Combinational and Sequential Difference
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 25th, 2023

The major difference between combinational and sequential circuits is that the combinational circuits have outputs that are dependent only on the present inputs. In contrast, sequential circuits have a series of inputs and outputs and the output of the sequential circuit depends both on the present inputs and the previous outputs. Both circuits are the major components of digital electronics.
Difference between Combinational and Sequential Circuits PDF
Combinational and Sequential Circuits have their own functionalities which are different from each other. We will be discussing the difference between combinational and sequential circuits after discussing the roles and responsibilities of each one individually. Here, we will discuss the basic differences between combinational and sequential circuits, after that, we will dive into each one individually for a brief introduction.
Table of content
Difference Between Combinational and Sequential Circuits
Combinational and sequential circuits are the most commonly utilized electric circuits in digital electronics. Combinational and Sequential Circuits are two main categories of circuits identified in digital electronics, one of which is time-independent and the other time-dependent. It is an important part of the GATE ECE syllabus.
Key Differences Between Combinational and Sequential Circuits
|
Metrics/ Parameters |
Combinational Circuit |
Sequential Circuit |
|
Usage of memory or Storage area |
Combinational Circuit does not require any memory element to store the output. |
Sequential Circuit requires a memory element to store the previous state output. |
|
Feedback |
It requires no feedback for generating the next output. |
Sequential Circuit requires feedback as it relies on the previous output/feedback and the current input. |
|
Speed |
Combinational Circuit performs faster in comparison with sequential circuits. |
Its performance is slow because it uses memory elements. |
|
Elementary blocks |
It uses logic gates as an elementary block. |
Sequential Circuit uses flip-flops as elementary blocks. |
|
Complexity |
Combinational Circuit is easy to use and handle. |
It is complex to use and handle in comparison to combinational circuits. |
|
Example |
Encoder, Decoder, Multiplexer, etc. |
Flip-flops and Counters. |
What is a Combinational circuit?
A combinational circuit is one in which we combine the various different gates to form a circuit. The output of the combinational circuit is determined by the present inputs, regardless of the previous inputs.
We have a variety of combinational circuits available to us for performing a variety of tasks such as Adder, Subtractor, Multiplexer, De-multiplexer, Encoder, Decoder, etc.

Characteristics of a Combinational Circuit
Having known the definition of combinational circuits and their functionalities, let us now discuss the characteristics of the combinational circuit. Following are the characteristics:
- The Combinational circuits do not consist of any memory element.
- At any point in time, the output only depends on the present inputs
- There can be an “n” number of inputs and an “m” number of outputs possible for a combinational circuit where n and m are integers.
What is a Sequential Circuit?
In simple language a combinational circuit with a memory element is a sequential circuit, this is the most basic difference between combinational and sequential circuits. It is a special circuit that has a sequence of inputs and outputs. Unlike combinational circuits, the output depends on the present inputs and previous outputs.
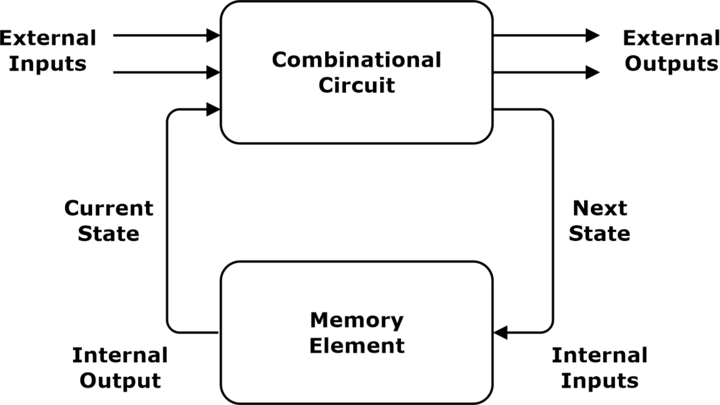
Types of Sequential Circuits
Sequential circuits can be further divided into two types based on clock signal usage. These circuits are widely used in frequency division, pulse counting and finding the mod of the circuit, etc. Following are the two types:
- Asynchronous sequential circuits: They do not use the clock signals instead they make use of the pulses. The un-clocked flip-flops are the memory elements of asynchronous circuits. Though many differences between combinational and sequential circuits the asynchronous sequential circuits are similar to combinational circuits along with feedback.
- Synchronous Sequential circuits: They make use of clock signals and synchronize the memory element’s states with the clock signals. The output is stored in the memory elements called latches or flip-flops (Bi-stable multivibrator).
Differences in Operation between Combinational and Sequential Circuits
Combinational and sequential circuits operate differently from each other. Here are some key differences in their operations:
| Operation | Combinational Circuit | Sequential Circuit |
|---|---|---|
| Logic Operation | Performs logical operations on inputs only and generates outputs based on the current input values. | Uses the current input values and the circuit’s previous state to generate output values. |
| Feedback | No feedback. | Has feedback, meaning that the output is fed back as input. |
| Timing | No timing considerations. | Has timing considerations, as the output depends on the current state of the circuit, which takes time to change. |
| Design | Easier to design. | More difficult to design. |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Combinational and Sequential Circuits
Here are some advantages and disadvantages of combinational and sequential circuits:
| Advantages | Disadvantages | |
|---|---|---|
| Combinational Circuits | Simplicity, high speed, low cost, low power consumption | Lack of memory, limited functionality, susceptibility to glitches |
| Sequential Circuits | Memory, flexibility, complexity, reliability | Complexity, slower speed, higher cost, higher power consumption, potential for timing issues |
Check out:


