- Home/
- GATE ELECTRONICS/
- GATE EC/
- Article
Capacitors in Parallel
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 25th, 2023

Capacitors in parallel provide a higher value of equivalent capacitance. Series and parallel combination of capacitors is a powerful tool for reducing circuits. A capacitor stores electrostatic energy in the form of an electric field. The voltage connected across the capacitors in parallel is the same and equal to the supply voltage.
For AC supply, the higher the capacitance, the more amount of time taken by the capacitor for charging and discharging. Capacitors in parallel provide higher equivalent capacitance. The article elaborates on capacitors in parallel, the formula to find the equivalent capacitance of capacitors in parallel, and current and voltages in capacitors in parallel.
Download Formulas for GATE Electronics & Communication Engineering – Control System
Table of content
Define Capacitors in Parallel
A capacitor is a device that stores charge. The equivalent capacitance of capacitors in parallel is the individual sum of all the capacitance connected in parallel. Hence, the net capacitance increases. Multiple capacitors in parallel can be replaced by an equivalent single capacitor.
The capacitance of an equivalent single capacitor is the individual sum of all capacitors in parallel. Hence, the equivalent capacitance increases, and therefore by connecting the capacitors in parallel, the circuit can store more energy.
Download Formulas for GATE Electronics & Communication Engineering – Digital Circuits
Equivalent Capacitance of Capacitors in Parallel
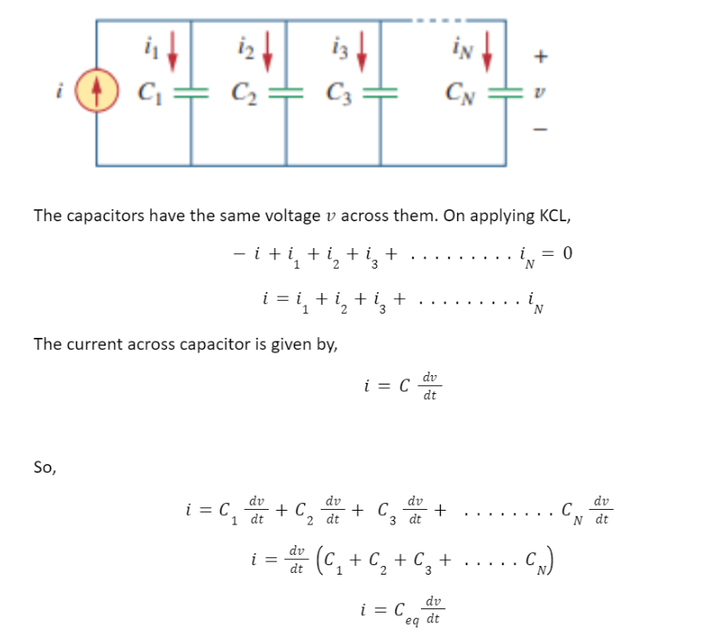
In order to obtain the equivalent capacitance Ceq of N capacitors in parallel, consider the circuit shown below:
The capacitors have the same voltage v across them. On applying KCL,
Where Ceq is the net equivalent capacitance of capacitors in parallel as shown in the circuit below and is given by,
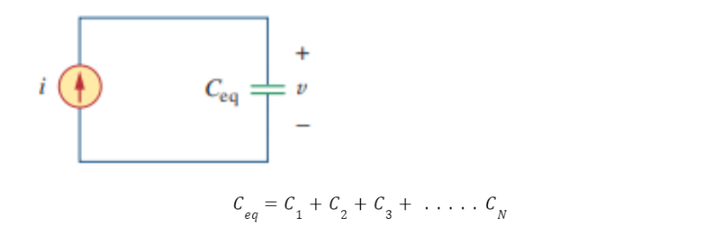
Voltage and Current in Capacitors in Parallel
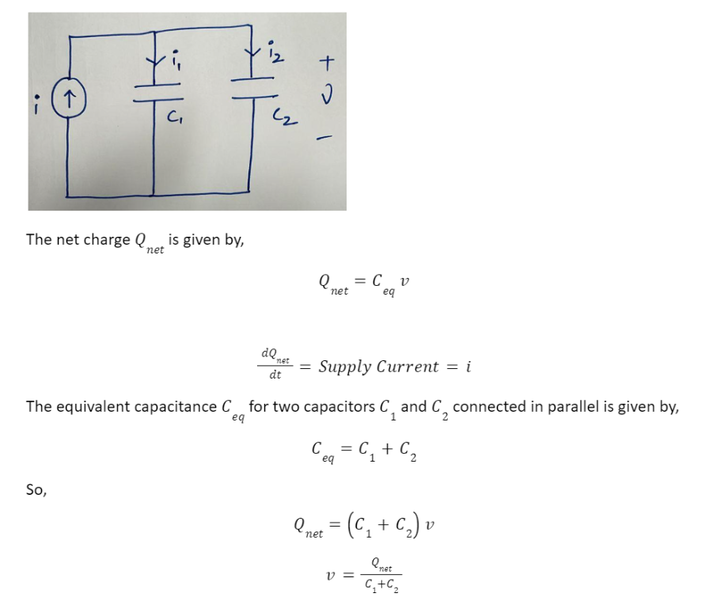
The voltage v across capacitors in parallel is the same and equal to the supply voltage. However, the current has multiple paths to flow so the current divides across the capacitors. Consider two capacitors C1 and C2 connected in parallel as shown below:
The net charge Qnet is given by,
The current across capacitors can be written as,
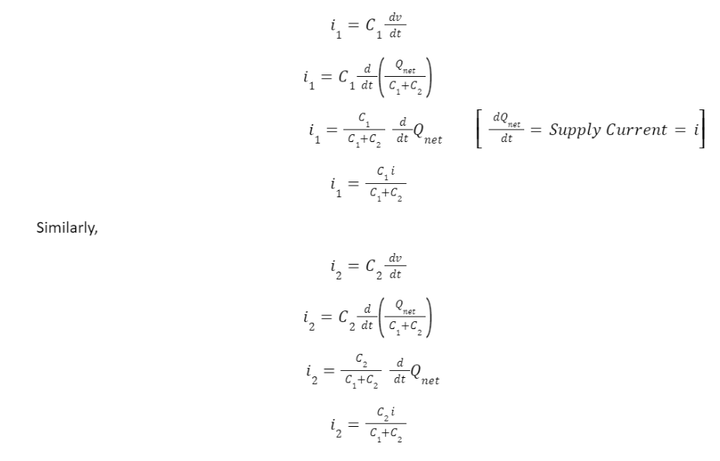
Download Formulas for GATE Electronics & Communication Engineering – Electronic Devices
Capacitors in Parallel Formula
The overall equivalent capacitance of capacitors in parallel is the individual sum of all the capacitance of capacitors. Mathematically it can be written as:
Ceq= C1+ C2+ C3+ . . . . . CN for N parallel connected Capacitors
The voltage across all the capacitors will be the same as they are in parallel, but the current divides across the capacitors.
For two capacitors C1 and C2 connected in parallel, the current across them i1 and i2, respectively, is given by:
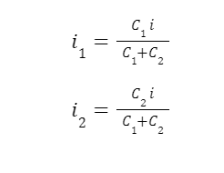
If all the capacitors in parallel have the same value of capacitance, then, the current divides equally among all the capacitors. If N capacitors of equal capacitance are connected in parallel, the current across each capacitor is given by,
in=i/N
where,
- i= total supply current,
- in= current across the nth capacitor


