Degree of Static Indeterminacy
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 25th, 2023

In civil engineering design structures, almost all structures are stable; they may be determinate or indeterminate. A Structure can be analyzed with the help of equilibrium and compatibility equations. Degree of static indeterminacy is a term that is associated with indeterminate structures. Structures that need only equilibrium equations for their analysis are called determinate structures, and structures that need both equilibrium equations and compatibility equations are called indeterminate structures.
The degree of indeterminacy of a structural member or whole structure can be of two types. It may be Static indeterminacy or Kinematic indeterminacy. The degree of static indeterminacy can be defined as the number of redundant forces present in the structure. These redundant forces must be independent of each other. Redundant forces can be defined as those that can not be calculated with the help of equilibrium equations.
Download Formulas for GATE Civil Engineering – Structural Analysis
Table of content
What is Degree of Static Indeterminacy?
We need to know about the support reactions and equilibrium equations to calculate the degree of static indeterminacy.
Degree of Static Indeterminacy Definition
The degree of static indeterminacy is calculated by subtracting the available equilibrium equations from the total number of unknown reactions present in the structure. It also depends upon the direction of loading on the beam. So, it can be said that the degree of static determinacy will be different for the inclined loading and vertical loading acting over the same beam.
Degree of Static Indeterminacy Formula
In the case of inclined loading on the beam, three equilibrium equations will be available. Still, in the case of pure vertical loading, only two numbers of equilibrium equations will be available. As in the case of vertical loading, there will not be any signs of horizontal equilibrium. Hence the value of static determinacy changes in both cases. If we talk about a general formula for calculating the static determinacy, it will be
Ds=Dse+Dsi; and Dse = R-3 (for the 2D structure)
Dse=R-6 (for the 3D structure)
where R is the number of total reactions.
Download Formulas for GATE Civil Engineering – Environmental Engineering
Degree of Static Indeterminacy of Beams
Any structure can calculate static indeterminacy by adding external and internal static indeterminacy. But in the case of beams, internal static indeterminacy is equal to zero. Hence, the degree of static indeterminacy of beams is equal to the external static indeterminacy only, which can be calculated by the sum of all the redundant reactions in the beam.
Degree of Static Indeterminacy of a Fixed Beam
In the case of a fixed beam, there will be fixed supports at both ends of the beam. If a fixed beam has an inclined loading over it, then the degree of static indeterminacy will be 6 – 3 = 3. But if a fixed beam has only vertical loading over it, then, in this case, the degree of static indeterminacy will be 4 – 2 = 2.
Degree of Static Indeterminacy of Propped Cantilever
The degree of static indeterminacy of a propped cantilever is the extra number of reactions available than the equilibrium equations in the beam. Equilibrium equations in the beam will depend upon whether the loading will be inclined or purely vertical. In the case of inclined loading on the beam, there will be three equilibrium equations. Still, in the case of vertical loading, there will be only two equilibrium equations because, in this case, the equation for horizontal equilibrium is insignificant.
Download Formulas for GATE Civil Engineering – Irrigation & Hydrology
Degree of Static Indeterminacy of Propped Cantilever Beam having Vertical loading
In the case of a propped cantilever beam, there is fixed support at one end of the beam, and a hinge supports the other end of this beam. So the total number of reactions for such a beam is 2+1=3 in the case of vertical loading. And there are only two numbers of equilibrium equations available in this beam condition. Hence, the degree of static determinacy will be 3 – 2 = 1.
Degree of Static Indeterminacy in Two-hinged Arch
For the calculation of the degree of static indeterminacy in the two hinged arches, first, we need to understand the arch. An arch is a structure that can support vertical loading as well as inclined loading. Arch may be classified as two hinged arch and three hinged arches based on the number of hinges available in the structure. In the case of two hinged arches, hinges are provided only on supports. Still, in three hinged arch structures, an additional hinge is provided in between the arch’s span, making it a determinate structure by inducing one more equilibrium equation for the structure.
So, in the case of two hinged arches, there are four numbers of support reactions, with each support consisting of two reactions, one in the horizontal direction and the other in the vertical direction. And indeterminacy can be calculated by subtracting the equilibrium equations from the total number of support reactions. Hence, the degree of static indeterminacy in two hinged arches equals 4 – 3 = 1.
Degree of Static Indeterminacy of Cantilever Beam
For the calculation of the degree of static indeterminacy of the cantilever beam, first, we need to understand the support reactions associated with the cantilever beam. The cantilever beam is a beam that has fixed support at one end, and the other end of this beam is free. So, the total number of support reactions will equal three when it is subjected to inclined loading. And there will be only two support reactions when it is subjected to vertical loading across its span.
So, a cantilever beam’s degree of static indeterminacy will be 3 – 3 = 0; when it is subjected to inclined loading on its span. And it will be equal to 2 – 2 = 0; when it is subjected to pure vertical loading on its whole span.
Degree of Static Indeterminacy of a Rigid Jointed Plane Frame
First, we need to understand the support reactions and joint structure associated with the frame to calculate the degree of static indeterminacy of a rigid joint plane frame. A rigid joint plane frame is a framed structure in which all the joints are rigidly connected. So, the movement of members occurred simultaneously. Here an example of a rigid jointed plane frame is shown below.
Degree of Static Indeterminacy Solved Question
Question: What will be the degree of indeterminacy of the frame showing the figure
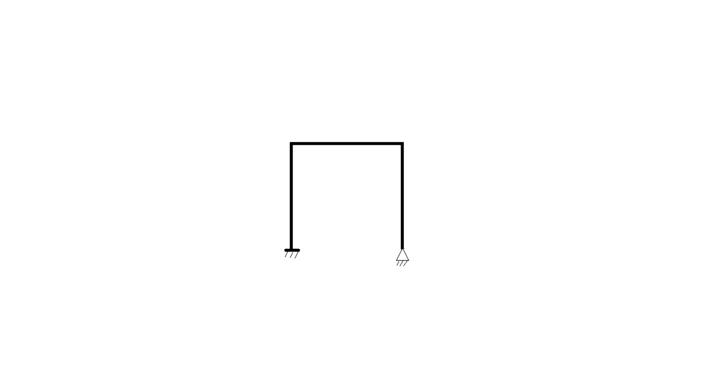
Solution:
Here, in this framed structure
Total number of members m=3, Total number of joints j=4, Total number of reactions r=3+2=5.
So the degree of static indeterminacy DS=DSe+DSi
And, DSe=R-3=5-3=2, DSi=0.
So, DS=2
Related Important Links
|
Important GATE Topics |
|
| Lan Full Form | Propped Cantilever Beam |
| Torsional Force | POP Full Form |
| RTC Full Form | Fcfs Scheduling Full Form |
| Types Of Loads | E-Commerce Mcq |
| Laser Full Form | Rankine Formula |


