Basic IP Support Protocols Study Notes for GATE CS and CSE Exams
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 25th, 2023

In this article, we will discuss the fundamental concepts and protocols that form the backbone of modern computer networks. Understanding these protocols is crucial for anyone seeking a solid foundation in networking. IP (Internet Protocol) is a fundamental building block of the Internet, enabling communication between devices across various networks. To facilitate efficient and reliable data transmission, a range of support protocols has been developed to work in conjunction with IP. These protocols provide additional functionalities and services that enhance the overall performance, security, and manageability of IP-based networks.
Throughout this study notes, we will explore key support protocols, including but not limited to Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP), Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP), and Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). Each protocol plays a vital role in maintaining the smooth operation of IP networks, ensuring proper addressing, routing, error detection, and network management. Here, we are providing the complete study notes on the Basic IP Support Protocols for the preparation of the GATE, Computer Science Engineering Exam.
Table of content
What are Basic IP Support Protocols?
Basic IP Support Protocols are essential components of the modern Internet infrastructure that facilitate efficient communication and data transfer across networks. These protocols play a crucial role in establishing and maintaining connections between devices, enabling the seamless exchange of information. Understanding these fundamental protocols is essential for network administrators, engineers, and anyone involved in managing and troubleshooting network connectivity.
IP, or Internet Protocol, serves as the backbone of the Internet, responsible for addressing and routing packets of data between devices. However, the successful transmission of data relies on additional support protocols that address various aspects of network communication. Basic IP Support Protocols encompass a range of protocols that assist in tasks such as host configuration, error detection and correction, and network management.
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is one of the major protocols of the TCP/IP protocol suite. The main goal of Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is to map an IPv4 address (32-bit Logical Address) to its corresponding MAC Address (48-bit Physical Address). Network Applications use IPv4 Addresses to communicate with other devices at the Application Layer. The data link layer deal with the MAC address (48-bit Physical Address) for addressing, and this address (physical address) is configured into the network card of the system permanently.
Note- The main responsibility of ARP is to translate an IP address into a physical address.

Note: ARP determines the hardware address/physical address, also called the Media Access Control (MAC) address, of a host from its well-known IP address.
The important terms associated with ARP are :
- ARP Cache: After resolving the MAC address, the ARP sends it to the source where it stores in a table for future reference. The subsequent communications can use the MAC address from the table
- ARP Cache Timeout: It indicates the time for which the MAC address in the ARP cache can reside
- ARP request: This is nothing but broadcasting a packet over the network to validate whether we came across the destination MAC address or not.
ARP request packet contains:
- The physical address of the sender.
- The IP address of the sender.
- The physical address of the receiver is zero seconds.
- The IP address of the receiver.
Note, that the ARP packet is encapsulated directly into the data link frame.
- ARP response/reply: It is the MAC address response that the source receives from the destination which aids in further communication of the data.
Cases When ARP is Used
- Case-1: The sender is a host and wants to send a packet to another host on the same network.
- Use ARP to find another host’s physical address
- Case-2: The sender is a host and wants to send a packet to another host on another network.
- The sender looks at its routing table.
- Find the IP address of the next hop (router) for this destination.
- Use ARP to find the router’s physical address
- Case-3: the sender is a router and received a datagram destined for a host on another network.
- The router checks its routing table.
- Find the IP address of the next router.
- Use ARP to find the next router’s physical address.
- Case-4: The sender is a router that has received a datagram destined for a host in the same network.
- Use ARP to find this host’s physical address.
NOTE: An ARP request is broadcast, and an ARP response is a Unicast.
What is Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol?
In simple words, DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) can be defined as a set of rules that is responsible for the dynamic configuration and management of hosts in a network. It dynamically assigns an IP address and other network managing parameters to the system so that it can communicate with other devices (IP networks).
- Dynamic – Automatically
- Host – Any computer that is connected to the network
- Configuration – To configure a host means to provide network information(IP address, subnet mask, Gateway address) to a host
- Protocol – Set of rules
Basically, the main role of a DHCP server is to configure a host in a network dynamically.
