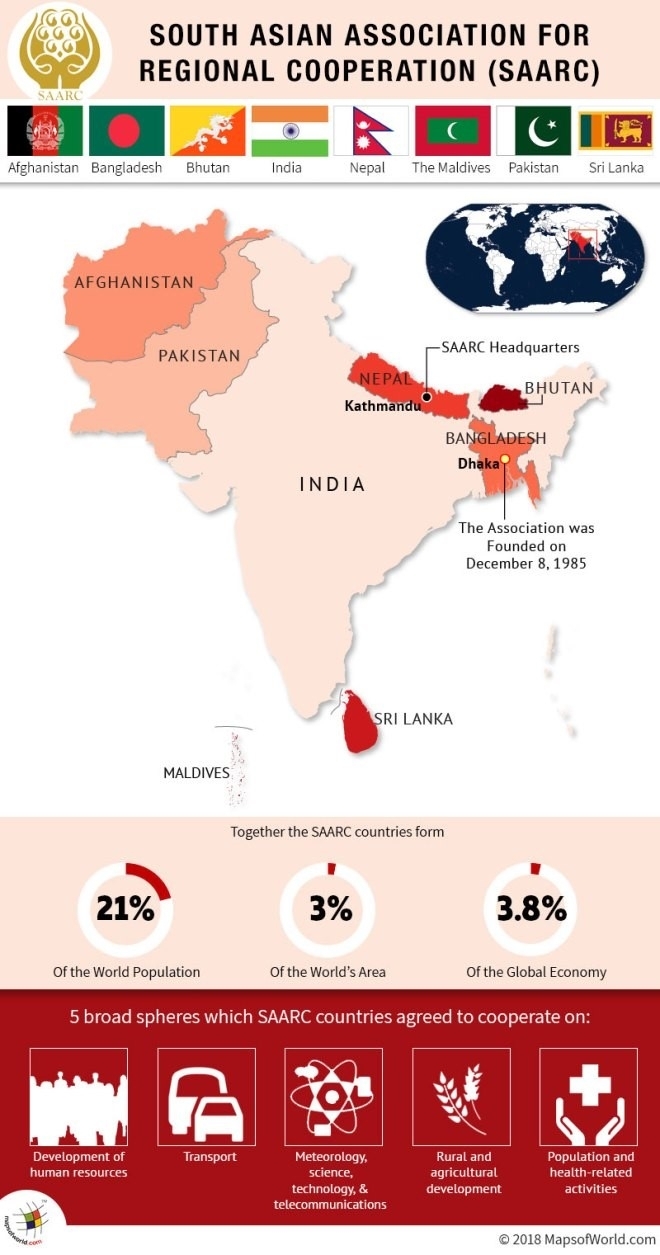
SAARC stands for the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation. SAARC is an economic and political organization of eight countries in South Asia. SAARC was formed in 1985 with Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Sri Lanka, and Pakistan as the heads who adopted the charter formally. Afghanistan joined as the 8th member of SAARC in 2007. The headquarters and secretariat of the SAARC are in Kathmandu, Nepal. The main objective of SAARC is to promote economic growth, social progress, and cultural development within the South Asia region.
SAARC aims to promote the welfare of the people; accelerate economic growth, social progress, and cultural development; and strengthen collective self-reliance. The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation also seeks to contribute to mutual trust and understanding among the member countries. This article will throw light on SAARC full form, its countries, objectives, functions, and importance.
Table of content
-
1.
SAARC
-
2.
SAARC Countries
-
3.
Objectives of SAARC
-
4.
SAARC Full Form
-
5.
Functions of SAARC
-
6.
South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation: Highlights
-
7.
SAARC – Latest News
-
8.
History of SAARC
-
9.
Principles of SAARC
-
10.
Structure of SAARC
-
11.
Achievements of SAARC
-
12.
Importance of SAARC
-
13.
India and SAARC Relations
-
14.
Role of SAARC – Impact on the Indian Economy
-
15.
SAARC Development Fund (SDF)
-
16.
Challenges to SAARC
-
17.
SAARC UPSC
SAARC
SAARC is the acronym for South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation, which was established on December 8, 1985, when eight countries – Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Maldives, Nepal, and India signed the sharp charter in Dhaka. The SAARC headquarters are located in Kathmandu, Nepal.
SAARC UPSC Notes
Mr. Weerakoon, a Sri Lankan diplomat, is the 14th Secretary-General of the SAARC. He assumed charge in March 2020. SAARC summits are usually held biennially and hosted by member states in alphabetical order. The member state hosting the summit assumes the Chair of the Association.
