- Home/
- Other State Exams (Other State PSC)/
- Article
India-Nepal Relations
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 13th, 2023

India Nepal Relations is having a tough time in the recent period with Redrawing of Political Maps of Nepal, increased Chinese involvement in the Nepal etc. This has increased the importance for the India-Nepal Relations for UPSC IAS Exam. In this article, we are providing you with a detailed analysis of India-Nepal Relations.
Table of content
India-Nepal Relations: Evolution; India-Nepal Treaty 1950; Areas of Cooperation; Contentious Issues; Border Disputes; Way Forward
India and Nepal shares cultural, religious, historical as well as geographical ties. The Grand Himalayas connect both the countries together. With Nepal being a landlocked country India provides a major route for trade and transport to Nepal. Both countries share an open border with each other. It’s said that India and Nepal share the “Roti-Beti Rishta” with each other. The history can be traced back to the Anglo-Nepalese War (1814-1816) which ended with the treaty of Sagauli. India has played a great role since the signing of the India-Nepal Peace and Friendship Treaty in the 1950s for the development and peace of the region. Both countries have a rich exchange of Diaspora and cultural linkages, as Nepal being the single most Hindu majority country. But in recent times there have arisen some tensions among the two countries, let us analyse the issue in detail.
Evolution Of India-Nepal Relations
- Till 1951 Nepal was ruled by the Ranas. In 1951 a political deal between King Tribhuvan and Pandit Nehru led to the establishment of Monarchy and end of the rule of Rana.
- In 1959 a Constitution was adopted by King Mahindra which established Constitutional monarchy and multiparty democracy in the country. This constitution was merely a figurehead as most of the powers were still in the hand of the king.
- After the Royal Massacre of 2001, King Gyanendra came to power. His period was marked by the rise in violence by Maoists and civil movements.
- India was threatened by the rise of Maoist as it might have repercussions for the safety of Indian borders.
- In April 2006, a Jan Andolan led to the end of Monarchy and in November 2006 a Comprehensive Peace Agreement was signed between Maoist and various Political parties to pave the way for the elections.
- Finally, on 24th May 2008 Shah dynasty come to an end and Nepal became Republic after 240 years of Monarchical rule.
India Nepal Treaty of 1950
- This was signed on the backdrop of the invasion of Tibet by Chinese forces in 1950.
- It was a deal for mutual peace and friendship, wherein India provided support in terms of security to Nepal.
- This treaty grant Rights to Indian and Nepalese people to work, reside and even obtain citizenship in each others territory.
Areas Of cooperation-
- Economic Relations–
- India is Nepal’s largest trading partner and the largest source of foreign investment. T
- here are several hydroelectricity projects running between Nepal and India like Kosi-gandaki, Arun-3 and Pancheshwar Multipurpose dam projects etc.
- There is large Diaspora of Nepal In India, almost 80 lakh people of Nepal works in India and thus serve as a major source of remittances for Nepal.
- Also, large numbers of Indians also work in Nepal.
- Both countries have a free trade agreement with each other.
- Cultural Relations–
- Both countries share cultural ties, in terms of having a large number of Hindu population. Almost 80% of Nepal’s population is Hindu.
- There is regular movement of people for pilgrimage purposes between India and Nepal.
- The bordering areas of Indian states of U.P., Bihar and Uttrakhand have a lot of cultural similarities with those of Nepal.
- For centuries scholars from Nepal visits India Universities specially Banaras Hindu University.
- Education Related Relations–
- India provides support to students of Nepal with various scholarships for University education.
- Also, several government services of India are open to Nepal’s citizens.
- Security Relations:
- The Ghurkha regiment of India consists of recruits from Nepal.
- Also as per the Indo-Nepal Friendship treaty of 1950, India provides security assistance to Nepal in terms of arms and ammunitions.
- Other Areas of Cooperation–
- India and Nepal cooperate in terms of Information technology, telemedicine, biodiversity conservation and healthcare.
- They also share a common platform of BIMSTEC and SAARC.
- There are also various rail-link project and highway connecting projects are going on between two countries.
