ABO Full Form: In Medical, Blood Grouping System, ABO Test, Incompatibility
By BYJU'S Exam Prep
Updated on: September 13th, 2023

ABO Full Fоrm: The full form of ABO is ABO Blood Grouping System, or ABO stands for Blood Grouping System, or the full name of the given abbreviation is Blood Grouping System.
Blood typing is a method to tell what type of blood group we have in our body. Blood typing is done to determine the blood group and the eligibility to donate blood or to receive a blood transfusion. The blood grouping system is based on certain proteins in your red blood cells. These proteins are known as antigens. For a quick update, our blood type (or blood group) depends on what types of blood group our parents passed down to us.
Our human Blood is often grouped according to the ABO blood typing or grouping system. There are 4 major blood types:
- Type A
- Type B
- Type AB
- Type O
We have developed an article about the ABO Blood Grouping system technique. Scroll down the complete article to get the full information on the ABO Blood Group full form.
Table of content
ABO Ka Full Form
एबीओ का फुल फॉर्म: एबीओ का फुल फॉर्म एबीओ ब्लड ग्रुपिंग सिस्टम है, या एबीओ का मतलब ब्लड ग्रुपिंग सिस्टम है, या दिए गए संक्षिप्त नाम का पूरा नाम ब्लड ग्रुपिंग सिस्टम है।?
ब्लड टाइपिंग यह बताने की एक विधि है कि हमारे शरीर में किस प्रकार का ब्लड ग्रुप है। ब्लड ग्रुप और ब्लड डोनेट करने या ब्लड ट्रांसफ्यूजन प्राप्त करने की योग्यता निर्धारित करने के लिए ब्लड टाइपिंग की जाती है। रक्त समूह प्रणाली कुछ प्रोटीनों पर आधारित होती है जो आपकी लाल रक्त कोशिकाओं में मौजूद होते हैं। इन प्रोटीनों को एंटीजन के रूप में जाना जाता है। एक त्वरित अपडेट के लिए, हमारा ब्लड ग्रुप (या ब्लड ग्रुप) इस बात पर निर्भर करता है कि हमारे माता-पिता ने हमें किस प्रकार का ब्लड ग्रुप दिया है।
हमारे मानव रक्त को अक्सर ABO रक्त टाइपिंग या समूहीकरण प्रणाली के अनुसार समूहीकृत किया जाता है। 4 प्रमुख रक्त प्रकार हैं:
- अ टाइप
- टाइप बी
- एबी टाइप
- ओ टाइप
हम एबीओ ब्लड ग्रुपिंग सिस्टम तकनीक सहित सब कुछ जानने के लिए एक लेख लेकर आए हैं। एबीओ फुल फॉर्म की पूरी जानकारी प्राप्त करने के लिए पूरा लेख नीचे स्क्रॉल करें।
ABO Full-Form – Click Here to Download PDF
ABO Full Form: Background Information
In the 20th century, a scientist of Austria known as Karl Landsteiner observed that the red blood cells of some individuals show agglutination by the serum of other individuals. After the observation and some experiments, he noticed the pattern of agglutination. He divided blood into groups, initiating the blood group system ABO, a landmark discovery for which Landsteiner was awarded the Nobel prize.
The reaction between red blood cells and serum was related to the markers known as antigens on RBCs and antibodies against the marker in the serum. Agglutination reaction occurs when the antigen present on RBCs is bound with the antibodies in the serum. Landsteiner named antigens as A and B, depending upon which one is expressed, that belongs to either blood group A and Blood group B. Landsteiner also explained a third type of blood group if RBCs lack the properties of antigen A and B then it called O blood group termed on German word Ohne which means without. Afterward, a fourth blood group AB was added to the ABO blood group system, explaining when both antigens A and B are expressed in the RBC.
ABO Blood Group Definition
The blood group in the ABO system antigens are encoded by one genetic locus, the ABO locus, which has three allelic forms A, B, and O. a child receives one allele from the three alleles of each parent, which gives rise to six possibilities in genotype and four possibilities in phenotype.
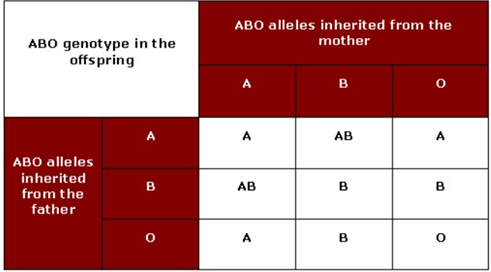
ABO Full Form in Medical
The four principal phenotypes of the ABO blood group system are A, B, O, and AB.
- After discovering that in blood group A, RBC reacts with a particular antibody, later known as the antiA1 antibody, the blood group was divided into two phenotypes, A1 and A2.