SAARC Countries
During SAARC’s foundation, seven SAARC countries are mainly located in South Asia, i.e. India, Pakistan, Bhutan, Nepal, Bangladesh, Maldives, and Sri Lanka. Afghanistan became its eighth member in April 2007 at the SAARC’s 14th summit.
SAARC is a grouping modeled on the European Union that came into being in the mid-1980s – but has little to show for itself by way of regional or economic integration. There are 8 founding members and 9 observer members of the SAARC:
Founding SAARC Members
The 8 founding members are:
- India
- Afghanistan
- Bangladesh
- Bhutan
- Nepal
- Pakistan
- Sri Lanka
- The Maldives
Observer SAARC Member Countries
There are currently nine Observers of SAARC, namely:
- Australia
- China
- EU
- Japan
- Mauritius
- Iran
- Republic of Korea
- Myanmar
- The United States
The SAARC region lies in the southern Himalayas, surrounded by the Hindu Kush mountains. The SAARC region is a landmass of 3.3 % of the world and has one-fifth of the population. The present SAARC countries can be categorized into different groups.
- Land-locked countries (3) – Bhutan, Nepal, and Afghanistan;
- Islands countries (2) – Sri Lanka and the Maldives;
- India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh, which have the Indian Ocean in the South and South West and the Indo-Gangetic plains stretching along with these countries.
Objectives of SAARC
The organization aims to promote economic growth, social progress, and cultural development in South Asia. Each decision taken by SAARC and every policy framed by it is guided by the overall objectives it had set for itself in the charter. Following are the functions and Objectives of SAARC as defined in its charter:
- To improve the quality of life of people in South Asia.
- Providing every individual with the opportunity to live with dignity and fulfill their potential by accelerating regional economic growth and cultural development and maintaining social progress.
- To strengthen and promote South Asia’s collective self-reliance.
- To improve mutual trust and understanding among the member countries and appreciate the solution to the problems.
- Actively promote mutual assistance and cooperation in the economy, society, technology, and culture.
- Boost cooperation with other developing nations.
- Build up cooperation among themselves in international forums on matters of common interest.
- Cooperate with international and regional organizations having common aims and objectives.
SAARC Full Form
SAARC Full Form is South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation. SAARC has successfully fostered financial integration and growth among its member states. We have curated SAARC full form in a few important languages like Hindi, Tamil, Urdu, and Bengali.
| SAARC Full Form in Hindi | दक्षिण एशियाई क्षेत्रीय सहयोग संगठन |
| SAARC Full Form in Tamil | தெற்காசிய நாடுகளின் பிராந்தியக் கூட்டமைப்பு |
| SAARC Full Form in Urdu | جنوبی ایشیائی علاقائی تعاون کی تنظیم |
| SAARC Full Form in Bengali | দক্ষিণ এশীয় আঞ্চলিক সহযোগিতা সংস্থা |
Read:
Functions of SAARC
The functions of SAARC, as defined in its charter, are as follows:
- To promote the welfare of the South Asian population by improving their quality of life.
- It helps boost economic growth, cultural development, and social progress and allows everyone to live their life with full dignity and potential.
- To strengthen and promote the concept of self-sustenance among South Asian countries.
- To help the member countries develop coordination and cooperation with other developing countries.
South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation: Highlights
Let us look at the important points regarding SAARC such as its establishment year, countries included under the list, the total number of members in it, its headquarters, and more.
| SAARC Established | On December 8, 1985, in Dhaka, Bangladesh |
| SAARC Countries | 8 Countries – India, Bangladesh, Nepal, Sri Lanka, Maldives, Bhutan, Afghanistan, Pakistan |
| Observers SAARC Members | 9 Observers – Australia, European Union (E.U), Iran, Japan, Mauritius, South Korea, United States of America (USA), China, Myanmar |
| SAARC Headquarters | Kathmandu, Nepal |
| SAARC Structure – Important Bodies | South Asian University (SAU) – India
South Asian Regional Standards Organization (SARSO) – Dhaka SAARC Development Fund (SDF) – Bhutan SAARC Arbitration Council (SARCO) – Pakistan |
| 1st Secretary General of SAARC | Abul Ahsan (Bangladesh) |
| Current Secretary-General of SAARC | Esala Ruwan Weerakoon (Sri Lanka) – Took office from 1st March 2020 |
| Last SAARC Member | Afghanistan (April 2007) |
| Last SAARC Summit | 19th SAARC Summit in Pakistan (Cancelled) |
SAARC – Latest News
Over the years, SAARC has strived to promote economic collaboration, cultural cooperation, and technological development in the South Asia region. Even during the Covid-19 pandemic, a Coronavirus Emergency Fund was set up by the SAARC member countries to mitigate the risks associated with the pandemic in the South Asian region. This was done in March 2020 during a video conference of the SAARC Heads of State.
