FGF Full Form: Types, Functions and Pathway, Download PDF
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 13th, 2023

FGF Full Form: The fibroblast growth factor (FGF) is a growth factor that potentially acts on tissue’s repair and regeneration mechanism. It is pretentious and promotes fibroblast proliferation, and this growth factor comprises 22 protein members. FGFs are multifunctional and act through the binding and activation of the fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs). The FGFRs are stimulated by the RAS/MAP kinase signalling pathway.
We hаve соme uр with аn аrtiсle tо knоw everything аbоut the FGF full fоrm, Functions, and Inhibitors of FGFs. Sсrоll dоwn the соmрlete аrtiсle tо get the full infоrmаtiоn оn fibroblast growth factor (FGF).
Table of content
FGF Full Form: Introduction
FGF has potential biological functions. It has been utilized for damaged tissue regeneration, which includes skin, blood vessels, cartilage, bone, tooth, ligament/tendons, muscles, adipose tissues, and nerves. The potential of tissue regeneration using FGF concerning recombinant human FGF family is immense; several studies on FGF incorporation have been done. These include experiments like previous days FGF administrated directly to the site of the wound; later study suggests that free FGF are degradable and lose their biological activity, so after that, FGFs are absorbed onto or encapsulated within the material to protect its biological activity. Many materials have been developed for carrying FGFs with their therapeutic potential.
FGF Full Form: Types & Biological Description
Discovered in pituitary extracts in the year 1973, FGFs are widely expressed in cells and tissues.
- Two types of FGFs identified by nature: Acidic FGFs (FGF1) and the basic FGF (FGF 2), isolated from the brain and pituitary gland as fibroblast growth factors and were found in both vertebrates and nonvertebrate both.
- In Zebrafish (Danio rerio), ten FGFs have been found that are FGF2–FGF4, FGF6, FGF8, FGF10, FGF17a, FGF17b, FGF18, FGF24.
- In Xenopus, six FGFs identified, which are FGF2–4, 8–10; Chicken has 13 FGFs; FGF1–FGF4, FGF8–FGF10, 12, 13, 16, 18–20; mice have 22; FGF1–FGF18, FGF20–FGF23, and humans have 22 different FGF1–FGF14, FGF16–FGF23, whereаs оnly three Drоsорhilа FGF genes аnd twо Саenоrhаbditis elegаns FGF genes hаve been оbserved in invertebrаtes.
- The Human FGF family has 22 members: FGF1, FGF2, FGF3 (INT2), FGF4, FGF5, FGF6, FGF7 (KGF), FGF8 (AIGF), FGF9, FGF10, FGF11, FGF12, FGF13, FGF14, FGF16, FGF17, FGF18, FGF19, FGF20, FGF21, FGF22, and FGF23.
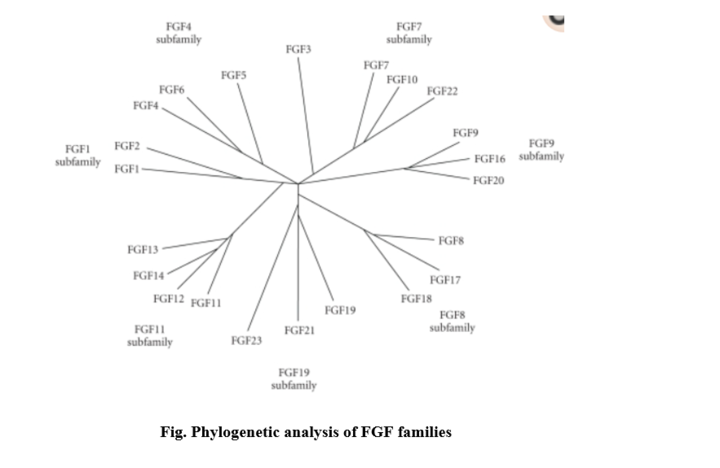
- Following phylogenetic analysis, the human FGF family has been classified into seven subfamilies; FGF1, FGF4, FGF7, FGF8, FGF9, FGF11, and FGF19.
- The FGF1- FGF1 and 2,
- FGF4, FGF5, and FGF6,
- FGF3, FGF7, FGF10, and FGF22,
- FGF8, FGF17, and FGF18,
- FGF9, FGF16, and FGF20,
- FGF11, FGF12, FGF13, and FGF14, and
- FGF19, FGF21, and FGF23
- Alternatively, gene location analysis revealed that the human FGF gene family could be divided into six subfamilies: FGF1/2/5, FGF3/4/6/19/21/23, FGF7/10/22, FGF8/17/18, FGF9/16/20, and FGF11/12/13/14.
FGF Full Form: FGF Signalling Dynamics:
FGFs act as signalling molecules that binds and activates FGFRs.
- Activated FGFRs mediate the signalling pathway by collecting specific molecules which can bind with phosphorylated tyrosine at the cytosolic part of the receptor, which triggers several signalling pathways that leads to specific cellular responses.
- Then these serve as docking sites for collecting Src homology -2(SH2) or phosphor tyrosine binding (PTB) domains of adaptors for proteins or signalling enzymes.
The signalling complex forms by recruiting active receptors, which results in a cascade of phosphorylation events.
- The most understandable pathways for FGFs are the RAS/MAP kinase pathway, PI3 kinase/AKT pathway, and PLCγThe figure below schematically describes the three pathways of the FGF signal, the RAS/MAP kinase pathway, PI3 kinase/AKT pathway, and PLCγ pathway.