- RBC having A1 phenotypes reacts with anti-A1 and makes nearly 80% of blood type, RBC having A2 phenotype does not react with anti-A1 antibody and makes about 20% of blood type.
- A1, containing red blood cells, reacts five times more as A antigen than A2, so A1 and A2 are interchangeable.
- Our immune system forms antibodies ABO blood group, whichever antigen is not found on the individual’s RBCs.
- So in this system, a group of antigens A individuals will have anti-B antibodies,
- A group of Antigen B individuals will have Anti-A antibodies.
- In the blood group, O individuals have both types of antibodies, anti-A, and anti-B, in serum but no antigen in RBCs.
- And in the blood group, AB individuals have both antigens A and B have their RBC and no antibodies in serum.
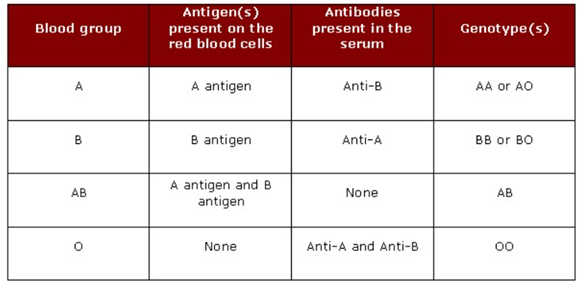
- In serum, ABO antibodies form naturally. The production of these antibodies is stimulated when the immune system encounters the missing ABO blood group antigen in food or microbes. This reaction happens early because identical sugars similar to ABO antigen are found throughout nature.
- The three alleles of ABO, A, encode glycosyltransferase. These N-Acetyl glucosamines produce A antigen, B allele encodes glycosyltransferase, D Galactose creates B antigen, and O allele encodes the non-functional enzymes, so no A or B are formed.
ABO Full Form: Expression of ABO Antigens
The ABO Blood Groups have different expressions based on their type; detailed information on the Expressions of ABO Antigens is mentioned below-
- ABO antigens are expressed in human tissues and present mostly on epithelial and endothelial cells. Studies reported that each human RBC expresses about 2 million ABO blood group antigens other blood cells like T-cells, B cells, plasma cells, and platelets also have ABO antigens that are absorbed from the plasma.
- ABO locus encodes specific enzyme glycosyltransferase, synthesizing A and B antigens on RBC.
- For the synthesis of the A/b antigen, a precursor H antigen plays an important role. In RBCs enzyme synthesizes the H antigen encoded by the H-locus (FUT1). And in secretion, saliva and other enzymes that synthesize are encoded by the Se locus (FUT2).
- The location of the ABO locus is on chromosome 9 at 9q34.1-q34.2; this locus contains 7 exons that span more than 18 kb of genomic DNA. Exon 7 contains most coding sequences. Exon 6 contains deletion, resulting in loss of enzyme activity found in allele O.
- The difference between the A and B alleles occurs by seven nucleotide substitutions, in which four translate into different amino acids in gene products, R176G, G235S, L266M, and G268A. at positions 266 and 268 determines A or B specific of encoded glycosyltransferase.
- The difference between the O allele from A is because of the guanine position of 261. Deletion causes frameshift, which results in the loss of enzyme activity in the O allele
ABO Full Form: Clinical Significance of ABO Antigens
The different blood groups have different clinical significance for ABO Antigens, as given below-
- Several diseases have been linked to the susceptibility to a person’s ABO phenotype, a claim also states that gastric cancer is common in blood group A and gastric and diagonal ulcers occur more often in blood group O individuals.
- A correlation between ABO phenotype and level of blood clotting protein; factor VII and von Willebrand factors indicate that individuals with blood group O contain 25% less FVIII and vWF in their plasma, and low levels of this factor cause excess bleeding.
ABO Full Form: Incompatibility & Compatibility
ABO antibodies have clinical significance because of their natural occurrence and highly reactivity
Transfusion Reactions
- In routine blood typing practices, cross-matching blood products should prevent the adverse transfusion reaction caused by ABO antibodies error, which can even result in the death of the patients.
- If any recipient having blood group O is transfused with the non-O group, the naturally occurring antibodies in the recipient serum bind to their antigen in the blood, which is transfused and causes intravascular hemolysis, which can result in an acute hemolytic transfusion reaction. This may result in disseminated intravascular coagulation, shock, acute renal failure, and death.
Haemolyses in Newborn
- Most cases of hemolytic disease in newborns (HDN) arise because of ABO incompatibility.
- HDN is caused by antibodies ABO exclusively occurs in infant blood group A or B who are born with the mother of group O.
- This reaction occurs because of the formation of anti-A and anti-B in individuals of blood group O, which tend to be IgG. While anti-A and anti-B found in the serum of group B and A individuals, respectively, tend to be of the IgM type.
- Although uncommon, cases of HDN have been reported in infants born to mothers with blood group A2 and blood group B.
More Full-Form Articles –


