Difference Between IPv4 and IPv6
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 25th, 2023

Difference between IPv4 and IPv6: The IP address is the numeric address. It is an identifier for a device on a network or computer. Every device has to have an IP address for communication purposes. The IP address consists of two parts- the network and host parts. The IP address is of two types:
- IPv4
- IPv6
The basic difference between IPv6 and IPv4 is the size of the address, as IPv6 is 128 bits, whereas the IPv4 is 32 bits in size. The IPv6 is the next generation of IP addresses.
Table of content
What is IP Address?
IP(Internet protocol) is a unique identifier assigned to each device connected to a computer network. Computers use IP addresses to communicate with each other over the internet and on other networks.
The Internet Protocol is a set of rules for communication over the internet, such as streaming video, connecting to a website or sending mail. The task of IP is to deliver the packet from the source host to the destination host solely depending on the IP address in the packet header.
What is IPv4?
Before knowing the difference between IPv4 and IPv6 first, we understand IPv4. IPv4 is the fourth version of the internet protocol. IPv4 is the current version(not for long) of IP addresses. The IPv4 is 32 bits numeric address written as four numbers separated by a dot(.). Computers and networks do not read the IP addresses in this standard numeric format. They can understand numbers in binary format only as:
66 . 94 . 29 . 13 in decimal
01000010 . 01011110 . 00011101 . 00001101 in binary format
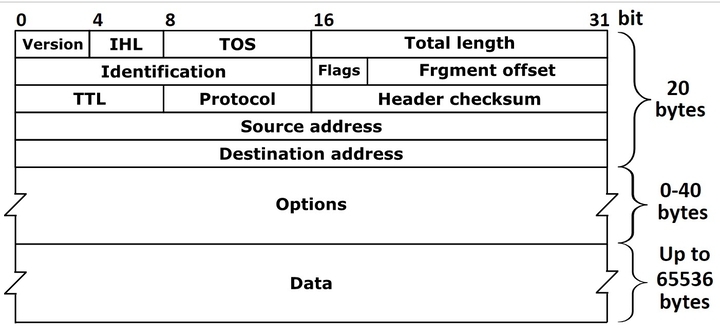
The IPv4 has a header size of 20 to 60 bytes. Whenever the device accesses the internet, it assigns a unique numerical IP address, as shown above.
The structure of IPv4(Internet Protocol version 4) is as follows:
What is IPv6?
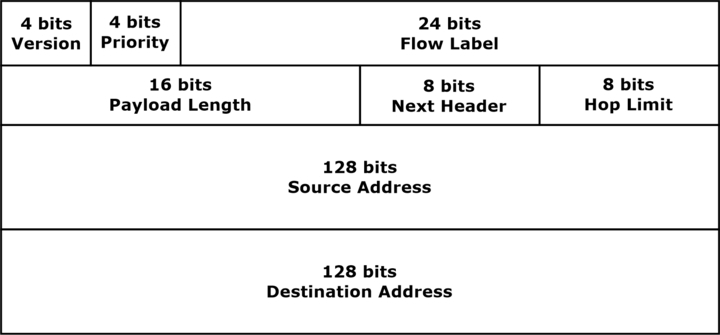
Before knowing the difference between IPv4 and IPv6, let us understand IPv6. IPv6 is the next generation of IP addresses. The IPv6 is the internet layer protocol, and it is a version sixth of the internet protocol. The IPv6 is of 128 hexadecimal addresses. The IPv6 address has various parts: the global prefix, subnet ID, and interface ID. The IPv6 is better than the IPv4 in terms of complexity and efficiency.
Global Unicast 2001:0db8:0000:0000:a111:b2222:c333:abcd
The structure of IPv6(Internet Protocol version 6) is as follows:
Difference Between IPv4 and IPv6
The table shows the difference between the Ipv4 and IPv6. In this table, the difference between IPv4 and IPv6 is shown based on the length, the number of unique IP addresses, the range of IP address etc.
|
IPv4 |
IPv6 |
|
The length of IPv4 is 32 bit. |
The length of IPv6 is 128 bits. |
|
In IPv4, around 4 billion unique IP addresses are generated(232). |
In IPv6, around 340 trillion unique IP addresses are generated(2128). |
|
The range of IPv4 address is 0 to 255. For example, 172.253.45.255 |
The range of IPv6 address is 0 to FFFF(65536). For example: 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334 |
|
The IPv4 address consists of 4 octets each of 8 bits. |
The IPv6 address consists of 8 octets each of 16 bits. |
|
IPv4 is a numeric address separated by a dot(.). |
IPv6 is an alphanumeric number separated by a colon(:). |
|
IPv4 is classified into five classes. |
IPv6 does not have any class. |
|
In IPv4, fragmentation is done at the sender and forward routers. |
In IPv6, fragmentation is done on the sender-side only. |
|
In IPv4, the header size ranges from 20 to 60 bytes. |
In IPv6, the header size is fixed of 40 bytes. |
BYJU’s Exam Prep Online Classroom Program
Thanks
#DreamStriveSucceed


