- Home/
- CDS & Defence/
- Article
An ideal voltage source is one which has – (a) Infinite Internal Resistance (b) Zero Internal Resistance (c) Very High Internal Resistance (d) Very Low Internal Resistance
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 25th, 2023
An ideal voltage source is one that has zero internal resistance. An ideal voltage source (V) in series with internal resistance makes up a usable voltage source (R ). The perfect current source has infinite resistance. Zero conductance is the same as infinite resistance. Thus, the conductance of the ideal current source is zero.
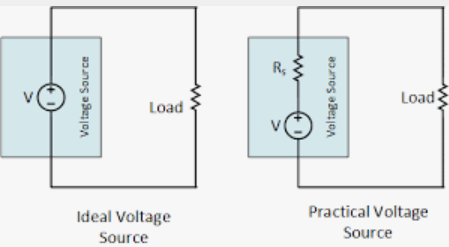
Ideal Voltage Source
The figure can serve as a representation of both an ideal and a real voltage source.
- Practical Current Source: When used in parallel with high resistance or low conductance, a practical current source is the same as an ideal current source.
- It is a voltage generator whose output voltage is always the same regardless of the output current’s value. A circuit component that maintains the desired voltage across its terminals despite the presence of current in those terminals is referred to as an ideal voltage source.
- Regardless of the amount, direction, or total charge given, the ideal voltage source keeps the same voltage difference across its terminals. In the real world, ideal voltage sources don’t exist.
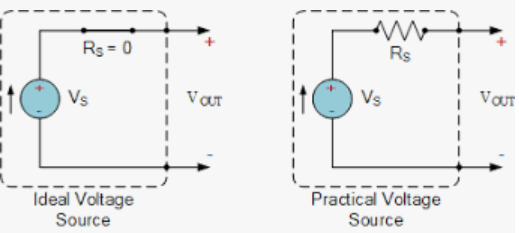
Current sources that are both ideal and realistic are depicted in the image below.
Summary:
An ideal voltage source is one which has – (a) Infinite Internal Resistance (b) Zero Internal Resistance (c) Very High Internal Resistance (d) Very Low Internal Resistance
A voltage source with negligible internal resistance is the ideal one. A usable voltage source is created by connecting an ideal voltage source (V) in series with internal resistance (R).