Issues between India and Nepal
- Border dispute:
- India and Nepal have border dispute at two regions over an 1800 km long border:
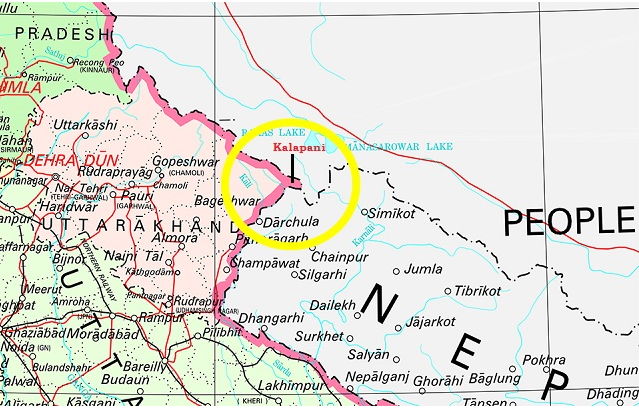
- Kalapani (consisting of Kalapani, Lipulekh and Limpiyadhura):
- Nepal considers it as part of Darchula district of Nepal. This spot specially Lipulekh pass lies on tri-junction of India- Nepal and China border and thus have strategic significance. In 2015 China recognised India’s sovereignty over this pass. And recently India has started building a new road on this pass to connect India and China. But Nepal is protesting this construction.
- Recently Nepal has brought a constitutional amendment and changed the map of Nepal (Cartographic Assertion) depicting Kalapni area as a part of Nepal.
-
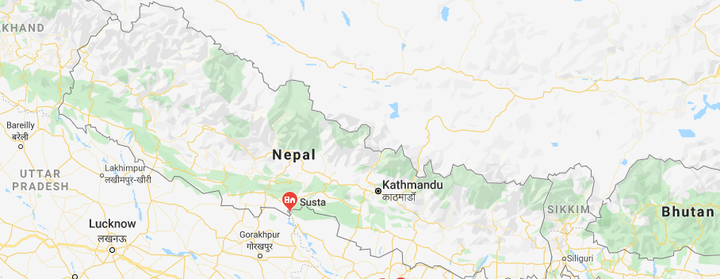
- Susta Area(West Champaran, BIHAR):
- Nepal considers a part of its territory.
- The main reason for this dispute is due to the change of course by the Gandak River.
- Susta Area(West Champaran, BIHAR):
- New Citizenship law–
- Nepal government is also trying to amend citizenship law, which requires an Indian woman marrying a Nepal’s groom to have at least 7 years of residency to attain the citizenship of Nepal.
- The dispute over Madhesis and new Constitution:
- The new constitutions adopted by Nepal’s constituent assembly undermine the rights of Madhesis.
- Madhesis are people of India, who for years have been resided in Nepal.
- The demarcation of territory for political purpose is considered to be inadequate for the representation of the Madhesis.
- India has protested this move and imposed a road blockade in 2015. This severed the ties between the two countries.
- Other Issues:
- Other sources of tensions include the Demonetisation of 2016 and respective problem faced by Nepal’s government in converting the money.
- Delayed implementation of projects by the Indian government is also a cause of contention.
- Further Indian side face problem due to Fake currency and illicit trade arising from Nepal.
Role of China–
- According to many experts, the reason for the current tension between India and Nepal is due to Chinese rising influence in the region as well as in Nepal.
- The PM KP Oli’s nearness with Chinese President and recent deals between both countries has raised concerns for New Delhi.
- China has invested heavily in Nepal in recent years and scholars consider this as a part of China’s Cheque book diplomacy.
- Chinese intrusion may lead to security threats for India as Nepal acts as a buffer state between India and China.
Way Forward:
- The dispute needs to be resolved in a peace full manner. India should refrain from interfering in internal matters of Nepal.
- There is an urgent need to bring changes in the Treaty of Peace and Friendship, 1950 to make it more relevant in the current geopolitical scenario.
- Also, India should focus on timely implementation of projects.
- There should be greater cooperation in the regions of healthcare, education, trade, I.T. sector and other areas.
- India and Nepal should mutually cooperate with each other and enhance their centuries-old ties.
Check Other Important Articles of International Relations:
Are you preparing for State PCS exam,
UPSC & State PCS Green Card (100+ Mock Tests)
Check other links also:


