- Home/
- GATE MECHANICAL/
- GATE ME/
- Article
Riveted Joints
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 25th, 2023

In riveted joints, rivets are used to make the joints and to fasten the sheet metal. A rivet is a short cylindrical device having a head at the top of the cylinder and a narrow one at the bottom. The short cylindrical portion of the rivet is called a shank, and the narrow bottom portion of the rivet is known as the tail of the rivet. The rivets are an essential part of riveted joints.
As the purpose of the rivet is to fasten the sheet metal, it should sufficiently ductile and tough. Mostly the material used in rivets is steel (nickel steel or low carbon steel), and copper, aluminium, or brass is used. The rivets used in riveted joints can be manufactured by the cold heading process or by the hot forging process. In case of the cold heading, the process to eliminate stresses set up in the rivet heat treatment must be required. Here, we will see the types and failures of Riveted Joints.
Download Formulas for GATE Mechanical Engineering – Machine Design
What are Riveted Joints?
The riveted joint is a permanent joint. It is also known as permanent fastener joints. If the riveted joint is made, then the component can be disassembled only by damaging those components. For assembling the component by riveted joint large mechanical force is required.
Riveted Joints Function
The main function of riveted joints is to provide strength and tightness to the joint. Strength is essential to prevent the failure of riveted joints or assembly, and to make it leakproof in case of boiler, aircraft, naval ship hull joint should be as tight as possible.
Download Formulas for GATE Mechanical Engineering – I C Engine
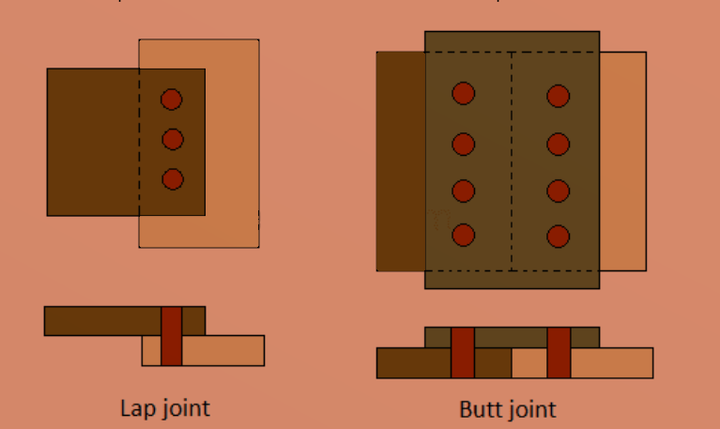
Riveted Joints Types
As per the assembly, design consideration, operating condition rived joint has been made accordingly, we can classify the riveted joint base on the number of rows of a rivet, arrangement of rivet in an adjacent row, and as per the application. Based on the method of placing the plates, The riveted joints are mainly of two types:
- Lap joint – In this joint two plates are riveted when one plate overlaps other
- But joint – In the case of the butt joint, the joint is made by placing the cover plate over the two plates either on one side or both sides of the plates.
Failure of Riveted Joint
We can say the joint failed either it is failed due to the plate or by rivets; it is dependent on the strength of the plate material and the place of the rivet place. According to this riveted joint may fail in the following ways:
- Due to Crushing of the Plate or Rivets
- Due to the Shearing of Rivets
- Due to the Tearing of the Plate Across a Row of Rivets
- Due to Tearing of Plate at an Edge
Download Formulas for GATE Mechanical Engineering – Industrial Engineering
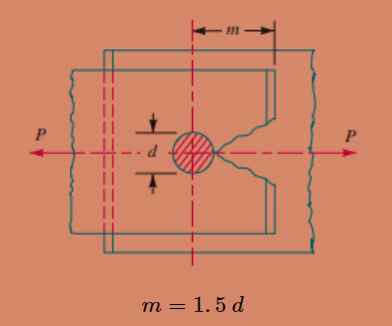
Due to Tearing of Plate at an Edge
This type of failure will occur where the strength of the plate is less than the strength of the rivet and rivets are very close toward the edge of the plate. So, the failure of the joint is at the edge of the plate. The limiting distance between the edge of the plate and the rivet is greater than or equal to 1.5 times the diameter of the rivet as shown in the figure.
