- Home/
- GATE ELECTRONICS/
- GATE EC/
- Article
Cut Set Matrix Concept of Electric Circuit
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 25th, 2023

A cut set matrix is a minimal collection of interconnected graph branches that, when removed, cause the graph to be divided into precisely two sections. Graph theory is the graphical representation of any electric circuit. Complex circuits can be easily analyzed by converting them into network graphs. From the network graphs, the incidence matrix, fundamental loop matrix or tie-set matrix, and cut-set matrix can be determined.
The cut-set matrix is used to solve any electric circuit or network problem by utilizing their equivalent graphs. The article elaborates on the cut set matrix, the procedure for finding this matrix, the properties of the cut-set matrix, and its equivalent KCL and KVL equations in matrix form.
Table of content
What is Cut Set Matrix?
A cut-set is a minimum set of elements that when removed, separates the graph into two groups of nodes. A cut-set is a minimum collection of branches in a connected graph such that removing these branches decreases the graph’s rank by one.
Cut-Set Matrix Definition
A fundamental cut-set contains only one branch of the tree. Therefore, for a given tree, the number of fundamental cut-sets is equal to the number of twigs present. Cut-set matrix is represented by QC and is defined as a rectangular matrix whose rows correspond to cut-sets and columns correspond to the branches of a graph. The cut-set matrix can have the following values:
[Qij] = 1; if branch j is in the cut-set i and orientations coincide
[Qij] = -1; if branch j is in the cut-set i and orientations do not coincide
[Qij] = 0; if branch j is not in the cut-set i
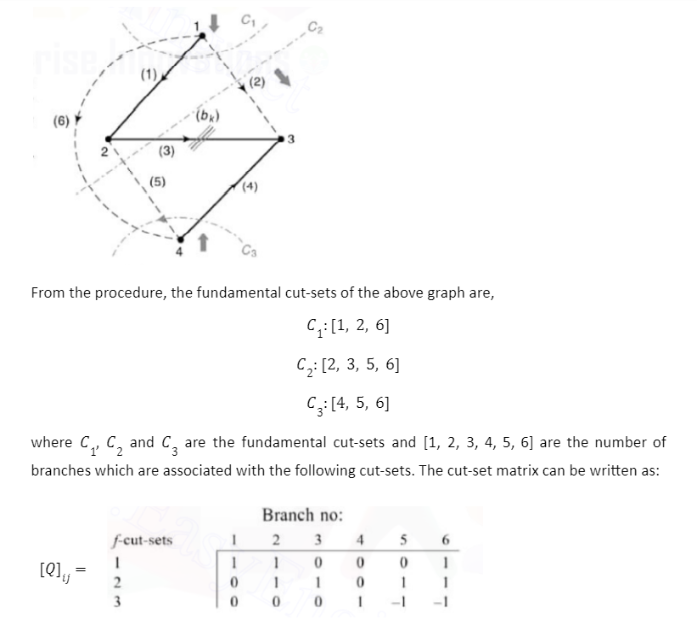
Procedure to Find Fundamental Cut-Sets
To find the fundamental cut-sets and write an equivalent cut-set matrix, firstly select a tree of the graph. Fundamental cut-sets are denoted by Cn. Consider the graph shown below illustrating the fundamental cut-sets. The procedure to find the fundamental cut-sets is:
- Select one of the possible trees of the given graph.
- Focus on one particular tree branch at once.
- Check whether removing the focused branch from the tree disconnects the tree into two separate parts.
- All the links which go from one part of this disconnected tree to the other, together with the focused branch form one fundamental cut-set.
- Repeat the same for other tree branches as well to get the fundamental cut-sets.
The number of fundamental cut-sets will always be equal to the number of twigs present in the tree.
Properties of Cut-Set Matrix
The procedure to find the fundamental cut-sets is already discussed. There are some properties of the cut set matrix that need to be fulfilled for the validation of these fundamental cut-sets. These properties are:
- A fundamental cut-set can contain only one branch of a tree and the remaining elements are links.
- A cut-set divides the tree into two separate parts after removing the tree branch of that particular cut-set.
- Each branch of the cut-set has one of its terminal’s incidents at a node in one subset of the tree and its other terminal at a node in the other part of the tree.
- The direction of the cut-set is chosen the same as the direction of the branch current of the tree in that cut-set.
