- Home/
- GATE MECHANICAL/
- GATE ME/
- Article
Constant Acceleration
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 25th, 2023

Whenever an object moves with constant acceleration, its velocity changes at a constant rate. Examining the motion of objects traveling with constant acceleration can help us understand how certain variables change about others. In other words, they provide a link between time, position, velocity, and acceleration.
Constant Acceleration PDF [GATE Notes]
We can use the equations to identify the fourth unknown variable if we know three of these variables. It is worth noting that constant acceleration indicates that instantaneous acceleration (acceleration at any given point) equals average acceleration over some time interval. Let us discuss in detail constant acceleration.
Download Formulas for GATE Mechanical Engineering-Engineering Mechanics
Table of content
Constant Acceleration
Because acceleration is the rate of change in velocity, which is a vector, changes in this number can affect the vector’s magnitude and direction. On the other hand, this lesson will concentrate on magnitude changes; then, the term speed may be used to replace the term velocity. Here, every action will be thought of as being carried out in a straight line. Although acceleration can be zero, positive, or negative, it is frequently misinterpreted as a synonym for speed. This is true when the acceleration for a straight-line motion is positive. A negative acceleration indicates that the item is slowing down, whereas a null acceleration indicates that the speed does not change.
One may become perplexed when learning about continuous acceleration because acceleration relates to change. It is vital to realize, however, that this transformation occurs rapidly. A constant acceleration indicates that the speed changes consistently throughout the movement. One may become perplexed when learning about continuous acceleration because acceleration relates to change. It is vital to realize, however, that this transformation occurs rapidly. A constant acceleration indicates that the speed changes consistently throughout the movement.
Download Formulas for GATE Mechanical Engineering – Strength of Materials
Constant Acceleration Formula
One must first comprehend all the variables in its formula to understand how to calculate constant acceleration.
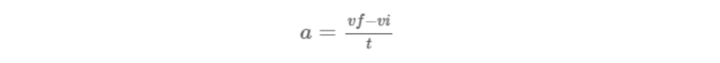
Here,
a = Acceleration
vf = Final Velocity
vi= Initial Velocity
t = Time
We’re all aware that putting our foot down on the accelerator causes an automobile to accelerate. The acceleration of a particle is the rate at which its velocity changes over time. If the particle’s velocity changes at a constant rate, this rate is called constant acceleration.
Constant Acceleration Examples
Some examples of constant acceleration that we come across in our daily lives are as follows:
- A ball is rolling downhill on an inclined plane.
- A package that fell from an aircraft.
- The Moon’s orbiting the Earth.
- A stone fell or dropped from a tower.
- Tennis ball tossed up vertically.
- Water dripping from a shower nozzle.
Download Formulas for GATE Mechanical Engineering – Machine Design
Variable Acceleration
The area under the acceleration time curve reflects the change in velocity if acceleration is a function of time. If acceleration is a displacement function, then the area under the acceleration distance curve equals half the difference in velocities squared.
Get complete information about the GATE exam pattern, cut-off, and all those related things on the BYJUS Exam Prep official youtube channel.