- India led the SAARC member countries in the fight against the pandemic and hosted a virtual health-secretary-level meeting with the member nations on February 18, 2021, to discuss the Covid-19 crisis. It also contributed Covid vaccines to several member nations.
- In today’s era, as the world is undergoing a major change in every aspect, regional associations are fast becoming an important and effective stage for political and economic interaction.
- Nations’ regional, political, and religious blocks now provide platforms for several countries to exert power in global affairs.
- SAARC strives to attain sustainable economic growth by respecting territorial integrity, sovereign equality, and national independence.
History of SAARC
The concept of regional, political, and economic cooperation in South Asia was first conceived in 1980. Though the idea was discussed in three major conferences (the Asian Relations Conference, the Baguio Conference, and the Colombo Powers Conference) between 1947 and 1954, Ziaur Rahman (the ex-President of Bangladesh) made a formal proposal on May 2, 1980, to establish SAARC.
In 1985, the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) was founded in Dhaka, Bangladesh. The SAARC aimed to promote economic activities and alleviate poverty in South Asia.
- The SAARC was formed under Article 52 of the United Nations Charter.
- It provided regional arrangements or agencies for dealing with matters related to maintaining international peace and security.
- SAARC has been dormant for several years due to regional tensions; tangible measures have been taken to fight against the ongoing viral outbreak.
- The SAARC member countries differ greatly in land area, GDP (Gross Domestic Product), and population, although they share a similar human and economic development level.
- They also share an unusual feature of having a common border with another member country.
Principles of SAARC
The cooperation within the framework of the SAARC states that:
- The principles of sovereign equality, territorial integrity, non-interference in the affairs of other states, and political independence are to be respected.
- Bilateral and multilateral cooperation is not to be replaced by such corporations, but it should be a component of their own.
- Such corporations won’t be inconsistent with multilateral and bilateral obligations.
Structure of SAARC
The member countries of SAARC have collectively constituted four specialized bodies of SAARC. The following are the specialized bodies of SAARC:
- SAARC Arbitration Council- Pakistan: This is an intergovernmental body based in Pakistan to perform legal work within the region to provide a fair settlement of industrial trade, commercial banking, or any other dispute.
- SAARC development fund- Bhutan: It is a Bhutan-based funding body whose primary purpose is to fund collaborations in social sectors like development and poverty reduction.
- South Asian University- India: The South Asian University is situated in India, where the South Asian University awards degrees and certificates.
- South Asian Regional Standard Organisation- Dhaka: The South Asian regional standards organization is based in Dhaka. It was established to enhance and achieve cooperation and coordination among the member countries to develop harmony within the region to facilitate inter-regional trade and access to the global market.
| Specialized Body of SAARC | Location | Country |
| SAARC Arbitration Council (SARCO) | Islamabad | Pakistan |
| SAARC Development Fund (SDF) | Thimphu | Bhutan |
| South Asian University (SAU) | New Delhi | India |
| South Asian Regional Standards Organization (SARSO) | Dhaka | Bangladesh |
Achievements of SAARC
SAARC is accredited with the following achievements of launching:
- SAARC Agreement on Trade in Services (SATIS): SATIS is following the GATS-plus’ positive list’ approach for trade in services liberalization.
- SAARC University: Establish a SAARC university in India, a food bank, and an energy reserve in Pakistan.
- SAPTA: South Asia, the Preferential Trading Agreement for promoting trade among member countries came into effect in 1995.
- SAFTA: A South Asia Free Trade Agreement confined to goods but excluding all services like information technology was signed to reduce customs duties of all traded goods to zero by 2016.
- Free Trade Area (FTA): The member countries have established a Free Trade Area (FTA), which will increase their internal trade and considerably lessen some states’ trade gap.
Importance of SAARC
As the largest regional cooperation organization, SAARC’s importance in stabilizing and effectively transforming the region is becoming increasingly self-evident. Other than this, SAARC holds the following importance:
- The SAARC is a very important body as it consists of 21% of the world’s population, 3% of the world’s area, and 3.8% of the global economy, equal to 2.9 trillion US dollars.
- There is a synergy among the member countries of SAARC as they have some common grounds in tradition, dress, food, and political viewpoints.
- SAARC countries have problems like poverty, technology, backwardness, illiteracy, malnutrition, employment, industrial backwardness, poor GDP, socioeconomic conditions, etc. These can be sorted at this level by welcoming some common solutions provided by the member countries.