It is an application layer protocol that provides:
- Subnet Mask (Option 1 – e.g., 255.255.255.0)
- Router Address (Option 3 – e.g., 192.168.1.1)
- DNS Address (Option 6 – e.g., 8.8.8.8)
- Vendor Class Identifier (Option 43 – e.g., ‘unifi’ = 192.168.1.9 ##where unifi = controller)
DHCP is based on a client-server model and based on discovery, offer, request, and ACK.
Here is how the DHCP process works when you go online
- You go on your computer to connect to the Internet.
- The network requests an IP address (this is actually referred to as a DHCP discover message).
- On behalf of your computer’s request, the DHCP server allocates (leases) to your computer an IP address. This is referred to as the DHCP offer message.
- Your computer (remember—you’re the DHCP client) takes the first IP address offer that comes along. It then responds with a DHCP request message that verifies the IP address that’s been offered and accepted.
- DHCP then updates the appropriate network servers with the IP address and other configuration information for your computer.
- Your computer (or whatever network device you’re using) accepts the IP address for the lease term.
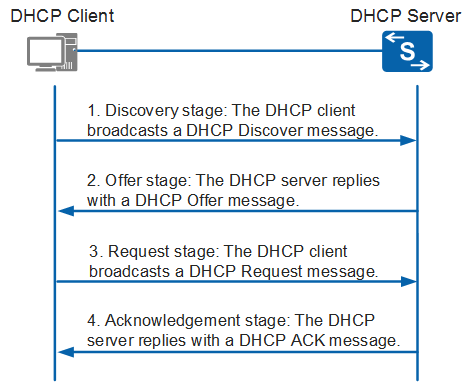
DHCP discover message
This is the first message in the communication process between any client and server. Discovr message is provoked by the client host to discover any available DHCP server/servers in the network. So this message is broadcasted in the network and received by each device of that network in order to determine the DHCP server.
DHCP offer message
This message is sent as a response from the DHCP server to the requesting host in this message specifying the unleased IP address with other TCP configuration information. DHCP offer message is broadcasted by the server.
DHCP request message
When a requesting client gets an offer message, it again acknowledges it by broadcasting a DHCP request message. The client will generate a gratuitous ARP to find whether there is any other host present in the network with the same IP address. If the client gets no reply from the other host, so t means there is no host with the same TCP configuration in the network, and then the message is broadcasted to the server acknowledging the acceptance of the IP address, and a Client ID is also added in DHCP request message.
Note DHCP request message is broadcasted after the ARP request is broadcasted by the host to check whether any other host is not using offered IP address. If there is no reply from any other host, then the client host broadcast the DHCP request message to the server acknowledging the acceptance of the IP address with other TCP/IP Configuration.
DHCP acknowledgment message
A DHCP acknowledgment message is sent in response to the request message received, the DHCP server will make an entry specifying the client ID and then bind the offered IP address with the lease time. Finally, the client will have the IP address provided by the server.
DHCP negative acknowledgment message
Whenever a DHCP server receives a request for an IP address that is invalid so it sends a DHCP Nak (Negative acknowledgment) message to the client. For example -when the server has no unused IP address or the pool is empty, then a DHCP Nak message is sent to the client by the server.
Advantages – The advantages of using DHCP include
- Centralized management of IP addresses
- Ease of adding new clients to a network
- Reuse of IP addresses reduces the total number of IP addresses that are required
- Simple reconfiguration of the IP address space on the DHCP server without needing to reconfigure each client
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) is an Internet layer protocol used by network devices to diagnose network communication issues. Mainly ICMP is used to determine whether data is reaching desired correct destination in a timely manner or not. Generally, ICMP protocol is used on network devices, such as routers, gateway, etc.
What Is ICMP Used For?
IP (Internet Protocol) doesn’t have any inbuilt mechanism for detecting and sending error and control messages. So, IP depends on Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) to provide error control. It is used for error reporting and management-related queries. ICMP is a supporting protocol that is mostly used by networking devices such as routers for sending error messages and operations information.
When two devices are connected over the Internet, the ICMP generates errors to share with the sending device so that any of the data didn’t get to its intended destination.
Source Quench Message
A source quench message is a request to the host(destination) to decrease the traffic rate for message sending. Or in simple words, we can say that when receiving host detects that the traffic rate (rate of sending packets) is too fast, then it sends the source quench message to the source to slow down the message sending speed (rate) so that no packet can be lost.