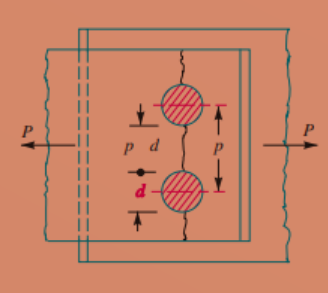
Due to the Tearing of the Plate Across a Row of Rivets
As we insert the rivet into the plate, the hole needs to have made, which causes a reduction in the cross-sectional area of the plate, so the high tensile stress concentration will generate along the pitch length of the plate, which causes the tear of the plate across the rivets as shown in the figure.
The resistance offered by the plate against tearing is known as tearing resistance or tearing value or tearing strength of the plate.
Pt= At.σt
Pt=(P−d) t.σt
Where
- P = Pitch of the rivets.
- d = Diameter of the rivet hole,
- t = thickness of the plate, and
- σt= Permissible tensile stress for the plate material.
Whenever the applied load is greater than the tearing resistance load this type of failure of the rivet will occur.
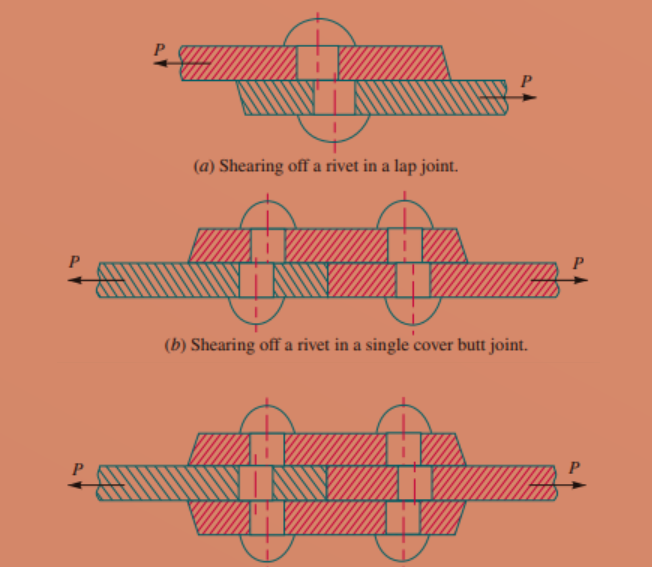
Due to the Shearing of Rivets
Due to the tensile load in the plate, shear stress will develop in the rivet. If the rivets can’t able to resist the stress, the rivet will get shear off as shown in the figure. So we can define the shearing resistance or shearing strength as the resistance offered by a rivet.
In the case of lap joint and single cover butt joint the rivet will be subjected to a single share, whereas in the case of double cover butt joint rivet will be subject to double shear. The shearing resistance or pull to shear the rivet per pitch length is given by
Ps = n∗ As ∗ 𝜏
Ps = n∗ 𝜋/4∗d2∗ 𝜏………..For single shear
Ps = n∗2∗ 𝜋/4∗d2……..For double shear (Theoretically)
Where,
- d = Diameter of the rivets,
- 𝜏= limiting shear stress for the rivet,
- n = No. of rivets per pitch length.
- σt= Permissible tensile stress for the plate material.
Due to Crushing of the Plate or Rivets
The crushing of the plate or rivet is the phenomenon of becoming an oval shape of the rivet, which causes the joints to become loose and failure of the rivet to occur. The projected area of the rivet or hole on a diametral plane is responsible for resisting the crushing. The resistance offered by a rivet is known as crushing resistance or crushing strength. It is given by the equation: Pc= n*d*t*σc
Where,
- d = Diameter of the rivets,
- t = Thickness of plate,
- n = No. of rivets per pitch length.
- σc = Permissible crushing stress for the plate or rivet material.