- SAARC has significantly contributed to the development of civil society and track-two initiatives.
- SAARC members are among the top troop-contributing countries to UN peacekeeping missions.
- With the US withdrawal from Afghanistan, a joint peacekeeping force from the SAARC region under the UN aegis could be explored to fill the power vacuum that terrorist and extremist forces would otherwise fill.
India and SAARC Relations
SAARC holds a geostrategic significance for India. It can counter China’s OBOR initiative by engaging Nepal, Bhutan, the Maldives, and Sri Lanka in the development process and economic cooperation. It offers India a platform to showcase its leadership in the region by taking up extra responsibilities.
SAARC will be a game-changer for India’s Act East Policy. Linking South Asian economies with South-East Asia will bring further economic integration and prosperity to India, mainly focusing on the services Sector. SAARC will thus provide primacy to the country’s immediate neighbors and help create mutual trust and peace within the region.
Role of SAARC – Impact on the Indian Economy
SAARC countries and most people residing there depend on agriculture. They often have poor education, lack science and technology, and suffer from overpopulation. The agriculture-based economy is likely to persist and dominate in years to come for the SAARC countries.
The economic development model revolves around food for the growing population, fodder for livestock, and raw materials and the industry market is likely to remain the main market goods.
- Most of the SAARC countries depend on developed countries for aid and trade. In this regard, the South Asian Free Trade Association (SAFTA) came into operation on January 1, 2006.
- SAFTA aims to remove trade barriers, establish a ministerial-level mechanism for administering the treaty, and eliminate tariffs and dispute settlement among SAARC countries.
- The exchange of mutual goods among the SAARC countries is more relevant, cheap, and cost-effective.
- This provides vast scope for mutual cooperation in various areas.
SAARC Development Fund (SDF)
The SAARC Development Fund is separate from that announced by Prime Minister Narendra Modi during a video conference with the heads of government of all South Asian countries. The SDF was constituted in April 2010 by the heads of the eight SAARC Member States. The fund will be utilized for:
- Poverty alleviation
- Social development focusing on education
- Health
- Human resource development
- Support to a vulnerable or disadvantaged segment of society
- Funding needs of communities
- Micro-enterprises and rural infrastructure development
The SDF Secretariat is based in Thimphu. It is mandated to build regional integration and economic cooperation through project funding in all the eight SAARC Member States through its Economic, Infrastructure, and Social segments. Currently, SDF is implementing 90 projects in SAARC member states under its three funding windows with a total commitment of $198.24 million.
Challenges to SAARC
The first and most important challenge that SAARC is facing is the continuous tensions between India and Pakistan over the issue of Kashmir, which is directly hampering the likelihood of SAARC. Other than this, other SAARC challenges include:
- The annual meeting frequency of SAARC is considerably low. Ideally, the members of SAARC should get engaged on a common platform at least twice annually.
- Because of the broad range of cooperation, energy, and resources get diverted.
- There has been a lack of satisfactory implementation of the SAARC free trade agreement.
SAARC UPSC
SAARC holds importance in the international relations and Current Affairs section of the UPSC Exam. It comes under the GS Paper 2 syllabus of the Mains exam. When a solid and firm foundation is established, a candidate must refer to the International Relations Books for UPSC to get a complete overview and critical analysis of the topic.
The South Asian identity of the nations is reflected in SAARC as an organization, both historically and currently. Refer to the following SAARC UPSC questions to understand the type of queries asked in the exam related to the topic.
SAARC Sample Questions
Question: Consider the statements: (1) The first SAARC Summit was held in Dhaka, Bangladesh, (2) 20 SAARC Summits have been held to date, (3) As of 2015, SAARC comprises 3% of the world’s area, 3.8% of the global economy, and 21% of the world’s population, (4) The 20th SAARC Summit was held in New Delhi. Which of the statements above is not correct? A) 1 only, B) 2 and 3 only, C) 4 only, and D) None of the above
Answer: (4 only) The 20th SAARC Summit was held in New Delhi
Question: Which one of the following countries was the last one to become a member of the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC)? (A) Afghanistan, (B) Nepal, (C) Sri Lanka, (4) Mauritius
Answer: Afghanistan
Question: Where was the 17th SAARC (2011) Conference held? (A) Addu City, (B) Dhaka, (C) Colombo, (D) Male
Answer: Addu City
Question: South Asian University jointly established by eight SAARC Member States is at: (A) Kathmandu, (B) Islamabad, (C) New Delhi, (D) Dhaka
Answer: New Delhi
Mains Question: Discuss the SAARC’s potential and challenges in becoming a successful example of regional collaboration.