- ICMP will take the source IP from the discarded packet and informs to source by sending the source quench message. The source will reduce the speed of transmission so that router will be free from congestion.
- When the congestion router is far away from the source the ICMP will send a hop-by-hop source quench message so that every router will reduce the speed of transmission.
Parameter Problem
Whenever the router receives data packets then the calculated header checksum should always be equal to the received header checksum then only the packet is accepted by the router otherwise rejected.
- If there is a mismatch packet will be dropped by the router. ICMP will take the source IP from the discarded packet and informs to source by sending a parameter problem message.
Time Exceeded Message
- When some fragments are lost in a network then the holding fragment by the router will be dropped then ICMP will take the source IP from the discarded packet and informs the source, of discarded datagram due to the time to live field reaches to zero, by sending the time exceeded message.
Destination Un-reachable
- The destination is unreachable and is generated by the host or its inbound gateway to inform the client that the destination is unreachable for some reason.
- There is no necessary condition that only the router gives the ICMP error message some time destination host sends an ICMP error message when any type of failure (link failure, hardware failure, port failure, etc.) happens in the network.
Redirection Message
- Redirect requests data packets be sent on an alternate route. The message informs to a host to update its routing information (to send packets on an alternate route).
- If the host tries to send data through a router R1 and R1 sends data on a router R2 and there is a direct way from the host to R2. Then R1 will send a redirect message to inform the host that there is a best way to the destination directly through R2 available. The host then sends data packets for the destination directly to R2. The router R2 will send the original datagram to the intended destination.
- But if datagram contains the routing information of the packet then this message will not be sent even if another better route is available. As redirected messages should only be sent by the gateways and not by the Internet hosts.
- Whenever a packet is forwarded in the wrong direction later it is redirected in a current direction and then ICMP will send the re-directed message.
Network Address Translation (NAT)
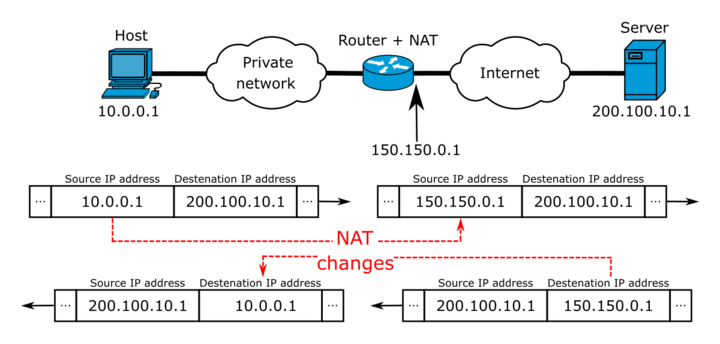
- To access the Internet, one public IP address is needed, but we can use a private IP address in our private network. The idea of NAT is to allow multiple devices to access the Internet through a single public address. To achieve this, the translation of a private IP address to a public IP address is required.
- Network Address Translation (NAT)is a process in which one or more local IP address is translated into one or more Global IP address and vice versa in order to provide Internet access to the local hosts.
- Also, it does the translation of port numbers i.e. masks the port number of the host with another port number, in the packet that will be routed to the destination. It then makes the corresponding entries of IP address and port number in the NAT table. NAT generally operates on a router or firewall.
Network Address Translation (NAT) working
Mostly, Network Address Translation is configured with the border router i.e. the router which has one interface in the local network and one interface in the global network. When a packet travels outside the local (inside) network, then NAT transforms that local (private) IP address into a global (public) IP address. When a packet enters into the local network, the global (public) IP address is changed into a local (private) IP address.
If NAT addresses got finished, i.e., no more address is left in the configuring pool then the packets will be dropped and an Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) host unreachable packet will be sent to the destination.
Advantages of NAT
- NAT conserves legally registered IP addresses.
- It provides privacy as the device’s IP address, sending and receiving the traffic, will be hidden.
- Eliminates address renumbering when a network evolves.
The disadvantage of NAT
- Translation results in switching path delays.
- Certain applications will not function while NAT is enabled.
- Complicates tunneling protocols such as IPsec.
- Also, the router being a network layer device, should not tamper with port numbers(transport layer) but it has to do so because of NAT.