Cut-Set Matrix and KVL
With the cut-set matrix, the branch voltages can be expressed in terms of the tree-branch voltages. A cut-sets consists of only one branch of the tree together with any links which must be cut to divide the tree into two parts. Consider the following graph along with the tree as shown below:
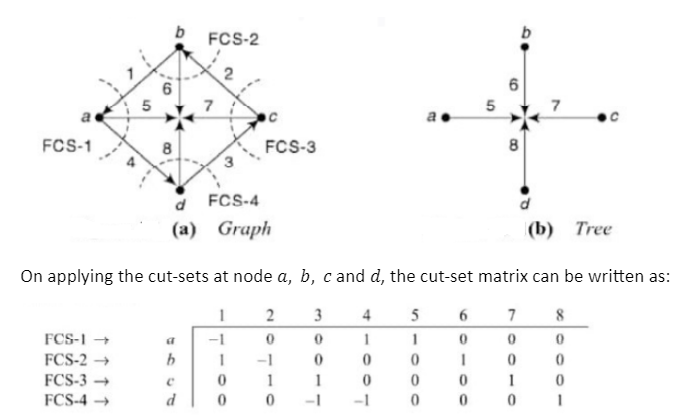
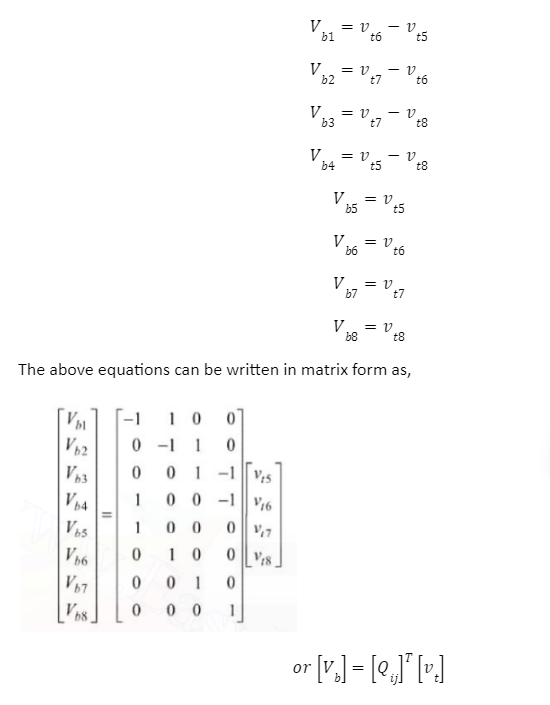
Let vt5, vt6, vt7, and vt8 be the tree branch voltages and Vb1, Vb2, Vb3, Vb4, Vb5, Vb6, Vb7, and Vb8 be the branch voltages then,
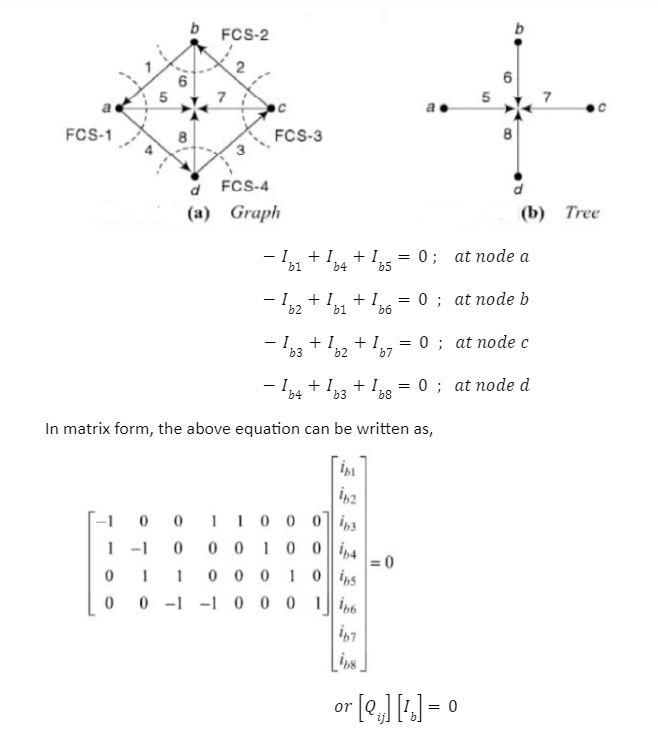
Cut-Set Matrix and KCL
Consider the same graph and tree used in the cut-set matrix and KVL as mentioned below. If Ib1, Ib2, Ib3, Ib4, Ib5, Ib6, Ib7, and Ib8 are the branch currents of respective branches, then, the current at node a, b, c, and d can be obtained by applying KCL as,
| Important Topics for Gate Exam | |
| Brittle Material | Capacitors in Parallel |
| Capacitors in Series | Carnot Cycle |
| Cement Test | Clamping Circuit |
| Clipping Circuit | CMOS Fabrication |
| CMOS Converter | Column Base |


