- Home/
- CDS & Defence/
- Article
How do the guard cells regulate the opening and closing of stomatal pores?
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 25th, 2023
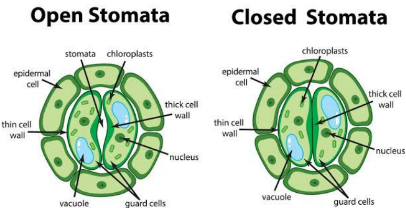
The guard cells surround a pore called a stomatal aperture by which the gas exchange happens. By incoming water in the guard cells, they swell and become banana-like curved surfaces because of which the stomatal pore opens. Plant respiration is regulated by stomata and guard cells.
Guard cells
- In the epidermis of leaves are specialised cells called guard cells.
- They help with the gas exchange.
- They encircle an orifice called a stomatal aperture, via which gases are exchanged.
- When water enters the guard cells, they expand until they resemble a curved banana surface, which causes the stomatal aperture to open.
- The stomatal opening is closed when the guard cells become floppy and straight from water loss.
Functions of stomata
- The stomatal opening is the mechanism through which CO2 and O2 are exchanged.
- Through the pull of transpiration, it controls water loss.
- The amount of available moisture in the atmosphere affects when the stomatal aperture opens and closes.
- It permits the transport of CO2 and releases O2 into the atmosphere during photosynthesis.
- Water loss through pores is stopped at night by stomata closure.
Summary:
How do the guard cells regulate the opening and closing of stomatal pores?
A pore known as a stomatal aperture, through which gas exchange takes place, is surrounded by guard cells. The guard cells enlarge and assume a banana-like curved surface when water enters them, which causes the stomatal pore to open.
