What is Paging in Operating System?
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 25th, 2023

Paging in OS is the static memory allocation technique in the operating system in which the physical address space of a process is to be non-contiguous. When a new process arrives, its size(in pages) is determined. If the process has n pages in logical memory, then n frames must be available in the physical or main memory.
Download Paging in OS PDF
Paging in Operating system is a memory management technique used by operating systems to handle virtual memory. The operating system maintains the job table, page table, and frame table to support paging in OS (operating system). Here, this article will discuss Paging in OS, its address translation, characteristics, and important points.
Table of content
-
1.
What is Paging in OS?
-
2.
Types of Paging in OS
-
3.
Fixed-size Paging in Operating System
-
4.
Variable-size Paging in Operating System
-
5.
Address Translation in Paging in OS
-
6.
Characteristics of Paging in Operating System
-
7.
Demand Paging in OS
-
8.
Important Points for Paging in Operating System (OS)
-
9.
Benefits of Paging in OS
-
10.
Page Replacement Algorithms
-
11.
Advantage of Paging in Operating System
What is Paging in OS?
Paging in OS is a dynamic and flexible technique that can load the processes in the memory partitions more optimally. The basic idea behind paging is to divide the process into pages so we can store these pages in the memory at different holes(partitions) and use these holes efficiently.
In a paged memory system, the physical memory is divided into fixed-size pages, typically 4KB or 8KB in size. Likewise, the logical memory is divided into the same-sized blocks called page frames. The mapping between logical pages and physical pages is maintained in a data structure called the page table.
Define Paging in OS
The paging in OS is used to support non-contiguous memory allocation. Secondary memory will be divided into fixed-sized partitions of equal size, and each of these is called a page. Similarly, the main memory is divided into equal fixed-size partitions; each called a frame.
Download Formulas for GATE Computer Science Engineering – Operating Systems
Types of Paging in OS
In operating systems, paging is a memory management technique used to organize and manage memory in a computer system. There are primarily two types of Paging in OS commonly used in operating systems:
- Fixed-size paging
- Variable-size paging
Both fixed-size paging and variable-size paging have their advantages and trade-offs. Fixed-size paging provides simplicity and ease of management but can lead to internal fragmentation. Variable-size paging reduces fragmentation but requires more complex data structures and management algorithms.
Fixed-size Paging in Operating System
In fixed-size paging, the memory is divided into fixed-sized blocks or pages. Each page has a fixed size, typically a power of 2 (e.g., 4KB or 8KB). The entire logical address space of a process is divided into pages of the same size. This approach simplifies memory management, as each page can be easily allocated or deallocated. However, it can lead to internal fragmentation if the memory allocated to a process is not fully utilized.
Under fixed-size Paging in OS, the logical address space is divided into pages, and the physical memory is divided into frames of the same size. The page table maps logical pages to physical frames, allowing for efficient memory access and management.
Variable-size Paging in Operating System
In variable-size paging, the memory is divided into variable-sized blocks or pages. The size of each page is not fixed and can vary depending on the memory requirements of the process. Variable-size Paging in OS aims to reduce internal fragmentation by allocating memory in smaller chunks based on the actual memory needs of a process. This approach helps in more efficient memory utilization.
Variable-size paging requires maintaining additional data structures, such as segment tables or page tables with variable-size entries, to map logical addresses to physical frames. These data structures store information about the size and location of each page, allowing for flexible memory allocation.
Address Translation in Paging in OS
The address translation in paging in OS is an address space that is the range of valid addresses available in a program or process memory. It is the memory space accessible to a program or process. The memory can be physical or virtual and is used for storing data and executing instructions. The two main types of address space are described below:
- Logical address space
- Physical address space
Download Formulas for GATE Computer Science Engineering – Computer Networks
Characteristics of Paging in Operating System
The characteristics of the paging in OS(operating system) is that there is no external fragmentation by assuming the size of the main memory is in powers of 2. Processes can use all frames in the physical or main memory.
Paging in OS(operating system), the internal fragmentation may occur only on the last page of a process. The physical memory used by a process is no longer contiguous (non-contiguous). The logical memory of a process is still contiguous.
Demand Paging in OS
Demand paging is a memory management scheme where pages are brought into memory only when they are demanded by the running process, reducing memory wastage and improving overall system performance.
When a page that is not present in memory is accessed, a page fault occurs, prompting the operating system to fetch the required page from secondary storage into memory. This approach allows for more efficient memory utilization as only the necessary pages are loaded, reducing initial memory overhead and allowing for larger program sizes to be accommodated.
Important Points for Paging in Operating System (OS)
The hardware defines the page size in paging in OS. All the frames and pages in the memory are of the same size. Some of the important points for the paging in OS(operating system) are as follows:
- Whenever the process is created, paging in OS will be applied to the process, and a page table will be created. The base address of the page table will be stored in the PCB.
- Paging in OS is for every process, and every process will have its own page table.
- Page Table of the processes will be stored in the main memory.
- There is no external fragmentation in the paging in OS because the page size is the same as the frame size.
- The internal fragmentation exists on the last page, and internal fragmentation in the paging in OS is considered, where P is the page size.
- Maintaining the page table is considered an overhead (burden) for the system.
Paging in OS Diagram
The below diagram explains the technique of mapping a logical address to a physical address in paging in OS(operating system): 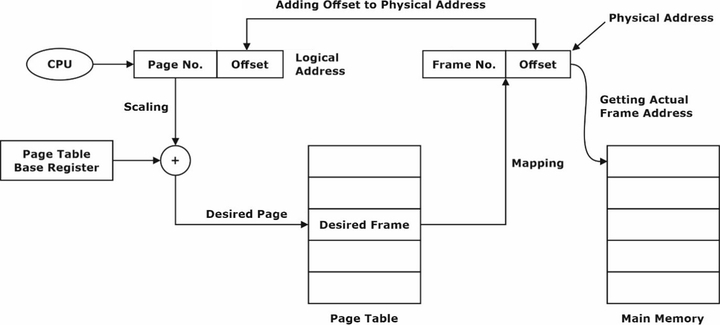
In the above diagram of the translation of logical to a physical address in paging in the operating system as the CPU generates a logical address containing the page number and offset. Then, corresponding to the page number, we check the frame number in which it is stored from the page table. The frame number is then added with the offset value to get the physical address, and then the memory is accessed with it.
Benefits of Paging in OS
Check out various benefits of Paging in Operating system:
- Increased Memory Utilization: Paging in OS enables efficient utilization of physical memory by allocating memory in smaller fixed-size chunks. This allows the operating system to allocate memory to processes on-demand, rather than reserving a continuous block of memory for each process. As a result, multiple processes can share the available physical memory effectively.
- Simplified Memory Management: Paging in OS simplifies memory management by removing the requirement for contiguous memory allocation. Each process is allocated a sequence of non-contiguous pages, which can be scattered throughout the physical memory. This flexibility enables efficient memory allocation and deallocation, making it easier for the operating system to manage available memory resources.
- Memory Protection: Paging in OS provides an additional layer of memory protection. Each page can be marked as read-only, read-write, or not accessible, preventing unauthorized access to memory regions. This helps in isolating processes from each other, enhancing system security and stability.
- Virtual Memory: Paging in OS forms the foundation for virtual memory systems. By using paging, the operating system can provide each process with a virtual address space that is larger than the available physical memory. Virtual memory allows the operating system to transparently swap pages in and out of physical memory to disk, enabling efficient memory usage even when the physical memory is limited.
Page Replacement Algorithms
When a process requests a page that is not present in physical memory, a page fault occurs. The operating system needs to determine which page to evict from physical memory to make space for the requested page. Various page replacement algorithms, such as FIFO (First-In-First-Out), LRU (Least Recently Used), and Optimal, are used to select the victim page for eviction. These algorithms aim to minimize the number of page faults and optimize the overall system performance.
Advantage of Paging in Operating System
Paging in OS is a fundamental technique used in modern operating systems to efficiently manage memory resources. By dividing memory into fixed-size pages and mapping virtual addresses to physical addresses, paging provides increased memory utilization, simplified memory management, memory protection, and supports virtual memory systems.
Page replacement algorithms further enhance the efficiency of paging by determining which pages to swap in and out of physical memory. As operating systems continue to evolve, paging remains a vital component in ensuring optimal system performance and resource management.