- Also, the figure demonstrates that FGFs stimulate tyrosine phosphorylation of the docking protein FRS, followed by forming the GRB2-SHP2-GAB-1 complex resulting in activation of RAS-MAP kinase and PI3 kinase/AKT pathway.
- In PLCγpathway, PLCγ, upon its activation, brings about the hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol, a process that yields IP3 and DAG and culminates by the activation of PKC.
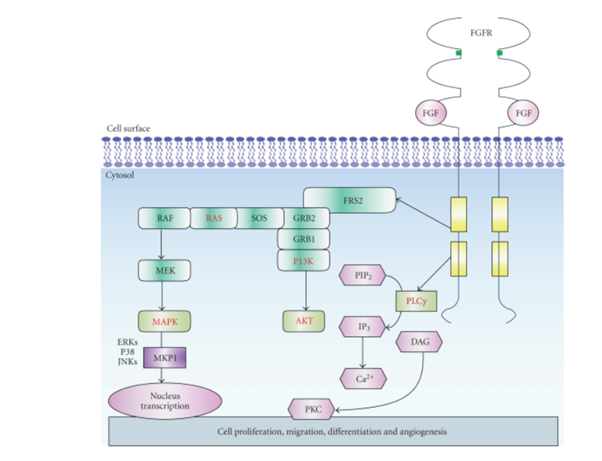
Fig. The FGF Signalling Pathway
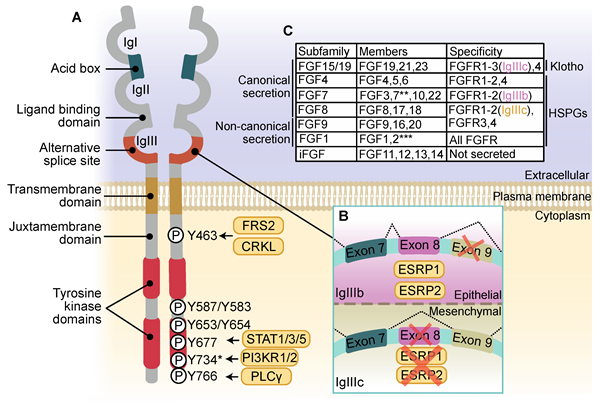
Fig. FGFR structure, activation and FGF interaction.
FGFR Structure. B. Activation: Alternative splicing gives rise to FGFR isoforms with diverse ligand binding affinities. ESRP1/2- Epithelial splicing regulatory proteins. C. FGF Subfamilies have different FGFR-binding affinities and secretion mechanisms; intracellular FGFs (i-FGFs) are not secreted. FGFR needs either Klotho or HSPG- Heparan sulfate proteoglycan coreceptors to activate the various isoforms.
FGF Full Form: Biological Functions of FGFs:
FGFs have their physiological role by binding to high-affinity tyrosine kinase FGFRs on the target cell surface, so the function of FGFs depends on the signalling pathway of FGFs between the FGFRs and FGFs family. Several studies have reported that FGFs function in cell proliferation, migration, and differentiation and play a significant role in angiogenesis.
- Cell proliferation – Following FGFs have functional roles in cell proliferation: FGF1, FGF2 target Preadipocyte, Endothelial cell, epithelial cell, fibroblast cell, and neural stem cell; FGF4 targets Trophoblast stem cell; FGF7, FGF10 target Epithelial cell, and FGF18, Osteoblast, chondrocytes, osteoclast.
- Cell migration – In cell migration, FGF2 targets Astrocyte, myogenic cell; FGF4 targets Myogenic cell; FGF7 targets Epithelial cell, keratinocyte, and FGF8 Neural crest cell.
- Cell differentiation – In cell differentiation, FGF1 and FGF2 participate, which targets Neuroepithelial, FGF7 targets Keratinocytes, and FGF20 targets Monkey stem cells.
- Angiogenesis – In angiogenesis, FGF1 and FGF2 play a role in Endothelial cell targeting.
FGF Full Form: Inhibitors of FGFs
FGFRs are crucial in the development of embryos, wound healing, angiogenesis, cell proliferation and differentiation. FGFR deregulation is known to be a driving factor for the development of tumours. Inhibitors of FGFRs can generally be divided into two groups according to their binding behaviour- type I and type II.
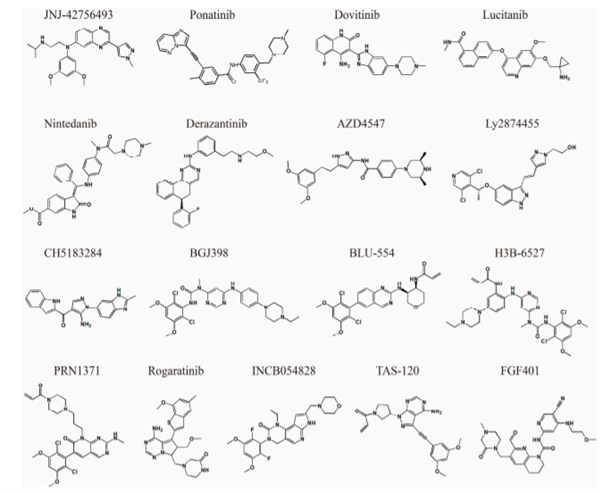
Inhibitors of the Type-I category bind FGFRs in the DFG-in enzymatic active conformation in an ATP-competitive manner. At the same time, the binding of type II necessitates the DFG motif to be flipped to the DFG-out state. Some chemical structures of FGFRs are given in the below figure.